All forces arise from the interactions between different objects
... gravitational force, there exists a duality between strong and weak coupling. A coupling constant describes how strong an interaction is. A larger coupling constant means a stronger force; hence, the coupling constant is of the order of 10 -41 and it is derived from the masses of the proton and elec ...
... gravitational force, there exists a duality between strong and weak coupling. A coupling constant describes how strong an interaction is. A larger coupling constant means a stronger force; hence, the coupling constant is of the order of 10 -41 and it is derived from the masses of the proton and elec ...
PHYS 221 General Physics I - South Central College eCatalog
... Identify how work is accomplished by gravitational force. Explain how work is accomplished by using spring force. Acquire an understanding of power and how it is applied. ...
... Identify how work is accomplished by gravitational force. Explain how work is accomplished by using spring force. Acquire an understanding of power and how it is applied. ...
Rolling, Torque, and Angular Momentum
... Fnet = dp/dt expresses the close relation between force and linear momentum for a single particle. There is also a close relationship between torque and angular momentum: Tnet = dl/dt The vector sums of all the torques acting on a particle is equal to the time rate of change in the angular momentum ...
... Fnet = dp/dt expresses the close relation between force and linear momentum for a single particle. There is also a close relationship between torque and angular momentum: Tnet = dl/dt The vector sums of all the torques acting on a particle is equal to the time rate of change in the angular momentum ...
toolkit - The Open University
... Bohr orbits in which the magnitude of the angular momentum is an integer multiple of ~ = h/2π (where h is Planck’s constant). It further assumes that electrons do not emit electromagnetic radiation as long as they remain in one of the allowed orbits, but that emission (or absorption) of electromagn ...
... Bohr orbits in which the magnitude of the angular momentum is an integer multiple of ~ = h/2π (where h is Planck’s constant). It further assumes that electrons do not emit electromagnetic radiation as long as they remain in one of the allowed orbits, but that emission (or absorption) of electromagn ...
31 - University of South Alabama
... 36. •• IP Hydrogen atom number 1 is known to be in the 4f state. (a) What is the energy of this atom? (b) What is the magnitude of this atom's orbital angular momentum? (c) Hydrogen atom number 2 is in the 5d state. Is this atom's energy greater than, less than, or the same as that of atom 1? Explai ...
... 36. •• IP Hydrogen atom number 1 is known to be in the 4f state. (a) What is the energy of this atom? (b) What is the magnitude of this atom's orbital angular momentum? (c) Hydrogen atom number 2 is in the 5d state. Is this atom's energy greater than, less than, or the same as that of atom 1? Explai ...
Problems for the course FYS4130
... λ3 (d) Entropy is not an additive quantity. The states created by permutation of the particles are actually the same, so the partition function ZN should be divided by N!. In the main approximation it will result in the expression ...
... λ3 (d) Entropy is not an additive quantity. The states created by permutation of the particles are actually the same, so the partition function ZN should be divided by N!. In the main approximation it will result in the expression ...
Tuesday, June 26, 2007 - UTA High Energy Physics page.
... angular momentum of the system can change. Both internal and external forces can provide torque to individual particles. However, the internal forces do not generate net torque due to Newton’s third law. Let’s consider a two particle system where the two exert forces on each other. ...
... angular momentum of the system can change. Both internal and external forces can provide torque to individual particles. However, the internal forces do not generate net torque due to Newton’s third law. Let’s consider a two particle system where the two exert forces on each other. ...
Quantum Chemistry II: Lecture Notes
... The electrons have an intrinsic angular momentum called spin. The spin operator satisfies all the properties imposed on a quantum angular momentum operator and its spin quantum number is 1/2 and it has the total angular momentum of √3ħ/2. The wavefunction of an atom/molecule must take the spin varia ...
... The electrons have an intrinsic angular momentum called spin. The spin operator satisfies all the properties imposed on a quantum angular momentum operator and its spin quantum number is 1/2 and it has the total angular momentum of √3ħ/2. The wavefunction of an atom/molecule must take the spin varia ...
Chapter 10b
... Black board example 11.6 Two mechanics are trying to open a rusty screw on a ship with a big ol’ wrench. One pulls at the end of the wrench (r = 1 m) with a force F = 500 N at an angle F1 = 80 °; the other pulls at the middle of wrench with the same force and at an angle F2 = 90 °. What is the net ...
... Black board example 11.6 Two mechanics are trying to open a rusty screw on a ship with a big ol’ wrench. One pulls at the end of the wrench (r = 1 m) with a force F = 500 N at an angle F1 = 80 °; the other pulls at the middle of wrench with the same force and at an angle F2 = 90 °. What is the net ...
Document
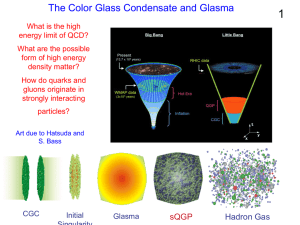
... Time dilation -> Classical field is glassy High phase space density -> Condensate Phase space density: Attractive potential ...
... Time dilation -> Classical field is glassy High phase space density -> Condensate Phase space density: Attractive potential ...
Lecture Notes
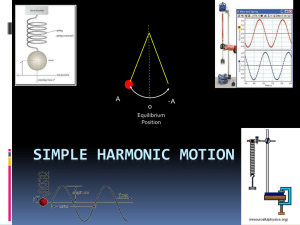
... is called the natural frequency. The same system can also be driven as shown in the figure by a moving support that oscillates at an arbitrary angular frequency d . Such a forced oscillator oscillates at the angular frequency d of the driving force. The displacement is given by: x (t ) xm cos ...
... is called the natural frequency. The same system can also be driven as shown in the figure by a moving support that oscillates at an arbitrary angular frequency d . Such a forced oscillator oscillates at the angular frequency d of the driving force. The displacement is given by: x (t ) xm cos ...
Spin filling of valley-orbit states in a silicon quantum dot
... (VO2 ) and it becomes energetically favoured for the second electron to occupy the latter, i.e. VO2 . At the kink the valley-orbit splitting equals the Zeeman energy, which is 0.10 meV at 0.86 T. With the interfacial electric field of ∼2×107 V/m extracted from Technology Computer-Aided-Design modeli ...
... (VO2 ) and it becomes energetically favoured for the second electron to occupy the latter, i.e. VO2 . At the kink the valley-orbit splitting equals the Zeeman energy, which is 0.10 meV at 0.86 T. With the interfacial electric field of ∼2×107 V/m extracted from Technology Computer-Aided-Design modeli ...
Linköping University Post Print Ion streaming instability in a quantum dusty magnetoplasma
... and electromagnetic waves6–8 in dense quantum plasmas. The latter, which are ubiquitous in compact astrophysical bodies9 共e.g., the interiors of white dwarf stars, magnetars and supernovae兲 as well as in micro- and nanoscale objects10 共e.g., nanowires, ultrasmall semiconductor devices兲, have an extr ...
... and electromagnetic waves6–8 in dense quantum plasmas. The latter, which are ubiquitous in compact astrophysical bodies9 共e.g., the interiors of white dwarf stars, magnetars and supernovae兲 as well as in micro- and nanoscale objects10 共e.g., nanowires, ultrasmall semiconductor devices兲, have an extr ...
Example2 - mrdsample
... pulled with a constant acceleration, which causes the gyroscope to start spinning. It takes 1.10 seconds to pull the string off of the axle and the gyroscope then spins for an additional 60.0 seconds before stopping. (a) Find the maximum angular speed of the gyroscope in rad/s. (b) Find the total nu ...
... pulled with a constant acceleration, which causes the gyroscope to start spinning. It takes 1.10 seconds to pull the string off of the axle and the gyroscope then spins for an additional 60.0 seconds before stopping. (a) Find the maximum angular speed of the gyroscope in rad/s. (b) Find the total nu ...