CHEM_2nd_Semester_Final_R eview
... 45. How many calories are needed to raise 450. grams of water from 21.0 oC to 85.5oC? 46. How many grams of water can be heated 46.0oC by 34.8 kJ? Reaction Rates 47. Define reaction rate. 48. What are the units for reaction rate? 49. Describe what happens to the concentration of reactants during a c ...
... 45. How many calories are needed to raise 450. grams of water from 21.0 oC to 85.5oC? 46. How many grams of water can be heated 46.0oC by 34.8 kJ? Reaction Rates 47. Define reaction rate. 48. What are the units for reaction rate? 49. Describe what happens to the concentration of reactants during a c ...
Chemistry 2nd Semester Final Exam Review Chemical Bonds Give
... 45. How many calories are needed to raise 450. grams of water from 21.0 oC to 85.5oC? 46. How many grams of water can be heated 46.0oC by 34.8 kJ? Reaction Rates 47. Define reaction rate. 48. What are the units for reaction rate? 49. Describe what happens to the concentration of reactants during a c ...
... 45. How many calories are needed to raise 450. grams of water from 21.0 oC to 85.5oC? 46. How many grams of water can be heated 46.0oC by 34.8 kJ? Reaction Rates 47. Define reaction rate. 48. What are the units for reaction rate? 49. Describe what happens to the concentration of reactants during a c ...
2nd Semester Final Review
... 45. How many calories are needed to raise 450. grams of water from 21.0 oC to 85.5oC? 46. How many grams of water can be heated 46.0oC by 34.8 kJ? Reaction Rates 47. Define reaction rate. 48. What are the units for reaction rate? 49. Describe what happens to the concentration of reactants during a c ...
... 45. How many calories are needed to raise 450. grams of water from 21.0 oC to 85.5oC? 46. How many grams of water can be heated 46.0oC by 34.8 kJ? Reaction Rates 47. Define reaction rate. 48. What are the units for reaction rate? 49. Describe what happens to the concentration of reactants during a c ...
Lectures 32-33 - U of L Class Index
... An old fashioned synonym for the term “chiral” is “optically active” which refers to the fact that chiral molecules rotate plane-polarized light (light in which the waves are all parallel). Any molecule which does not have an enantiomer (because it is superimposable with its mirror image) is termed ...
... An old fashioned synonym for the term “chiral” is “optically active” which refers to the fact that chiral molecules rotate plane-polarized light (light in which the waves are all parallel). Any molecule which does not have an enantiomer (because it is superimposable with its mirror image) is termed ...
AP Chemistry Syllabus 2013 Mawhiney
... 3. Distinguish between an electrolytic cell and a voltaic cell in terms of function, direction and ΔG. 4. Solve problems using Faraday's law. 5. Predict reaction products for both electrolytic and voltaic cells. 6. Use a table of Standard Reduction Potentials to compute cell voltages. 7. Diagram vol ...
... 3. Distinguish between an electrolytic cell and a voltaic cell in terms of function, direction and ΔG. 4. Solve problems using Faraday's law. 5. Predict reaction products for both electrolytic and voltaic cells. 6. Use a table of Standard Reduction Potentials to compute cell voltages. 7. Diagram vol ...
CHAPTER 3 - Ltcconline.net
... is the most abundant organic compound on Earth, Almost all carbohydrates are hydrophilic, or “water-loving,” adhering water to their surface. 2. Lipids A typical fat, or triglyceride, consists of: a. Fats perform essential functions in the human body including: Unsaturated: Saturated: Hydrogenation: ...
... is the most abundant organic compound on Earth, Almost all carbohydrates are hydrophilic, or “water-loving,” adhering water to their surface. 2. Lipids A typical fat, or triglyceride, consists of: a. Fats perform essential functions in the human body including: Unsaturated: Saturated: Hydrogenation: ...
Topic 12: Organic Chemistry
... Example equations When studying the organic reaction equations below, pay attention to how the products of each reaction is formed from the given reactants. You are often asked to predict a reactant or a product of a reaction. ...
... Example equations When studying the organic reaction equations below, pay attention to how the products of each reaction is formed from the given reactants. You are often asked to predict a reactant or a product of a reaction. ...
Answer Key - La Quinta High School
... takes place. However, the only evidence for this reaction is the release of heat energy, which should be evident as a temperature change for the mixture. Since water has a relatively high specific heat capacity, however, if the acid and base solutions are very dilute, the temperature may change only ...
... takes place. However, the only evidence for this reaction is the release of heat energy, which should be evident as a temperature change for the mixture. Since water has a relatively high specific heat capacity, however, if the acid and base solutions are very dilute, the temperature may change only ...
Chabot College
... 2. use a mechanistic approach to make reasonable predictions of major products formed in reactions involving hydrocarbons, alkyl halides, alcohols and ethers; 3. explain physical and chemical properties of groups studied based on structural analysis; 4. use spectroscopic data from infrared spectrosc ...
... 2. use a mechanistic approach to make reasonable predictions of major products formed in reactions involving hydrocarbons, alkyl halides, alcohols and ethers; 3. explain physical and chemical properties of groups studied based on structural analysis; 4. use spectroscopic data from infrared spectrosc ...
2.1 The Nature of Matter - Sonoma Valley High School
... neutrons and different mass. All isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties b/c their electrons are the same. ...
... neutrons and different mass. All isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties b/c their electrons are the same. ...
Further Physical and Organic Chemistry
... Compounds containing the Carbonyl Group Aromatic Chemistry Amines Amino Acids Polymers Structure Determination ...
... Compounds containing the Carbonyl Group Aromatic Chemistry Amines Amino Acids Polymers Structure Determination ...
syllabus for entrance examination - NTU.edu
... and m are both integral and are either 0, 1 or 2. The use of the integrated forms of first- and second-order rate equations is not required but the use of constancy of half-life as a test for first order kinetics is included. Simple calculations on half-life may be set. Questions will not be set req ...
... and m are both integral and are either 0, 1 or 2. The use of the integrated forms of first- and second-order rate equations is not required but the use of constancy of half-life as a test for first order kinetics is included. Simple calculations on half-life may be set. Questions will not be set req ...
Chapter 2 - OrgSites.com
... Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds 1. Most organic compounds contain ___ and ___. 2. Summarize what Stanley Miller was able to demonstrate in 1953. ...
... Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds 1. Most organic compounds contain ___ and ___. 2. Summarize what Stanley Miller was able to demonstrate in 1953. ...
Glossary of Key Terms in Chapter Two
... gain of oxygen or loss of hydrogen; e.g., the conversion of an alcohol to an aldehyde or ketone via the use of an oxidizing agent. phenol (12.7) an organic compound that contains a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to a benzene ring. primary (1˚) alcohol (12.4) an alcohol with the general formula RCH2OH ...
... gain of oxygen or loss of hydrogen; e.g., the conversion of an alcohol to an aldehyde or ketone via the use of an oxidizing agent. phenol (12.7) an organic compound that contains a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to a benzene ring. primary (1˚) alcohol (12.4) an alcohol with the general formula RCH2OH ...
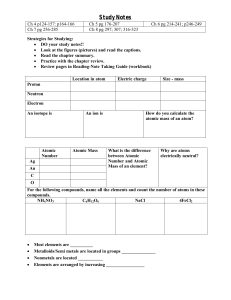
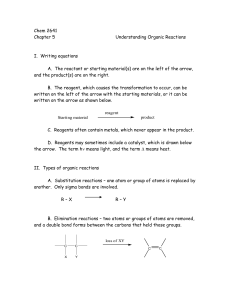
Chem 2641 Chapter 5 Understanding Organic Reactions I. Writing
... The initiation stage – Cl2 reacts with the uv light to form Cl. Propagation stage – The Cl. reacts with CH4 to form CH3. and HCl The CH3. reacts with Cl2 to form CH3Cl and Cl. Termination stage – any two radicals can combine to form a stable product. ...
... The initiation stage – Cl2 reacts with the uv light to form Cl. Propagation stage – The Cl. reacts with CH4 to form CH3. and HCl The CH3. reacts with Cl2 to form CH3Cl and Cl. Termination stage – any two radicals can combine to form a stable product. ...
BiochemistryMolecules
... Example: Glycerol 3. Molecules are commonly shown in “stick” form. This is a “lazy chemist” strategy to more quickly depict the structure of organic molecules. Since all organic molecules are built from carbon and hydrogen (and usually a lot of carbon and hydrogen atoms), these atoms are abbreviated ...
... Example: Glycerol 3. Molecules are commonly shown in “stick” form. This is a “lazy chemist” strategy to more quickly depict the structure of organic molecules. Since all organic molecules are built from carbon and hydrogen (and usually a lot of carbon and hydrogen atoms), these atoms are abbreviated ...
Covalent Bonds Ionic Bonds
... The outer electron is stripped from sodium and completes the chlorine atom’s outer shell Outer shell has 7 electrons ...
... The outer electron is stripped from sodium and completes the chlorine atom’s outer shell Outer shell has 7 electrons ...