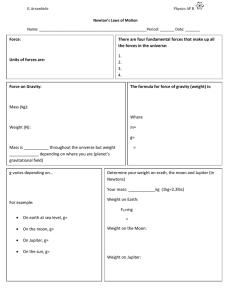
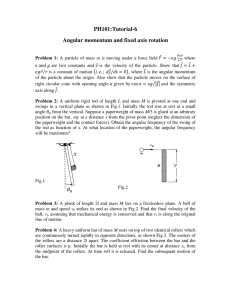
Physics I - Rose
... information on textbooks, but does give the weight of a one-pound object. Place a pound weight in one hand and the textbook on the other. The sensation on your hand is the weight of the object. The sensation from the textbook is about five times the sensation from the pound weight. So we conclude th ...
... information on textbooks, but does give the weight of a one-pound object. Place a pound weight in one hand and the textbook on the other. The sensation on your hand is the weight of the object. The sensation from the textbook is about five times the sensation from the pound weight. So we conclude th ...
Solution to Old Final exam w06
... Part III – Problems: Please Show your work clearly and completely for each of the following problems. Partial credit is only given to a work that is shown clearly. ...
... Part III – Problems: Please Show your work clearly and completely for each of the following problems. Partial credit is only given to a work that is shown clearly. ...
Rotational Motion
... Warm-up: Centripetal Acceleration Practice Assume a satellite in low Earth orbit has an acceleration, ...
... Warm-up: Centripetal Acceleration Practice Assume a satellite in low Earth orbit has an acceleration, ...
Learning Outcomes
... 6. Can I describe one example where the average speed of an object is measured in everyday life? 7. Can I describe one example where the instantaneous speed of an object is measured in everyday life? 8. Can I identify situations where average speed and instantaneous speed are different? 9. What is m ...
... 6. Can I describe one example where the average speed of an object is measured in everyday life? 7. Can I describe one example where the instantaneous speed of an object is measured in everyday life? 8. Can I identify situations where average speed and instantaneous speed are different? 9. What is m ...
Rotational Dynamics - curtehrenstrom.com
... Accounting for not only the force but also its location on the object is torque! • A torque is a twist as a force is a push or pull Torque is the vector cross product of the displacement of the force with respect to an arbitrary origin and the force that’s acting. = r x F ...
... Accounting for not only the force but also its location on the object is torque! • A torque is a twist as a force is a push or pull Torque is the vector cross product of the displacement of the force with respect to an arbitrary origin and the force that’s acting. = r x F ...
Forces, Motion, and Energy
... A. Common Reference Points II. Speed Depends on Distance and Time The SI unit for speed is ___meters per second_____m/s____. A. Determining Average Speed * Average speed = total distance traveled ÷ total time B. Recognizing Speed on a Graph * Speed can be shown on a graph of ____distance___ versus _ ...
... A. Common Reference Points II. Speed Depends on Distance and Time The SI unit for speed is ___meters per second_____m/s____. A. Determining Average Speed * Average speed = total distance traveled ÷ total time B. Recognizing Speed on a Graph * Speed can be shown on a graph of ____distance___ versus _ ...
A body acted on by no net force moves with constant velocity
... to move with constant speed in a straight line Inertial reference frames Galilean principle of relativity: Laws of physics (and everything in the Universe) look the same for all observers who move with a constant velocity with respect to each other. ...
... to move with constant speed in a straight line Inertial reference frames Galilean principle of relativity: Laws of physics (and everything in the Universe) look the same for all observers who move with a constant velocity with respect to each other. ...
Circular Motion and the Law of Gravity
... The circular motion will be described by the angle through which the object moves. All points are rotating except the point on the axis. Example from the textbook: The light bulb on the Ferris wheel is moving about an axis. The axis is a fixed point in the center of the Ferris wheel. Establish a ref ...
... The circular motion will be described by the angle through which the object moves. All points are rotating except the point on the axis. Example from the textbook: The light bulb on the Ferris wheel is moving about an axis. The axis is a fixed point in the center of the Ferris wheel. Establish a ref ...
Document
... How would the previous problem change if the boy threw the ball at an upward angle? In this type of problem yi ≠ 0. Therefore, we must account for the fact that gravity (g) first has to bring the upward velocity to a stop and then change the direction to downward. So the path of the object is a pa ...
... How would the previous problem change if the boy threw the ball at an upward angle? In this type of problem yi ≠ 0. Therefore, we must account for the fact that gravity (g) first has to bring the upward velocity to a stop and then change the direction to downward. So the path of the object is a pa ...
Sections 13.1-13.4 - University of Mary Hardin–Baylor
... weight is a derived unit. Typically, mass is specified in kilograms (kg), and weight is calculated from W = mg. If the gravitational acceleration (g) is specified in units of m/s2, then the weight is expressed in newtons (N). On the earth’s surface, g can be taken as g = 9.81 m/s2. W (N) = m (kg) g ...
... weight is a derived unit. Typically, mass is specified in kilograms (kg), and weight is calculated from W = mg. If the gravitational acceleration (g) is specified in units of m/s2, then the weight is expressed in newtons (N). On the earth’s surface, g can be taken as g = 9.81 m/s2. W (N) = m (kg) g ...
111
... 2) Which of the following statements is true about an object that moves with constant speed in a straight line? a) The net force acting on the object is zero. b) A net force acts on the object opposite to the direction of motion. c) A single constant force acts on the object in the direction of moti ...
... 2) Which of the following statements is true about an object that moves with constant speed in a straight line? a) The net force acting on the object is zero. b) A net force acts on the object opposite to the direction of motion. c) A single constant force acts on the object in the direction of moti ...
Newton`s Second Law - Philadelphia University
... weight is a derived unit. Typically, mass is specified in kilograms (kg), and weight is calculated from W = mg. If the gravitational acceleration (g) is specified in units of m/s2, then the weight is expressed in newtons (N). On the earth’s surface, g can be taken as g = 9.81 m/s2. W (N) = m (kg) g ...
... weight is a derived unit. Typically, mass is specified in kilograms (kg), and weight is calculated from W = mg. If the gravitational acceleration (g) is specified in units of m/s2, then the weight is expressed in newtons (N). On the earth’s surface, g can be taken as g = 9.81 m/s2. W (N) = m (kg) g ...
Lecture12
... • Torques require point of reference • Point can be anywhere • Use same point for all torques • Pick the point to make problem easiest (eliminate unwanted Forces from equation) ...
... • Torques require point of reference • Point can be anywhere • Use same point for all torques • Pick the point to make problem easiest (eliminate unwanted Forces from equation) ...
here
... Unclear work will not be graded. Use g=10m/s2. Write the conservation of energy equations for any mathematical problem. 1. Describe the law of conservation of energy in your own terms. 2. What are the units for: a) Kinetic Energy b) Spring Energy d) Work ...
... Unclear work will not be graded. Use g=10m/s2. Write the conservation of energy equations for any mathematical problem. 1. Describe the law of conservation of energy in your own terms. 2. What are the units for: a) Kinetic Energy b) Spring Energy d) Work ...
Name: Date:______ Period:_____ Chapter 19 Honors Study Guide
... 1. What is a reference point? The starting point you use to describe the motion or the position of an object 2. What is acceleration? Negative acceleration? The measure of how quickly the velocity of an object changes; when an object’s initial velocity is greater than its final velocity 3. Define sp ...
... 1. What is a reference point? The starting point you use to describe the motion or the position of an object 2. What is acceleration? Negative acceleration? The measure of how quickly the velocity of an object changes; when an object’s initial velocity is greater than its final velocity 3. Define sp ...
LVI AS Physics Self
... An experiment performed on the Moon finds that a feather falls 20.75 m from rest in 5 s. What is its speed as it hits the Moon's surface? ...
... An experiment performed on the Moon finds that a feather falls 20.75 m from rest in 5 s. What is its speed as it hits the Moon's surface? ...
PHYSICS 231 INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Lecture 12
... • Torques require point of reference • Point can be anywhere • Use same point for all torques • Pick the point to make problem easiest (eliminate unwanted Forces from equation) ...
... • Torques require point of reference • Point can be anywhere • Use same point for all torques • Pick the point to make problem easiest (eliminate unwanted Forces from equation) ...