Chemical Equilibrium
... ability to affect the equilibrium. Chemical equilibria can be shifted by changing the conditions that the system experiences. We say that we “stress” the equilibrium. When we stress the equilibrium, the chemical reaction is no longer at equilibrium, and the reaction starts to move back toward equilib ...
... ability to affect the equilibrium. Chemical equilibria can be shifted by changing the conditions that the system experiences. We say that we “stress” the equilibrium. When we stress the equilibrium, the chemical reaction is no longer at equilibrium, and the reaction starts to move back toward equilib ...
Chem. 1310 Fall 2005 Final Exam-white ... Name _________________________________ Section Number ___________________
... a. increase the entropy of the universe. b. decrease the energy of the universe. Answer: a 22. Which of the following are generally true? a. Intermolecular forces are weaker than covalent bonds. b. Intermolecular forces are more directional than covalent bonds. c. Any molecule in a gas experiences i ...
... a. increase the entropy of the universe. b. decrease the energy of the universe. Answer: a 22. Which of the following are generally true? a. Intermolecular forces are weaker than covalent bonds. b. Intermolecular forces are more directional than covalent bonds. c. Any molecule in a gas experiences i ...
1.4 Enthalpy
... Use a Bomb calorimeter (left). This apparatus reduces heat loss s the water is insulated from the surroundings. It is burnt in oxygen to ensure complete combustion. ...
... Use a Bomb calorimeter (left). This apparatus reduces heat loss s the water is insulated from the surroundings. It is burnt in oxygen to ensure complete combustion. ...
Arkema exhibits at CPhI 2006, Paris, from October 3
... green oxidation catalyst makes its own contribution to the demands of modern chemistry which makes environmental protection a priority. The Oxynitrox® S100 catalyst offers countless prospects in fine chemicals, in particular with its capacity to steer the selective oxidation of primary alcohols into ...
... green oxidation catalyst makes its own contribution to the demands of modern chemistry which makes environmental protection a priority. The Oxynitrox® S100 catalyst offers countless prospects in fine chemicals, in particular with its capacity to steer the selective oxidation of primary alcohols into ...
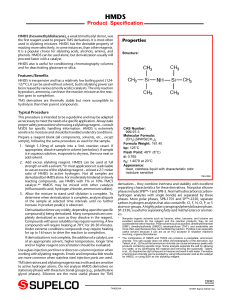
HMDS - Sigma
... atom of the silyl donor, producing a bimolecular transition state. The silyl compound leaving group (X) must posses low basicity, the ability to stabilize a negative charge in the transition state, and little or no tendency for π (p-d) back bonding between itself and the silicon atom. The ideal sily ...
... atom of the silyl donor, producing a bimolecular transition state. The silyl compound leaving group (X) must posses low basicity, the ability to stabilize a negative charge in the transition state, and little or no tendency for π (p-d) back bonding between itself and the silicon atom. The ideal sily ...
Ch3temp
... • Empirical- simplest whole-number ratio of atoms in a formula • Molecular - the “true” ratio of atoms in a formula; often a whole-number multiple of the empirical formula • We can determine empirical formulas from % composition data; a good ...
... • Empirical- simplest whole-number ratio of atoms in a formula • Molecular - the “true” ratio of atoms in a formula; often a whole-number multiple of the empirical formula • We can determine empirical formulas from % composition data; a good ...
EIT Review S2012 Part 2 Dr. J. Mack CSUS Department of Chemistry
... “p” orbitals hold up to 6 electrons “d” orbitals can hold up to 10 electrons ...
... “p” orbitals hold up to 6 electrons “d” orbitals can hold up to 10 electrons ...
cluster definition
... As mentioned above, both boxes contain bulk matter, and this implies that there are no boundaries at the edges of the simulation boxes. This is taken care of by the use of periodic boundary conditions, which means that the box is considered to be surrounded by identical copies of itself in all dire ...
... As mentioned above, both boxes contain bulk matter, and this implies that there are no boundaries at the edges of the simulation boxes. This is taken care of by the use of periodic boundary conditions, which means that the box is considered to be surrounded by identical copies of itself in all dire ...
lecture 11 catalysis_hydrogenation of alkenes
... RuCl2(PPh3)3 is believed to activate H2 heterolytically, a reaction accelerated by bases, such as NEt3. ...
... RuCl2(PPh3)3 is believed to activate H2 heterolytically, a reaction accelerated by bases, such as NEt3. ...
Chapter 9 Stoichiometry
... 5. Calculate the mass of a reactant or product from the mass of a different reactant or product. 6. Describe a method for determining which of two reactants is a limiting reactant. 7. Calculate the amount in moles of a product produced, given the amounts in moles of two reactants, one of which is in ...
... 5. Calculate the mass of a reactant or product from the mass of a different reactant or product. 6. Describe a method for determining which of two reactants is a limiting reactant. 7. Calculate the amount in moles of a product produced, given the amounts in moles of two reactants, one of which is in ...
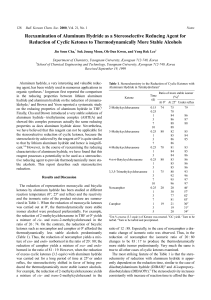
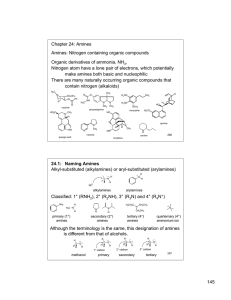
145 Chapter 24: Amines Amines: Nitrogen containing organic
... Symmetrical secondary and tertiary amines are named by adding the prefix di- or tri- to the alkyl group Unsymmetrical secondary and tertiary amines are named as N-substituted primary amines. The largest alkyl group is the parent name, and other alkyl groups are considered N-substituents. H H3CH2C ...
... Symmetrical secondary and tertiary amines are named by adding the prefix di- or tri- to the alkyl group Unsymmetrical secondary and tertiary amines are named as N-substituted primary amines. The largest alkyl group is the parent name, and other alkyl groups are considered N-substituents. H H3CH2C ...
Predictive thermodynamics for ionic solids and
... the further complication of the necessity for the user to identify suitable groups within the material under consideration. Many computer programs incorporate these methods, often as preliminary steps to a more complex analysis. The NIST WebBook26 provides a free service which implements the Benson ...
... the further complication of the necessity for the user to identify suitable groups within the material under consideration. Many computer programs incorporate these methods, often as preliminary steps to a more complex analysis. The NIST WebBook26 provides a free service which implements the Benson ...
CHEM 203 Material
... Principle: determining whether the bonded state of a given atom resembles more closely the preceding or the successive noble gas allows one to make important predictions about chemical reactivity: Example: the C atom in CH4 has formally acquired 4 electrons, thereby assuming the oxidation state of – ...
... Principle: determining whether the bonded state of a given atom resembles more closely the preceding or the successive noble gas allows one to make important predictions about chemical reactivity: Example: the C atom in CH4 has formally acquired 4 electrons, thereby assuming the oxidation state of – ...
Recrystallization: A Purification Technique
... remove small impurities from solid compounds. This technique exploits the property of compounds that, when temperature increases, solubility increases. The higher the temperature of the solvent, the more material can be dissolved. Slow cooling separates the saturated solute in the form of crystals a ...
... remove small impurities from solid compounds. This technique exploits the property of compounds that, when temperature increases, solubility increases. The higher the temperature of the solvent, the more material can be dissolved. Slow cooling separates the saturated solute in the form of crystals a ...