CHE 322
... conditions, to make the indicated large compound? In each case show the reaction that makes the C-C or C-O bond that links the pieces. All three must be different kinds of reactions. [Caution: parts of some reaction partners are missing in the given products due to replacement or subsequent reaction ...
... conditions, to make the indicated large compound? In each case show the reaction that makes the C-C or C-O bond that links the pieces. All three must be different kinds of reactions. [Caution: parts of some reaction partners are missing in the given products due to replacement or subsequent reaction ...
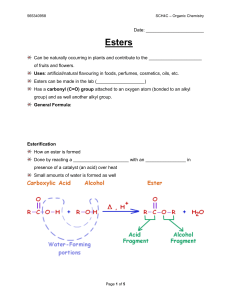
Esters - Mr. Lee`s Science
... Uses: artificial/natural flavouring in foods, perfumes, cosmetics, oils, etc. Esters can be made in the lab (___________________) Has a carbonyl (C=O) group attached to an oxygen atom (bonded to an alkyl group) and as well another alkyl group. General Formula: ...
... Uses: artificial/natural flavouring in foods, perfumes, cosmetics, oils, etc. Esters can be made in the lab (___________________) Has a carbonyl (C=O) group attached to an oxygen atom (bonded to an alkyl group) and as well another alkyl group. General Formula: ...
Test: "Chemical Equations" (General Chemistry)
... QUESTIONS 8-12 DEAL WITH THE REACTION BELOW. EACH COMPOUND CORRESPONDS WITH A LETTER ON YOUR ANSWER KEY. MARK ALL ANSWERS THAT APPLY. Given the balanced chemical equation: C6H12O6 (aq) + 6 O2 (g) 6 CO2 (g) + 6 H2O (l) ...
... QUESTIONS 8-12 DEAL WITH THE REACTION BELOW. EACH COMPOUND CORRESPONDS WITH A LETTER ON YOUR ANSWER KEY. MARK ALL ANSWERS THAT APPLY. Given the balanced chemical equation: C6H12O6 (aq) + 6 O2 (g) 6 CO2 (g) + 6 H2O (l) ...
Biological Molecules
... replaced by a phosphate group containing a polar functional group • The two fatty acid chains are hydrophobic • The phosphate head (being polar) is ...
... replaced by a phosphate group containing a polar functional group • The two fatty acid chains are hydrophobic • The phosphate head (being polar) is ...
Classifying Chemical Reactions 9-3
... We need one more oxygen in the products. Can’t change the formula, because it describes what it is (carbon monoxide in this example) ...
... We need one more oxygen in the products. Can’t change the formula, because it describes what it is (carbon monoxide in this example) ...
COURSE: Organic chemistry ACADEMIC YEAR:2016/2017 TYPE
... The course wants to give basic information on the principal properties of the organic compounds, allowing the student to understand the physical properties and the chemical behavior of every organic compounds. PRE-REQUIREMENTS General and inorganic chemistry SYLLABUS Electronic configuration. Bonds. ...
... The course wants to give basic information on the principal properties of the organic compounds, allowing the student to understand the physical properties and the chemical behavior of every organic compounds. PRE-REQUIREMENTS General and inorganic chemistry SYLLABUS Electronic configuration. Bonds. ...
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER-II Chemistry (Theory) Class-XII
... They prepare benzene diazonium chloride and stored it at room temperature. Due to holiday, they start preparing azodye but it cannot be prepared. Then their friend Reena told them to prepare benzene diazonium chloride again and to use it immediately to prepare azo dye and they proceed accordingly an ...
... They prepare benzene diazonium chloride and stored it at room temperature. Due to holiday, they start preparing azodye but it cannot be prepared. Then their friend Reena told them to prepare benzene diazonium chloride again and to use it immediately to prepare azo dye and they proceed accordingly an ...
Importance of Molecular Simulation for Studying Structural Properties
... interactions that dominate the organization of small objects at separations beyond an interatomic bond length. They give rise to forces that help systems lower their thermodynamic free energy. They should be distinguished from the basic chemical process of covalent bond formation associated with che ...
... interactions that dominate the organization of small objects at separations beyond an interatomic bond length. They give rise to forces that help systems lower their thermodynamic free energy. They should be distinguished from the basic chemical process of covalent bond formation associated with che ...
A`r ji r/ Ii
... 14. Suppose that during a reaction a chemistry student touches the eaker and observes that it feels COLD. The student should conclude that the chemical reaction is ...
... 14. Suppose that during a reaction a chemistry student touches the eaker and observes that it feels COLD. The student should conclude that the chemical reaction is ...
CfE Higher Chemistry Homework Unit 2: Natures Chemistry Soaps
... a. Compounds which combines with free radicals to form stable molecules. b. Compounds which cause free radical chain reactions c. Stable compounds used in skin care products which are made of vitamins. d. Compounds which break covalent bonds to form radicals. ...
... a. Compounds which combines with free radicals to form stable molecules. b. Compounds which cause free radical chain reactions c. Stable compounds used in skin care products which are made of vitamins. d. Compounds which break covalent bonds to form radicals. ...
2009_outline_4
... 4. Oxidation of Methyl Ketones (Haloform reaction) 5. Hydrolysis of Nitriles 6. Carbonation of Grignard Reagents (RMgX + CO2) ...
... 4. Oxidation of Methyl Ketones (Haloform reaction) 5. Hydrolysis of Nitriles 6. Carbonation of Grignard Reagents (RMgX + CO2) ...
Professor Marina Gatti
... Alkyl nucleophilic substitution and elimination reactions. Properties of haloalkanes. SN2 and SN1 mechanisms: factors influencing the reaction kinetics. E1 and E2 mechanisms. Competition between substitution and elimination. Alcohols, phenols and ethers. Nomenclature and acid-base properties of alco ...
... Alkyl nucleophilic substitution and elimination reactions. Properties of haloalkanes. SN2 and SN1 mechanisms: factors influencing the reaction kinetics. E1 and E2 mechanisms. Competition between substitution and elimination. Alcohols, phenols and ethers. Nomenclature and acid-base properties of alco ...
Code: I1 Title: Heterogeneous Catalysis Lecturer: Prof S D Jackson
... The course builds upon the knowledge gained in years 1 and 2. It will expand on the ideas of bonding through the use of examples from main group chemistry. The student will also learn about some of the general chemistry of these elements (particularly groups 13 – 16) in addition to some detailed stu ...
... The course builds upon the knowledge gained in years 1 and 2. It will expand on the ideas of bonding through the use of examples from main group chemistry. The student will also learn about some of the general chemistry of these elements (particularly groups 13 – 16) in addition to some detailed stu ...
Chemistry Review for End of year final honors
... 2.) A piece of metal is heated, then submerged in cool water. What will happen in the transfer of heat? (Where does the heat come from, where does it go to?) 3.) If the heat involved in a chemical reaction (q or ΔH) has a negative value, what does this ...
... 2.) A piece of metal is heated, then submerged in cool water. What will happen in the transfer of heat? (Where does the heat come from, where does it go to?) 3.) If the heat involved in a chemical reaction (q or ΔH) has a negative value, what does this ...
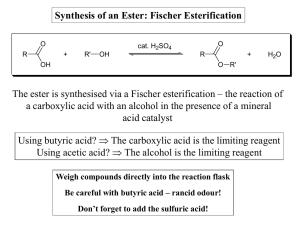
Synthesis of an Ester: Fischer Esterification The ester is synthesised
... As a result, they are partially extracted into the aqueous layer during work-up, reducing the amount recovered. ...
... As a result, they are partially extracted into the aqueous layer during work-up, reducing the amount recovered. ...
Lecture 5: Spectroscopy and Photochemistry I
... • Infrared radiation (λ = 0.8 - 300 µm) – Excites vibrational motions in molecules – With a very few exceptions, infrared radiation is not energetic enough to break molecules or initiate photochemical processes ...
... • Infrared radiation (λ = 0.8 - 300 µm) – Excites vibrational motions in molecules – With a very few exceptions, infrared radiation is not energetic enough to break molecules or initiate photochemical processes ...
Chapter 2 - Molecules of Life (Biochemistry) Periodic Table of
... • Electrons not shared equally! • One atom “hogs” the electrons! • This leads to the formation of hydrogen bonds.! ...
... • Electrons not shared equally! • One atom “hogs” the electrons! • This leads to the formation of hydrogen bonds.! ...
Organic Chemistry
... • Most of an organic compound does not react • Carbon-carbon and carbon-hydrogen single bonds almost never react • Carbon-carbon multiple bonds react with many reagents • Heteroatoms represent sites of reactivity in an organic molecule. • The reactive part of a molecule is called the FUNCTIONAL GROU ...
... • Most of an organic compound does not react • Carbon-carbon and carbon-hydrogen single bonds almost never react • Carbon-carbon multiple bonds react with many reagents • Heteroatoms represent sites of reactivity in an organic molecule. • The reactive part of a molecule is called the FUNCTIONAL GROU ...
NM Strand
... 52. A characteristic that can be observed or measured without changing the sample’s composition is 53. An experiment that determines the maximum number of grams of a substance that will dissolve in 100 grams of water measures: 54. Counting the number of cookies on a plate is what type of observation ...
... 52. A characteristic that can be observed or measured without changing the sample’s composition is 53. An experiment that determines the maximum number of grams of a substance that will dissolve in 100 grams of water measures: 54. Counting the number of cookies on a plate is what type of observation ...