WAP 217 Introduction - Midlands State University
... that an organism must maintain to allow proper functioning of its component cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems. Single-celled organisms are surrounded by their ...
... that an organism must maintain to allow proper functioning of its component cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems. Single-celled organisms are surrounded by their ...
Ecosystems and Communities
... An organism’s role; includes resources, living conditions, interactions ...
... An organism’s role; includes resources, living conditions, interactions ...
Lecture #1 Dynamics of Population growth & Feeding
... Would an infectious disease be a density independent or dependent limiting factor? Explain. ...
... Would an infectious disease be a density independent or dependent limiting factor? Explain. ...
6th Grade Science Scales * Unit 1: The Human Body
... Different tissues are, in turn, grouped together to form larger functional units, called organs. How living things must maintain a stable internal environment to survive Students will recognize or recall: Specific vocabulary such as: cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism, homeostasis Bas ...
... Different tissues are, in turn, grouped together to form larger functional units, called organs. How living things must maintain a stable internal environment to survive Students will recognize or recall: Specific vocabulary such as: cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism, homeostasis Bas ...
Lesson 3
... is respiration – the exchange of gases between the body and the environment. B. Respiration has two parts: 1. External respiration is the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide that takes place between air and the blood in the lungs. 2. Internal respiration is the exchange of gases between the blood ...
... is respiration – the exchange of gases between the body and the environment. B. Respiration has two parts: 1. External respiration is the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide that takes place between air and the blood in the lungs. 2. Internal respiration is the exchange of gases between the blood ...
Body Organization Study Guide
... 6. Which of the following statements describes how two organ systems work together? (p208 Figure 3) a) The skeletal system and muscular system make it possible to move b) The skeletal system and integumentary system work together to produce blood cells c) The muscles of the muscular system contract ...
... 6. Which of the following statements describes how two organ systems work together? (p208 Figure 3) a) The skeletal system and muscular system make it possible to move b) The skeletal system and integumentary system work together to produce blood cells c) The muscles of the muscular system contract ...
Gas Exchange in Mammals - Miss Jan`s Science Wikispace
... → higher demand for O2 and removal of CO2. Internal lungs are well protected from: → physical damage → drying out in a dry environment. Enables mammals to have a wider range of habitats e.g. dry, wet, water on land. Lungs have a higher surface area to maximise rate of diffusion of O2 into capillarie ...
... → higher demand for O2 and removal of CO2. Internal lungs are well protected from: → physical damage → drying out in a dry environment. Enables mammals to have a wider range of habitats e.g. dry, wet, water on land. Lungs have a higher surface area to maximise rate of diffusion of O2 into capillarie ...
In nature, organisms live together and long
... • When prey gets close enough, a sea anemone will use its tentacles to eject venomous stinging threads that paralyze its prey. Once its prey is subdued, a sea anemone uses its tentacles to grasp the prey and sweep it into its mouth. • Sea anemones don’t always stay in one place, though. They can sli ...
... • When prey gets close enough, a sea anemone will use its tentacles to eject venomous stinging threads that paralyze its prey. Once its prey is subdued, a sea anemone uses its tentacles to grasp the prey and sweep it into its mouth. • Sea anemones don’t always stay in one place, though. They can sli ...
flashcards_ecology - Maples Elementary School
... The relationship between plants and animals that shows who eats what. Energy is transferred from one organism to another through the food chain ...
... The relationship between plants and animals that shows who eats what. Energy is transferred from one organism to another through the food chain ...
Ecology and Population Biology Powerpoint
... 28. What is acid rain and what is the major cause of it? • Rain that is highly acidic (low pH) • CAUSE: air pollution that reacts with water in the air ...
... 28. What is acid rain and what is the major cause of it? • Rain that is highly acidic (low pH) • CAUSE: air pollution that reacts with water in the air ...
Anatomy and Physiology - Havelock Agricultural Education
... Rump- upper rounded part of the hindquarter (a.k.a. croup) Shoulder- above the elbow of the fore leg Stifle- joint above the hock Thigh- area between the rump and hock Whiskers- long hairs growing near the ...
... Rump- upper rounded part of the hindquarter (a.k.a. croup) Shoulder- above the elbow of the fore leg Stifle- joint above the hock Thigh- area between the rump and hock Whiskers- long hairs growing near the ...
Anatomy and Physiology
... Rump- upper rounded part of the hindquarter (a.k.a. croup) Shoulder- above the elbow of the fore leg Stifle- joint above the hock Thigh- area between the rump and hock Whiskers- long hairs growing near the ...
... Rump- upper rounded part of the hindquarter (a.k.a. croup) Shoulder- above the elbow of the fore leg Stifle- joint above the hock Thigh- area between the rump and hock Whiskers- long hairs growing near the ...
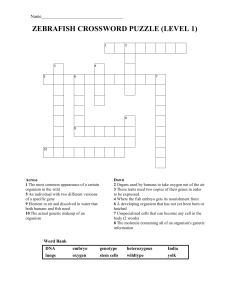
Zebrafish Crossword Puzzles
... Across 1 Tool used to pull small things out of water 4 Surrounds and protects the fish embryo 7 An individual with two identical copies of the same gene 12 How we test our ideas in science 14 Pumps blood through the body 15 The study of biological inheritance of traits 16 The most common appearance ...
... Across 1 Tool used to pull small things out of water 4 Surrounds and protects the fish embryo 7 An individual with two identical copies of the same gene 12 How we test our ideas in science 14 Pumps blood through the body 15 The study of biological inheritance of traits 16 The most common appearance ...
Name Date ______ Period
... single cells. Over time, these organisms grow and take on the characteristics of their species. Growth results in an increase in the amount of living material and the formation of new structures. All organisms grow, and different parts of organisms may grow at different rates. Organisms made up of o ...
... single cells. Over time, these organisms grow and take on the characteristics of their species. Growth results in an increase in the amount of living material and the formation of new structures. All organisms grow, and different parts of organisms may grow at different rates. Organisms made up of o ...
Short_and_long_term_effects_of_exercise
... Respiratory system is responsible receiving Oxygen into the body and dealing with waste products. There is an increase in lung volume Vital capacity is increased (max inspiration) Tidal volume increases during exercise Respiratory muscles get stronger become more efficient lungs get bigger. Pulmonar ...
... Respiratory system is responsible receiving Oxygen into the body and dealing with waste products. There is an increase in lung volume Vital capacity is increased (max inspiration) Tidal volume increases during exercise Respiratory muscles get stronger become more efficient lungs get bigger. Pulmonar ...
Respiratory Systems:
... As organisms get larger surface area to volume ratio decreases which: ◦ Limits the surface area available for diffusion. ◦ Increases the distances within the animal that oxygen must diffuse across ◦ Increasing the time needed for diffusion. ...
... As organisms get larger surface area to volume ratio decreases which: ◦ Limits the surface area available for diffusion. ◦ Increases the distances within the animal that oxygen must diffuse across ◦ Increasing the time needed for diffusion. ...
Patterns of Evolution
... • There are differences of opinion about interpretation and every person is entitled to his or her own opinion – the experts are not always objective • Our goal is to present the prevailing view and allow you to reach your own conclusions • Remember that everyone is entitled to their own opinion – y ...
... • There are differences of opinion about interpretation and every person is entitled to his or her own opinion – the experts are not always objective • Our goal is to present the prevailing view and allow you to reach your own conclusions • Remember that everyone is entitled to their own opinion – y ...
Connecting the body systems activity
... Activity: You will work in a group of 4 to complete the Bringing the Body Systems Together activity. Part 1 – Individual Systems What to Do: Members of the group will work together to answer the following questions about the four body systems that we have been studying. You will follow the example s ...
... Activity: You will work in a group of 4 to complete the Bringing the Body Systems Together activity. Part 1 – Individual Systems What to Do: Members of the group will work together to answer the following questions about the four body systems that we have been studying. You will follow the example s ...
A103 Anatomy and Physiology
... and biomedical sciences track. They are able to use the information from this module and apply them in modules such as Hematology, Clinical Chemistry, Histopathology and Medical Microbiology, Cell Cycle & Oncology, Proteomics, Genomics and Structural Biology. This module helps the students to make b ...
... and biomedical sciences track. They are able to use the information from this module and apply them in modules such as Hematology, Clinical Chemistry, Histopathology and Medical Microbiology, Cell Cycle & Oncology, Proteomics, Genomics and Structural Biology. This module helps the students to make b ...
Kingdom Animalia
... young animal is born or hatched with the same appearance and way of life it will have as an adult; no larval stage occurs. Although most invertebrates undergo indirect development, a few, such as grasshoppers, undergo direct development. ...
... young animal is born or hatched with the same appearance and way of life it will have as an adult; no larval stage occurs. Although most invertebrates undergo indirect development, a few, such as grasshoppers, undergo direct development. ...