Chapter 7 – Rotational Motion and the Law of Gravity
... 3. Tangential speed is equal to the distance from the axis time the angular speed or vt = r Note: is instantaneous angular speed. This equation is valid only when is measured in radians per unit of time. Tangential Acceleration – instantaneous linear acceleration is tangent to the circular pat ...
... 3. Tangential speed is equal to the distance from the axis time the angular speed or vt = r Note: is instantaneous angular speed. This equation is valid only when is measured in radians per unit of time. Tangential Acceleration – instantaneous linear acceleration is tangent to the circular pat ...
Which of the following statements are true of all free
... B. Gravity is the only force acting upon the object C. such objects accelerate at rate dependent upon their mass D. The net force on the object is equal to mg E. The acceleration of the object has a magnitude of 9.8 m/s/s. F. The velocity of the object is continuously changing G. None of these state ...
... B. Gravity is the only force acting upon the object C. such objects accelerate at rate dependent upon their mass D. The net force on the object is equal to mg E. The acceleration of the object has a magnitude of 9.8 m/s/s. F. The velocity of the object is continuously changing G. None of these state ...
January 2008
... A deuteron is a bound state of a neutron (charge 0, mass 939.5 MeV) and a proton (charge e, mass 938.2 MeV), Scattering measurements determine that the separation of the neutron and proton is about a = 1.5 fm and mass measurements determine that the binding energy is Eb = 2.226 MeV. Approximate the ...
... A deuteron is a bound state of a neutron (charge 0, mass 939.5 MeV) and a proton (charge e, mass 938.2 MeV), Scattering measurements determine that the separation of the neutron and proton is about a = 1.5 fm and mass measurements determine that the binding energy is Eb = 2.226 MeV. Approximate the ...
Honors Homework
... A projectile is fired in such a way that its horizontal range is equal to three times its maximum height. What is the angle of projection? ...
... A projectile is fired in such a way that its horizontal range is equal to three times its maximum height. What is the angle of projection? ...
Explaining Motion
... 1. The room you are sitting in is currently moving at about 400 m/s as a result of Earth spinning about its axis. The walls of the room are attached to Earth but, if you jump up into the air, you are not. Why does the west wall not move across and strike you? 2. Assume that you are pushing car acros ...
... 1. The room you are sitting in is currently moving at about 400 m/s as a result of Earth spinning about its axis. The walls of the room are attached to Earth but, if you jump up into the air, you are not. Why does the west wall not move across and strike you? 2. Assume that you are pushing car acros ...
Newton`s Second Law
... 2) Draw a free body diagram (FBD) which shows all forces acting on the object/ objects. Do not draw the components of the force on the FBD. 3) Specify a coordinate system. Take x-axis in direction of the motion and y-axis perpendicular to the motion. 4) Express every force in a vector form. 5) In or ...
... 2) Draw a free body diagram (FBD) which shows all forces acting on the object/ objects. Do not draw the components of the force on the FBD. 3) Specify a coordinate system. Take x-axis in direction of the motion and y-axis perpendicular to the motion. 4) Express every force in a vector form. 5) In or ...
Fall Final Review 15-16 File
... Understand the definition of a vector and a scalar and differentiate between the two Use trigonometry to add and resolve vectors Understand and apply the definition of a projectile Draw / recognize the free body diagrams and motion diagrams of a projectile Calculate the range (horizontal distance) o ...
... Understand the definition of a vector and a scalar and differentiate between the two Use trigonometry to add and resolve vectors Understand and apply the definition of a projectile Draw / recognize the free body diagrams and motion diagrams of a projectile Calculate the range (horizontal distance) o ...
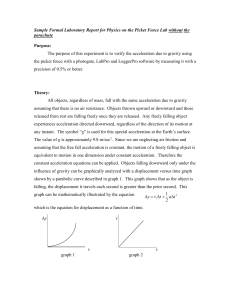
Sample Formal Laboratory Report for Physics on the Picket Fence Lab
... The purpose of the experiment was to verify the acceleration due to gravity which was done with 0.15% error and 0.56% precision. Since both the error and precision are small, it shows that the experimental was fairly consistent and the average value is very close to the accepted value of acceleratio ...
... The purpose of the experiment was to verify the acceleration due to gravity which was done with 0.15% error and 0.56% precision. Since both the error and precision are small, it shows that the experimental was fairly consistent and the average value is very close to the accepted value of acceleratio ...
Unit 7 Bell Ringers - Trimble County Schools
... = 20 grams Tennis Ball = 57 grams Baseball = 145 grams Softball = 178 grams Velocity ...
... = 20 grams Tennis Ball = 57 grams Baseball = 145 grams Softball = 178 grams Velocity ...
Chapter 8 Practice Test Name 1. A 30 kg object is set into orbit 7.5 x
... D. As a safety margin, the designer plans to make the rollercoaster go at twice the critical speed (twice as fast as you just calculated). At that speed, calculate the centripetal force on the rollercoaster. E. At that safer speed, calculate the normal force the track needs to provide at the highest ...
... D. As a safety margin, the designer plans to make the rollercoaster go at twice the critical speed (twice as fast as you just calculated). At that speed, calculate the centripetal force on the rollercoaster. E. At that safer speed, calculate the normal force the track needs to provide at the highest ...
Document
... bend the normally straight path of a particle into a circular or curved path is called the CENTRIPETAL FORCE. It is a pull on the body and is directed toward the center of the circle. Force on car Force on passenger Tendency for passenger to go straight ...
... bend the normally straight path of a particle into a circular or curved path is called the CENTRIPETAL FORCE. It is a pull on the body and is directed toward the center of the circle. Force on car Force on passenger Tendency for passenger to go straight ...
Chapter_1
... ___ 1. the particle’s speed. ___ 2. the particle’s acceleration. ___ 3. the particle’s average velocity. ___ 4. the particle’s instantaneous velocity. ___ 5. not covered in the reading assignment ...
... ___ 1. the particle’s speed. ___ 2. the particle’s acceleration. ___ 3. the particle’s average velocity. ___ 4. the particle’s instantaneous velocity. ___ 5. not covered in the reading assignment ...
Newton`s Laws - Dr. Robert MacKay
... • Next we need to understand what we mean by acceleration. • The acceleration of an object describes how fast its velocity changes. • If an object travels in a straight line with constant speed the acceleration is zero. • Whenever an object either changes speed of changes direction it is accelerati ...
... • Next we need to understand what we mean by acceleration. • The acceleration of an object describes how fast its velocity changes. • If an object travels in a straight line with constant speed the acceleration is zero. • Whenever an object either changes speed of changes direction it is accelerati ...