3.8 ADDITION OF WATER TO AN ALKENE H or enzyme + H-O
... Our example just shows one molecule of monomer as a reactant, although in fact there are large numbers of them that will react with each other to form the polymer: The one sided arrows indicate that one electron goes to each C atom. This is in contrast to the previous reaction pathways where both el ...
... Our example just shows one molecule of monomer as a reactant, although in fact there are large numbers of them that will react with each other to form the polymer: The one sided arrows indicate that one electron goes to each C atom. This is in contrast to the previous reaction pathways where both el ...
Communicating Research to the General Public
... which are, in theory, the houses for the electrons. Each orbital has a specific shape and characteristics. For the sake of this discussion we will only discuss the d orbitals, which are shown in Figure 1.4. Each of these orbitals can, at maximum, hold two electrons. The oxidation state of the transi ...
... which are, in theory, the houses for the electrons. Each orbital has a specific shape and characteristics. For the sake of this discussion we will only discuss the d orbitals, which are shown in Figure 1.4. Each of these orbitals can, at maximum, hold two electrons. The oxidation state of the transi ...
Learning Outcomes
... Compounds containing metals in high oxidation states tend to be oxidising agents whereas compounds with metals in low oxidation states are often reducing agents. Dative covalent bonding of ligands in transition metal complexes A complex consists of a central metal ion surrounded by ligands. Ligands ...
... Compounds containing metals in high oxidation states tend to be oxidising agents whereas compounds with metals in low oxidation states are often reducing agents. Dative covalent bonding of ligands in transition metal complexes A complex consists of a central metal ion surrounded by ligands. Ligands ...
carbon hydrolysis synthesis
... 3.1 Why Is Carbon So Important in Biological Molecules? The unique bonding properties of carbon are key to the complexity of organic molecules – The carbon atom is versatile because it has four electrons in an outermost shell that can accommodate eight electrons – Therefore, a carbon atom can bec ...
... 3.1 Why Is Carbon So Important in Biological Molecules? The unique bonding properties of carbon are key to the complexity of organic molecules – The carbon atom is versatile because it has four electrons in an outermost shell that can accommodate eight electrons – Therefore, a carbon atom can bec ...
Organic/Biological Chemistry
... Therefore, alkynes have one and two bonds between two C atoms. Ethyne (acetylene) is a reactive alkyne: HCCH. When acetylene is burned in the presence of oxygen (oxyacetylene torch) the temperature is about 3200 K. Alkynes are named in the same way as alkenes with the suffix -yne replacing the ...
... Therefore, alkynes have one and two bonds between two C atoms. Ethyne (acetylene) is a reactive alkyne: HCCH. When acetylene is burned in the presence of oxygen (oxyacetylene torch) the temperature is about 3200 K. Alkynes are named in the same way as alkenes with the suffix -yne replacing the ...
Document
... halogens > O, S >> N, C. This cleavage is heterolytic, and requires that the charge site migrates. This means that this reaction is less favoured than radical-site reactions. 4) Decomposition of cyclic structures To produce a fragment from a ring, 2 bonds must be broken. If only one bond is cleaved, ...
... halogens > O, S >> N, C. This cleavage is heterolytic, and requires that the charge site migrates. This means that this reaction is less favoured than radical-site reactions. 4) Decomposition of cyclic structures To produce a fragment from a ring, 2 bonds must be broken. If only one bond is cleaved, ...
Biochemistry Worksheet
... 15. Cohesion of water molecules produces ________________ tension making water seem like it has a "skin" on it. Surface tension enables some _____________ to walk across the surface of the water. 16. Water molecules attracting other types of molecules is called ...
... 15. Cohesion of water molecules produces ________________ tension making water seem like it has a "skin" on it. Surface tension enables some _____________ to walk across the surface of the water. 16. Water molecules attracting other types of molecules is called ...
File
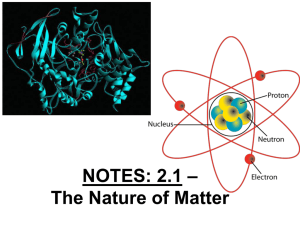
... Carbon has unique chemical properties that make it extremely versatile. • Carbon nucleus had 6 protons (and 6 neutrons) • Surrounded by an electron cloud containing 2 shells of 6 electrons total: 2 inner shell electrons 4 valence (outside) electrons Allow it to hook up and bond with many differ ...
... Carbon has unique chemical properties that make it extremely versatile. • Carbon nucleus had 6 protons (and 6 neutrons) • Surrounded by an electron cloud containing 2 shells of 6 electrons total: 2 inner shell electrons 4 valence (outside) electrons Allow it to hook up and bond with many differ ...
doc
... 4. History of the Periodic Table ______________________ (watch your spelling!) designed the first periodic table He arranged the elements by ________________________ atomic mass He left ________________ spaces according to similarities in columns of elements Mendeleev’s __________________ sp ...
... 4. History of the Periodic Table ______________________ (watch your spelling!) designed the first periodic table He arranged the elements by ________________________ atomic mass He left ________________ spaces according to similarities in columns of elements Mendeleev’s __________________ sp ...
Functional Hierarchical Structures from Peptide Building Blocks
... and peptide scaffolds as artificial enzymes and disease models, chemical origins of life and biopolymer-mineral composites as bone formation mimics. ...
... and peptide scaffolds as artificial enzymes and disease models, chemical origins of life and biopolymer-mineral composites as bone formation mimics. ...
Notes
... -the number of protons in an atom of an element •all atoms of an element have the same atomic # •written as a subscript next to the element’s symbol •in a neutral atom, the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons (balanced charges). ...
... -the number of protons in an atom of an element •all atoms of an element have the same atomic # •written as a subscript next to the element’s symbol •in a neutral atom, the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons (balanced charges). ...
3rd Quarter Test
... d) rates of the opposing reaction becomes equal 20) For a chemical system at equilibrium, a rise in temperature will a) favor the endothermic reaction b) favor the exothermic reaction c) decrease the rates of reaction d) have no effect upon the equilibrium 21) As 1 gram of H2O (g) changes to 1 gram ...
... d) rates of the opposing reaction becomes equal 20) For a chemical system at equilibrium, a rise in temperature will a) favor the endothermic reaction b) favor the exothermic reaction c) decrease the rates of reaction d) have no effect upon the equilibrium 21) As 1 gram of H2O (g) changes to 1 gram ...
General Chemistry (C) Sept
... Q1: What is a covalent bond? Q2: What compounds are formed with covalent bond? Molecular compounds and network compounds Localized electron-sharing model Bond Energy Bond strength and bond length Covalent radii Dipole moment and Polar bonds Multiple bonds:-bond, -bond, etc. Resonance and Electron ...
... Q1: What is a covalent bond? Q2: What compounds are formed with covalent bond? Molecular compounds and network compounds Localized electron-sharing model Bond Energy Bond strength and bond length Covalent radii Dipole moment and Polar bonds Multiple bonds:-bond, -bond, etc. Resonance and Electron ...
COVENANT UNIVERSITY College of Science and Technology
... Chemical Kinetics: Theory of the rates of reaction in both gas phase and solutions. Complex reactions and catalysis. Thermodynamics: Zeroth and third Law of thermodynamics, Statement of the Law, Evaluation of 3rd Law of Entropy from Cp Measurements, Tests and Applications. Chemical and phase equilib ...
... Chemical Kinetics: Theory of the rates of reaction in both gas phase and solutions. Complex reactions and catalysis. Thermodynamics: Zeroth and third Law of thermodynamics, Statement of the Law, Evaluation of 3rd Law of Entropy from Cp Measurements, Tests and Applications. Chemical and phase equilib ...