
APES Chapter 4 Study Guide - Bennatti
... Is interspecific competition a biotic factor or abiotic factor? ...
... Is interspecific competition a biotic factor or abiotic factor? ...
Mollusca
... The Soft-bodied animals The mollusks constitute one of the largest phyla of animals, both in numbers of living species (at least 47,000, and perhaps many more) and in numbers of individuals. A significant characteristic of mollusks is their possession of a coelom, a fluid-filled cavity that develop ...
... The Soft-bodied animals The mollusks constitute one of the largest phyla of animals, both in numbers of living species (at least 47,000, and perhaps many more) and in numbers of individuals. A significant characteristic of mollusks is their possession of a coelom, a fluid-filled cavity that develop ...
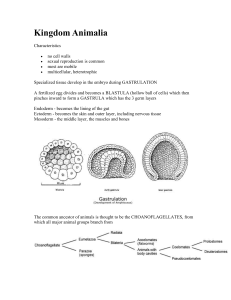
Kingdom Animalia
... Ectoderm - becomes the skin and outer layer, including nervous tissue Mesoderm - the middle layer, the muscles and bones ...
... Ectoderm - becomes the skin and outer layer, including nervous tissue Mesoderm - the middle layer, the muscles and bones ...
Food Web and Food ChainNotes
... saw the mongoose population explode do to no predator to keep this species in check. This lead to the island seeing ...
... saw the mongoose population explode do to no predator to keep this species in check. This lead to the island seeing ...
Cells Cells are the basic units of all living things Cells are composed
... Cells are the basic units of all living things Cells are composed of protoplasm Cell reproduction and metabolism takes place in the center nucleus Cytoplasm fluid surrounds the cell for growth, reproduction, repair Anabolism process of building larger molecules from smaller ones Catabolism breaks ...
... Cells are the basic units of all living things Cells are composed of protoplasm Cell reproduction and metabolism takes place in the center nucleus Cytoplasm fluid surrounds the cell for growth, reproduction, repair Anabolism process of building larger molecules from smaller ones Catabolism breaks ...
Annelids
... • Arenicola, the lugworm, lives in an L-shaped burrow in intertidal mudflats. It burrows by successive eversions and retractions of its proboscis. By peristaltic movements it keeps water filtering through the sand. The worm then ingests the food-laden sand. ...
... • Arenicola, the lugworm, lives in an L-shaped burrow in intertidal mudflats. It burrows by successive eversions and retractions of its proboscis. By peristaltic movements it keeps water filtering through the sand. The worm then ingests the food-laden sand. ...
what is an infectious disease?
... themselves and cause infectious disease. In addition, if beneficial organisms enter areas of the body where they are not normally found, these formerly harmless organisms can become potential pathogens ...
... themselves and cause infectious disease. In addition, if beneficial organisms enter areas of the body where they are not normally found, these formerly harmless organisms can become potential pathogens ...
You Can’t Have One Without the Other
... Describe connections between the immune system and other body systems. Design an experiment to demonstrate the relationship between the circulatory and respiratory systems. Summarize the relationship between oxygen debt and muscular contractions. Create labeled drawings of the lungs and diaphragm du ...
... Describe connections between the immune system and other body systems. Design an experiment to demonstrate the relationship between the circulatory and respiratory systems. Summarize the relationship between oxygen debt and muscular contractions. Create labeled drawings of the lungs and diaphragm du ...
You Can`t Have One Without the Other
... Describe connections between the immune system and other body systems. Design an experiment to demonstrate the relationship between the circulatory and respiratory systems. Summarize the relationship between oxygen debt and muscular contractions. Create labeled drawings of the lungs and diaphragm du ...
... Describe connections between the immune system and other body systems. Design an experiment to demonstrate the relationship between the circulatory and respiratory systems. Summarize the relationship between oxygen debt and muscular contractions. Create labeled drawings of the lungs and diaphragm du ...
Habitat
... Australian fauna: Survival in the desert • The three main challenges for Australian desert animals are body temperature, water and salt balance. • Temperature regulation in desert animals can be assisted by: – Behaviour which increases or decreases heat exchange with the environment – Changes in ci ...
... Australian fauna: Survival in the desert • The three main challenges for Australian desert animals are body temperature, water and salt balance. • Temperature regulation in desert animals can be assisted by: – Behaviour which increases or decreases heat exchange with the environment – Changes in ci ...
Human Body: End of Year Review [518071] Student Class Date 1
... B. coughing C. breathing D. blinking ...
... B. coughing C. breathing D. blinking ...
Feeding Relationships
... “The niche of an organism depends not only on where it lives but also on what it does. It may be said that the habitat is the organism's ‘address’, and the niche is its ...
... “The niche of an organism depends not only on where it lives but also on what it does. It may be said that the habitat is the organism's ‘address’, and the niche is its ...
Systems that Support Cellular Respiration Digestive System
... mammalian circulation • How red blood cells demonstrate the relationship of structure to function ...
... mammalian circulation • How red blood cells demonstrate the relationship of structure to function ...
Who Wants to Be a Millionaire?
... C. Glucose is Broken down For energy in the presence of oxygen ...
... C. Glucose is Broken down For energy in the presence of oxygen ...
Name - SchoolNotes
... Animal metabolism- all of the chemical processes that happen in the body Grown and Develop Grow- increase in size Development- change in form as the organism grows 2. What is homeostasis? The maintenance of a constant internal state in a changing environment Example: body temp and human muscles 3. ...
... Animal metabolism- all of the chemical processes that happen in the body Grown and Develop Grow- increase in size Development- change in form as the organism grows 2. What is homeostasis? The maintenance of a constant internal state in a changing environment Example: body temp and human muscles 3. ...
Body Systems in Vertebrate Animals
... respiration in gills and lungs; describe the two parts of a frog’s nervous system; differentiate between a sensory receptor and a sensory organ; differentiate between central and peripheral nervous systems, and between cranial and spinal nerves; list hormonecontrolled processes in animals; identify ...
... respiration in gills and lungs; describe the two parts of a frog’s nervous system; differentiate between a sensory receptor and a sensory organ; differentiate between central and peripheral nervous systems, and between cranial and spinal nerves; list hormonecontrolled processes in animals; identify ...
Environment and Ecology - Hawk Mountain Sanctuary
... The parts and characteristics of organisms (e.g. feathers, hibernation, leaf size) affect the ways they meet their needs in different environments (e.g. wetlands, forests, ocean). Characteristics of organisms are inherited from their parents. Organisms are made of parts and have characteristics that ...
... The parts and characteristics of organisms (e.g. feathers, hibernation, leaf size) affect the ways they meet their needs in different environments (e.g. wetlands, forests, ocean). Characteristics of organisms are inherited from their parents. Organisms are made of parts and have characteristics that ...
Organisms and Their Relationships Ecology Research Methods
... lab work - controlled setting and variable, but does not reflect organisms in the wild field work - performed in the wild, more accurate picture of interactions but ...
... lab work - controlled setting and variable, but does not reflect organisms in the wild field work - performed in the wild, more accurate picture of interactions but ...











![Human Body: End of Year Review [518071] Student Class Date 1](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010278867_1-3c3cf0e62fdf13fcdc1ae9141cb595a5-300x300.png)










