Exam Review Packet Table of Contents
... a) two points -‐ The radii of the alkali metal ions increase with increasing atomic number because: (i) the principle quantum number (or shell or energy level) increases (ii) there is an increase in ...
... a) two points -‐ The radii of the alkali metal ions increase with increasing atomic number because: (i) the principle quantum number (or shell or energy level) increases (ii) there is an increase in ...
Subject Area Standard Area Organizing Category Grade Level
... CHEM.A.2.2.2: Predict characteristics of an atom or an ion based on its location on the periodic table (e.g., number of valence electrons, potential types of bonds, reactivity). ...
... CHEM.A.2.2.2: Predict characteristics of an atom or an ion based on its location on the periodic table (e.g., number of valence electrons, potential types of bonds, reactivity). ...
Kinetics Presentation - Chemistrybyscott.org
... 2. CO2 (aq) + H2O(liq) e H2CO3(aq) 3. H2CO3(aq) e H+(aq) + HCO3–(aq) • Adding trace of NaOH uses up H+. Equilibrium shifts to produce more H2CO3. • Enzyme in blood (above) speeds up reactions 1 and 2 ...
... 2. CO2 (aq) + H2O(liq) e H2CO3(aq) 3. H2CO3(aq) e H+(aq) + HCO3–(aq) • Adding trace of NaOH uses up H+. Equilibrium shifts to produce more H2CO3. • Enzyme in blood (above) speeds up reactions 1 and 2 ...
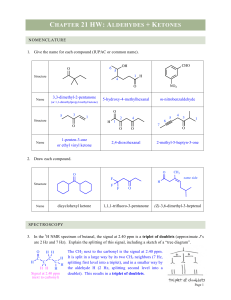
Ch 19 Aldehydes and Ketones
... - Aldehydes are more reactive than ketones for both steric and electronic reasons. - First, the H creates less steric hindrance so that the carbonyl C is more accessible. - Second, an organic group provides e- donating induction which stabilizes the + carbonyl C and makes it less reactive. - Formal ...
... - Aldehydes are more reactive than ketones for both steric and electronic reasons. - First, the H creates less steric hindrance so that the carbonyl C is more accessible. - Second, an organic group provides e- donating induction which stabilizes the + carbonyl C and makes it less reactive. - Formal ...
File
... strong signal at 1691 cm-1. Both signals represent vibration of the same kind of bond. Explain why the absorption in 2-cyclohexenone is at a lower wavenumber, including resonance structures. Both signals represent the IR stretching of the C=O bonds. 2-cyclohexenone has a lower wavenumber absorbance, ...
... strong signal at 1691 cm-1. Both signals represent vibration of the same kind of bond. Explain why the absorption in 2-cyclohexenone is at a lower wavenumber, including resonance structures. Both signals represent the IR stretching of the C=O bonds. 2-cyclohexenone has a lower wavenumber absorbance, ...
Unit 5 - Chemical Reactions - Student
... A chemical reaction is the process by which one or more substances are changed into one or more different substances. The original substances are called REACTANTS and the resulting substances are called PRODUCTS. According to the Law of CONSERVATION OF MASS, the total mass of the reactants are equal ...
... A chemical reaction is the process by which one or more substances are changed into one or more different substances. The original substances are called REACTANTS and the resulting substances are called PRODUCTS. According to the Law of CONSERVATION OF MASS, the total mass of the reactants are equal ...
Support Material
... Explain how vacancies are introduced in a solid NaCl crystal when divalent cations (M2+) are added to molten NaCl. ...
... Explain how vacancies are introduced in a solid NaCl crystal when divalent cations (M2+) are added to molten NaCl. ...
PDF File
... the observed K1/2 values equal the dissociation constants Kd (see also ref 37): The same K1/2 values were observed in concentration dependences in which the maximal rate constant for reaction varied by more than 10-fold, which was accomplished by a 2′-H substitution at position -1 and by varying the ...
... the observed K1/2 values equal the dissociation constants Kd (see also ref 37): The same K1/2 values were observed in concentration dependences in which the maximal rate constant for reaction varied by more than 10-fold, which was accomplished by a 2′-H substitution at position -1 and by varying the ...
AP Chemistry Notes and Worksheets 2014
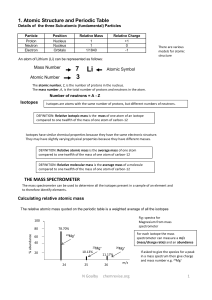
... o Compounds are formed when atoms of different elements combine in a constant composition. o Atoms are not changed in a chemical reaction, only rearranged. Dalton determined the first table of atomic weights. Many were wrong because of incorrect formulas. o Ex. OH for water with O having a mass of ...
... o Compounds are formed when atoms of different elements combine in a constant composition. o Atoms are not changed in a chemical reaction, only rearranged. Dalton determined the first table of atomic weights. Many were wrong because of incorrect formulas. o Ex. OH for water with O having a mass of ...
- StarBooks
... Dalton's Atomic Theory All substances are made up of tiny, indivisible particles called atoms. Atoms of the same element are identical in shape, size, mass and other properties. Atoms of different elements are different in all respects. Atom is the smallest unit that takes part in chemical combinati ...
... Dalton's Atomic Theory All substances are made up of tiny, indivisible particles called atoms. Atoms of the same element are identical in shape, size, mass and other properties. Atoms of different elements are different in all respects. Atom is the smallest unit that takes part in chemical combinati ...
Modeling the Solubility of Nitrogen Dioxide in Water Using
... system is a challenging task due to the complexities arising from the heterogeneous nature of the chemical reaction, the multiple components that are involved in the phase equilibria, ionic dissociation in water, self- and cross-associations among the molecules, and multiple chemical reactions that ...
... system is a challenging task due to the complexities arising from the heterogeneous nature of the chemical reaction, the multiple components that are involved in the phase equilibria, ionic dissociation in water, self- and cross-associations among the molecules, and multiple chemical reactions that ...
Answers - Pearson-Global
... Note: This is included because it is a simple example of a perfectly stable covalent compound where there aren’t four pairs of electrons around one of the atoms – in other words, it is nothing like a noble gas structure. Despite the impression often given at GCSE, such compounds are very common – al ...
... Note: This is included because it is a simple example of a perfectly stable covalent compound where there aren’t four pairs of electrons around one of the atoms – in other words, it is nothing like a noble gas structure. Despite the impression often given at GCSE, such compounds are very common – al ...
Vlsg-4-Protecting Groups I
... Examples of regioselective de-O-benzylation Selective de-O-benzylation of easily available polybenzylated precursors. This has been achieved in limited cases by: • catalytic hydrogenolysis • Catalytic hydrogen-transfer cleavage • Acetolysis • hypoiodite fragmentation • iodine-mediated addition-elim ...
... Examples of regioselective de-O-benzylation Selective de-O-benzylation of easily available polybenzylated precursors. This has been achieved in limited cases by: • catalytic hydrogenolysis • Catalytic hydrogen-transfer cleavage • Acetolysis • hypoiodite fragmentation • iodine-mediated addition-elim ...
Gas-Phase Reactions of Fe (CH2O)+ and Fe (CH2S)+ with Small
... yielding a great deal of information on “intrinsic” properties, such as kinetics, thermochemistry, and reaction mechanisms in the absence of solvation and counterion effects.1 The reactions with simple hydrocarbons have been particularly important, because they are closely related to solution organo ...
... yielding a great deal of information on “intrinsic” properties, such as kinetics, thermochemistry, and reaction mechanisms in the absence of solvation and counterion effects.1 The reactions with simple hydrocarbons have been particularly important, because they are closely related to solution organo ...
Mass Relationships in Chemical Reactions
... Write the chemical equation which represents the burning of glucose in presence of oxygen gas which produces carbon dioxide and water. To answer this question, follow the following steps: 1. Identify the reactants and the products and put an arrow in between. ...
... Write the chemical equation which represents the burning of glucose in presence of oxygen gas which produces carbon dioxide and water. To answer this question, follow the following steps: 1. Identify the reactants and the products and put an arrow in between. ...
Quantities in Chemistry
... Our policy at TSFX is to provide students with the most detailed and comprehensive set of notes that will maximise student performance and reduce study time. These materials, therefore, include a wide range of questions and applications, all of which cannot be addressed within the available lecture ...
... Our policy at TSFX is to provide students with the most detailed and comprehensive set of notes that will maximise student performance and reduce study time. These materials, therefore, include a wide range of questions and applications, all of which cannot be addressed within the available lecture ...
1 - A-Level Chemistry
... no lone / spare / non-bonded pair of electrons only score M2 if M1 correct or give ‘H’ in M1 ...
... no lone / spare / non-bonded pair of electrons only score M2 if M1 correct or give ‘H’ in M1 ...