Electron Configuration
... • Plank’s Theory is based on the relationship between frequency and the energy of the particle. • Energy = h x frequency • E = h • Plank’s Constant: – h = 6.6262 X 10-34 J-s ...
... • Plank’s Theory is based on the relationship between frequency and the energy of the particle. • Energy = h x frequency • E = h • Plank’s Constant: – h = 6.6262 X 10-34 J-s ...
F - Sfu
... the total momentum of the system remains constant. Note 1: If one of the components of the net external force is zero, the corresponding component of the total momentum of the system is conserved (even though the total momentum vector may or may not be conserved). Note 2: For a one-object system, th ...
... the total momentum of the system remains constant. Note 1: If one of the components of the net external force is zero, the corresponding component of the total momentum of the system is conserved (even though the total momentum vector may or may not be conserved). Note 2: For a one-object system, th ...
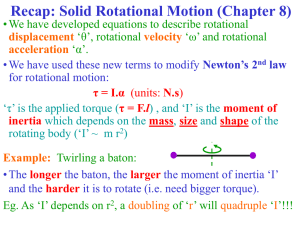
Momentum
... object 2 is equal and opposite to the impulse received by object 1. The change of momentum experienced by the two objects are equal and opposite. The total change in momentum for our two- object system, due to the collision, will be zero. The collision forces conserve the system’s momentum. The line ...
... object 2 is equal and opposite to the impulse received by object 1. The change of momentum experienced by the two objects are equal and opposite. The total change in momentum for our two- object system, due to the collision, will be zero. The collision forces conserve the system’s momentum. The line ...
Physics 12 Notes Modern Physics Learning Outcomes (Students will
... energy. The minimum amount of energy, Emin, of vibration of a vibrating molecule is proportional to the natural frequency of oscillation. Defining equation Emin = hf, where h is the constant of proportionality and is called Planck’s constant (h = 6.626 x 10-34 Js). The above implies that for a vibr ...
... energy. The minimum amount of energy, Emin, of vibration of a vibrating molecule is proportional to the natural frequency of oscillation. Defining equation Emin = hf, where h is the constant of proportionality and is called Planck’s constant (h = 6.626 x 10-34 Js). The above implies that for a vibr ...
Quantum fluctuations and thermal dissipation in higher derivative
... the zero temperature dissipative forces associated with the quantum critical point in the presence of a massive probe particle, the authors had found out a crossover corresponding to the z = 2 fixed point which they identified as a consequence of the fact that the inertial mass (m) of the particle b ...
... the zero temperature dissipative forces associated with the quantum critical point in the presence of a massive probe particle, the authors had found out a crossover corresponding to the z = 2 fixed point which they identified as a consequence of the fact that the inertial mass (m) of the particle b ...
Effective Field Theory Description of the Higher Dimensional
... defined in different dimensions. We find two equivalent CS theories, an abelian CS theory in 6 + 1 dimensions, and a SU (2) non-abelian CS theory in 4 + 1 dimensions. The quantum liquid constructed by ZH has orbital degrees of freedom scaling with R 4 and internal isospin degree of freedom scaling w ...
... defined in different dimensions. We find two equivalent CS theories, an abelian CS theory in 6 + 1 dimensions, and a SU (2) non-abelian CS theory in 4 + 1 dimensions. The quantum liquid constructed by ZH has orbital degrees of freedom scaling with R 4 and internal isospin degree of freedom scaling w ...
Scalars 2011
... it metamorphosized into a term involving a YangMills gauge field, with dimension staying at 4. See A. Zee, Gravity and Its Mysteries: Some Thoughts and Speculations, Int. J. Mod. Phys. 23 (2008) 1295, hep-th/0805.2183 C. N. Yang at 85, Singapore, November 2007 ...
... it metamorphosized into a term involving a YangMills gauge field, with dimension staying at 4. See A. Zee, Gravity and Its Mysteries: Some Thoughts and Speculations, Int. J. Mod. Phys. 23 (2008) 1295, hep-th/0805.2183 C. N. Yang at 85, Singapore, November 2007 ...
Physical meaning and derivation of Schrodinger
... However, the confusion surrounding the physical justification and derivation of the Schrodinger equation originates from inappropriate physical arguments. Based on first principles we have obtained a transparent and justified dynamical picture. Each eigenfunction of a bound particle is a specific su ...
... However, the confusion surrounding the physical justification and derivation of the Schrodinger equation originates from inappropriate physical arguments. Based on first principles we have obtained a transparent and justified dynamical picture. Each eigenfunction of a bound particle is a specific su ...
Momentum: The quantity of motion of a moving body, measured as a
... 3) Next, consider problem #2, except this time the ball and the can stick together upon colliding (non-elastic collision). What is the velocity for the combined objects after the collision? Pib = (0.050 kg)(7.0 m/s) = 0.35 kg m/s; Pic = 0 (the initial velocity = 0) Ptot = (0.05 + 0.01) kg vf-tot (N ...
... 3) Next, consider problem #2, except this time the ball and the can stick together upon colliding (non-elastic collision). What is the velocity for the combined objects after the collision? Pib = (0.050 kg)(7.0 m/s) = 0.35 kg m/s; Pic = 0 (the initial velocity = 0) Ptot = (0.05 + 0.01) kg vf-tot (N ...