OCR Physics A Using scalars and vectors Specification references
... certain direction. The direction of a vector is sometimes indicated by giving an angle to a reference direction, for example, north. Sometimes a vector has a positive direction and a negative direction, in this case, the negative direction is opposite to the positive direction. Acceleration is the r ...
... certain direction. The direction of a vector is sometimes indicated by giving an angle to a reference direction, for example, north. Sometimes a vector has a positive direction and a negative direction, in this case, the negative direction is opposite to the positive direction. Acceleration is the r ...
RevfinQans111fa02
... Two wheels initially at rest roll the same distance without slipping down identical inclined planes starting from rest. Wheel B has twice the radius but the same mass as wheel A. All the mass is concentrated in their rims, so that the rotational inertia's are I = mR2 . Which has more translational k ...
... Two wheels initially at rest roll the same distance without slipping down identical inclined planes starting from rest. Wheel B has twice the radius but the same mass as wheel A. All the mass is concentrated in their rims, so that the rotational inertia's are I = mR2 . Which has more translational k ...
Newton`s First Law
... Net Force: the Sum of the Forces • This car is moving with a constant velocity. • Fforward = road pushing the tires • Fresistance = force caused by friction and air • Forces are balanced ...
... Net Force: the Sum of the Forces • This car is moving with a constant velocity. • Fforward = road pushing the tires • Fresistance = force caused by friction and air • Forces are balanced ...
1 - Net Start Class
... representing the vx and vy velocity components during the course of the motion. The length of the arrows should represent the magnitude of the velocity components. Label each component. (Note that the velocity components are already shown for the first position.) ...
... representing the vx and vy velocity components during the course of the motion. The length of the arrows should represent the magnitude of the velocity components. Label each component. (Note that the velocity components are already shown for the first position.) ...
Starter Questions: Force and Motion
... 2. A 63 kg skater pushes off from a wall with a force of 300 N. What is the skater’s acceleration? ...
... 2. A 63 kg skater pushes off from a wall with a force of 300 N. What is the skater’s acceleration? ...
Physics 111
... • Components of vectors and unit vectors • Adding vectors by components (analytic method) • Vectors and the laws of physics • Multiplying vectors: – Scalar multiplication – Dot product – Cross product (vector product ...
... • Components of vectors and unit vectors • Adding vectors by components (analytic method) • Vectors and the laws of physics • Multiplying vectors: – Scalar multiplication – Dot product – Cross product (vector product ...
Physics – More Net Force Practice Problems
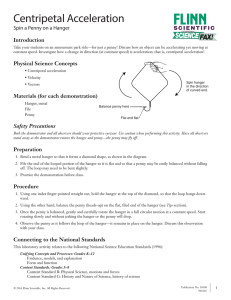
... 13) For each of these, the picture shown is a top-down view of the object so that weight and normal force are not considered. For each, determine the magnitude and direction of the net force acting on the object. Refer to the compass rose at the right. ...
... 13) For each of these, the picture shown is a top-down view of the object so that weight and normal force are not considered. For each, determine the magnitude and direction of the net force acting on the object. Refer to the compass rose at the right. ...
Summary of lesson
... When wind resistance equals the downward force of gravity, there are no net forces acting on the object. It stops accelerating. It moves with a constant downward speed called the terminal velocity. Although the force of gravity works on any object, the force of wind resistance is different. For exam ...
... When wind resistance equals the downward force of gravity, there are no net forces acting on the object. It stops accelerating. It moves with a constant downward speed called the terminal velocity. Although the force of gravity works on any object, the force of wind resistance is different. For exam ...
Motion
... A student walks 3 blocks south, 4 blocks west, and 3 blocks north. What is the displacement of the student? 1. 10 blocks east 2. 10 blocks west 3. 4 blocks east 4. 4 blocks west ...
... A student walks 3 blocks south, 4 blocks west, and 3 blocks north. What is the displacement of the student? 1. 10 blocks east 2. 10 blocks west 3. 4 blocks east 4. 4 blocks west ...
Lecture 10
... stop pushing an object, does it stop moving? Only if there is friction! In the absence of any net external force, an object will keep moving at a constant speed in a straight line, or remain at rest. This is Newton’s 1st Law, and it is also known as the Law of Inertia. ...
... stop pushing an object, does it stop moving? Only if there is friction! In the absence of any net external force, an object will keep moving at a constant speed in a straight line, or remain at rest. This is Newton’s 1st Law, and it is also known as the Law of Inertia. ...
1 - Hingham Schools
... A. The force on the apple is greater than the force on the Earth because the Earth is more massive. B. The force on the Earth is greater than the force on the apple because the Earth is more massive. C. The force on the apple is less than the force on the Earth because the tree is supporting the app ...
... A. The force on the apple is greater than the force on the Earth because the Earth is more massive. B. The force on the Earth is greater than the force on the apple because the Earth is more massive. C. The force on the apple is less than the force on the Earth because the tree is supporting the app ...
Motion, Forces &Machines PowerPoint presentation
... the rocket or how fast it went? • Both of those questions can be related to motion , forces and mechanics. ...
... the rocket or how fast it went? • Both of those questions can be related to motion , forces and mechanics. ...
Name____________________________________
... 12. The Newton is the SI unit of: a) force b) energy c) pressure d) mass 14. The tendency of an object to remain at rest or in motion is called: a. inertia. b. momentum. c. velocity. d. mass. 15. The velocity of an object changes if a. its speed changes b. its direction changes c. either its speed ...
... 12. The Newton is the SI unit of: a) force b) energy c) pressure d) mass 14. The tendency of an object to remain at rest or in motion is called: a. inertia. b. momentum. c. velocity. d. mass. 15. The velocity of an object changes if a. its speed changes b. its direction changes c. either its speed ...