AP Chemistry
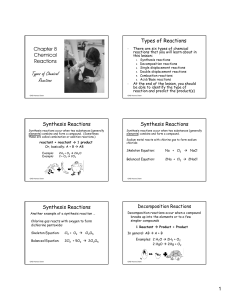
... balanced by placing coefficients in front of the chemical formulas for the reactants and products of a reaction, not by changing the subscripts in chemical formulas. Among the reaction types described in this unit are (1) combination reactions, in which two reactants combine to form one product; (2) ...
... balanced by placing coefficients in front of the chemical formulas for the reactants and products of a reaction, not by changing the subscripts in chemical formulas. Among the reaction types described in this unit are (1) combination reactions, in which two reactants combine to form one product; (2) ...
Answer Key, Problem Set 6 – complete, with explanations
... ions, I have shown the ions as “touching” here—you could have shown them with a bit of space in between them as well, as long as the amount of space in between was roughly “equal” for all adjacent ions). To further ...
... ions, I have shown the ions as “touching” here—you could have shown them with a bit of space in between them as well, as long as the amount of space in between was roughly “equal” for all adjacent ions). To further ...
chemical reactions and stoichiometry chemical reactions and
... Thus, both the English and the German chemical industries began with syntheses of dyes. Contemporary synthetic chemists know detailed information about molecular structures and use sophisticated computer programs to simulate a synthesis before trying it in the laboratory. Nevertheless, designing a c ...
... Thus, both the English and the German chemical industries began with syntheses of dyes. Contemporary synthetic chemists know detailed information about molecular structures and use sophisticated computer programs to simulate a synthesis before trying it in the laboratory. Nevertheless, designing a c ...
enthalpy change
... • combustion the symbol used can be ∆c H • formation the symbol used can be ∆f H • decomposition the symbol used can be ∆d H • dissolving to form a solution the symbol used can be ∆sol H • dilution of a solution the symbol used can be ∆dil H ...
... • combustion the symbol used can be ∆c H • formation the symbol used can be ∆f H • decomposition the symbol used can be ∆d H • dissolving to form a solution the symbol used can be ∆sol H • dilution of a solution the symbol used can be ∆dil H ...
PIB - Unit 6 - Chemical Reactions - Student
... A chemical reaction is the process by which one or more substances are changed into one or more different substances. The original substances are called REACTANTS and the resulting substances are called PRODUCTS. According to the Law of CONSERVATION OF MASS, the total mass of the reactants are equal ...
... A chemical reaction is the process by which one or more substances are changed into one or more different substances. The original substances are called REACTANTS and the resulting substances are called PRODUCTS. According to the Law of CONSERVATION OF MASS, the total mass of the reactants are equal ...
Organic Chemistry - UCR Chemistry
... and compounds related to them. These are ionic reactions in which one group on the molecule (a leaving group) is replaced by another group (a nucleophile). The transformation of haloalkanes (R-X) into alcohols (R-OH) where an OH group replaces the halogen (X) is an example of nucleophilic substituti ...
... and compounds related to them. These are ionic reactions in which one group on the molecule (a leaving group) is replaced by another group (a nucleophile). The transformation of haloalkanes (R-X) into alcohols (R-OH) where an OH group replaces the halogen (X) is an example of nucleophilic substituti ...
Chem 350 Jasperse Ch. 6 Summary of Reaction Types, Ch. 4
... with the reaction classification above a. If the reaction is cationic, don’t show anionic intermediates b. If the reaction is anionic, don’t show cationic intermediates 4. Usually conditions are ionic. 5. Use a reactive species, whether strong anion or an acid, to start the first step a. If acidic, ...
... with the reaction classification above a. If the reaction is cationic, don’t show anionic intermediates b. If the reaction is anionic, don’t show cationic intermediates 4. Usually conditions are ionic. 5. Use a reactive species, whether strong anion or an acid, to start the first step a. If acidic, ...
Solution
... 5.1.4 Structures of Polycations and Polyoxoanions The species of interest here are those in which metal ions are linked by hydroxyl (M-OH-M) and/or oxo (M-O-M) bridges. In the case of complexes based on M(II), M(III), and M(IV) atoms, the hydroxyl bridge is used almost exclusively. Table 5.1 present ...
... 5.1.4 Structures of Polycations and Polyoxoanions The species of interest here are those in which metal ions are linked by hydroxyl (M-OH-M) and/or oxo (M-O-M) bridges. In the case of complexes based on M(II), M(III), and M(IV) atoms, the hydroxyl bridge is used almost exclusively. Table 5.1 present ...
Energy is the essence of chemistry It determines which reaction can
... CH2==CH2(g) + HCl(g) → CH3—CH2Cl(g) ∆H° = -72 kJ The product has a lower enthalpy than the reactants, i.e. more stable. Average bond enthalpies can be used to calculate reaction enthalpies, o But the use of ∆H f is more accurate. Reason: ∆HB is an average of many compounds ∆H of is specific to each ...
... CH2==CH2(g) + HCl(g) → CH3—CH2Cl(g) ∆H° = -72 kJ The product has a lower enthalpy than the reactants, i.e. more stable. Average bond enthalpies can be used to calculate reaction enthalpies, o But the use of ∆H f is more accurate. Reason: ∆HB is an average of many compounds ∆H of is specific to each ...
Chapter 18
... Typically these ylides can be prepared by reacting triphenylphosphine with alkyl halide ...
... Typically these ylides can be prepared by reacting triphenylphosphine with alkyl halide ...
REVIEW and answers
... based on the existence of loosely held outer electrons which become delocalized; that is, they are free to move randomly from atom to atom in the metal. These electrons result in metals being malleable and ductile. Metals can also conduct electricity and heat. The more delocalized the electrons the ...
... based on the existence of loosely held outer electrons which become delocalized; that is, they are free to move randomly from atom to atom in the metal. These electrons result in metals being malleable and ductile. Metals can also conduct electricity and heat. The more delocalized the electrons the ...