Acta Chim. Slov. 2000, 47, 179−185. 179 Co(II), Ni(II) and Cu(II
... CuII, and L is Schiff base formed by condensation of 2-thiophenecarboxaldehyde and propylamine, N-[2-thienylmethylidene]-1-propanamine (TNAP), or ethylamine, N-[2thienylmethylidene]ethanamine (TNAE), have been prepared and characterised by elemental analysis, magnetic and spectroscopic measurements. ...
... CuII, and L is Schiff base formed by condensation of 2-thiophenecarboxaldehyde and propylamine, N-[2-thienylmethylidene]-1-propanamine (TNAP), or ethylamine, N-[2thienylmethylidene]ethanamine (TNAE), have been prepared and characterised by elemental analysis, magnetic and spectroscopic measurements. ...
Unit 4 Chemical Kinetics and Chemical Equilibrium
... product(s) for the following reaction. Which one will be the major product? ...
... product(s) for the following reaction. Which one will be the major product? ...
K c
... 1. The concentrations of the reacting species in the condensed phase are expressed in mol/L (M). In the gaseous phase, the concentrations can be expressed in M. 2. The concentrations of pure solids, pure liquids and solvents do not appear in the equilibrium constant expressions. 3. The equilibrium c ...
... 1. The concentrations of the reacting species in the condensed phase are expressed in mol/L (M). In the gaseous phase, the concentrations can be expressed in M. 2. The concentrations of pure solids, pure liquids and solvents do not appear in the equilibrium constant expressions. 3. The equilibrium c ...
Esterification and Esters
... In this expression, α depends on those rate coefficients in the above mechanism whose values are assumed to be high. Other mechanisms for the acid hydrolysis and esterification differ mainly with respect to the number of participating water molecules and possible intermediates (21−23). Applications ...
... In this expression, α depends on those rate coefficients in the above mechanism whose values are assumed to be high. Other mechanisms for the acid hydrolysis and esterification differ mainly with respect to the number of participating water molecules and possible intermediates (21−23). Applications ...
Chapter-16B
... Characteristic Reactions • in the general reaction, we showed the nucleophile as an anion; this need not be the case • neutral molecules such as water, alcohols, ammonia, and amines can also serve as nucleophiles • in the general reaction, we showed the leaving group as an anion to illustrate an im ...
... Characteristic Reactions • in the general reaction, we showed the nucleophile as an anion; this need not be the case • neutral molecules such as water, alcohols, ammonia, and amines can also serve as nucleophiles • in the general reaction, we showed the leaving group as an anion to illustrate an im ...
Supercritical Degradation of Unsaturated Polyester Resin
... without any recycling attempt. This is not sustainable in the long term, why such disposal routes have been regulated by EU directives such as End of Life Vehicles (ELV) and Waste Electrical Equipment (WEEE). ELV and WEEE have put more pressure on solving FR polymer waste problems through recycling ...
... without any recycling attempt. This is not sustainable in the long term, why such disposal routes have been regulated by EU directives such as End of Life Vehicles (ELV) and Waste Electrical Equipment (WEEE). ELV and WEEE have put more pressure on solving FR polymer waste problems through recycling ...
Fragmentations Associated with Organic Functional Groups
... anchimeric assistance (a kind of internal SN2 process): H CH3 ...
... anchimeric assistance (a kind of internal SN2 process): H CH3 ...
4Chemical Quantities and Aqueous Reactions
... atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2)—Earth’s most significant greenhouse gas in terms of climate change—is rising. More CO2 enhances the atmosphere’s ability to hold heat and may therefore lead to global warming, an increase in Earth’s average temperature. Since 1860, atmospheric CO2 levels have risen b ...
... atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2)—Earth’s most significant greenhouse gas in terms of climate change—is rising. More CO2 enhances the atmosphere’s ability to hold heat and may therefore lead to global warming, an increase in Earth’s average temperature. Since 1860, atmospheric CO2 levels have risen b ...
text
... The sign of ∆G indicates the direction in which a reaction moves to reach its equilibrium position. A reaction is thermodynamically favorable when its enthalpy, ∆H, decreases and its entropy, ∆S, increases. Substitut‑ ing the inequalities ∆H < 0 and ∆S > 0 into equation 6.2 shows that a reaction is ...
... The sign of ∆G indicates the direction in which a reaction moves to reach its equilibrium position. A reaction is thermodynamically favorable when its enthalpy, ∆H, decreases and its entropy, ∆S, increases. Substitut‑ ing the inequalities ∆H < 0 and ∆S > 0 into equation 6.2 shows that a reaction is ...
Absorption Spectra and Photolysis of Methyl Peroxide in Liquid and
... aerosols, and some of them are water soluble.12,25 Since photochemistry of large organic molecules is driven by functional groups, we use CH3OOH as a model compound to elucidate the general kinetic behavior of organic peroxides in the condensed phase. The condensed phase chemistry of these larger RO ...
... aerosols, and some of them are water soluble.12,25 Since photochemistry of large organic molecules is driven by functional groups, we use CH3OOH as a model compound to elucidate the general kinetic behavior of organic peroxides in the condensed phase. The condensed phase chemistry of these larger RO ...
13 CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM W MODULE - 5
... reaction, it is believed that all the reactants would be converted into products with the release or absorption of energy. This is not true in all cases. Many chemical reactions proceed only to a certain extent and stop. When analysed, the resulting mixture contains both the reactants and products. ...
... reaction, it is believed that all the reactants would be converted into products with the release or absorption of energy. This is not true in all cases. Many chemical reactions proceed only to a certain extent and stop. When analysed, the resulting mixture contains both the reactants and products. ...
9: Formation of Alkenes and Alkynes. Elimination Reactions
... The C-A and C-B bonds break in the elimination reaction, and a second bond forms between the two C's to form a C=C bond. "A-B" in Figure 9.01 may not be an actual reaction product, but we show it this way in this general example in order to keep the chemical bonds on both sides of the equation in ba ...
... The C-A and C-B bonds break in the elimination reaction, and a second bond forms between the two C's to form a C=C bond. "A-B" in Figure 9.01 may not be an actual reaction product, but we show it this way in this general example in order to keep the chemical bonds on both sides of the equation in ba ...
Chemistry 101L
... will be making. Remember to include room for multiple trials and average values, if appropriate. If appropriate, have room for classmates’ data. Now organize your list into things that are similar or data that should be compared. Tables columns/rows do not have to be listed in the same order that th ...
... will be making. Remember to include room for multiple trials and average values, if appropriate. If appropriate, have room for classmates’ data. Now organize your list into things that are similar or data that should be compared. Tables columns/rows do not have to be listed in the same order that th ...
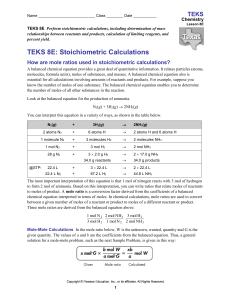
TEKS 5 - Online Learning Exchange
... How do you calculate percent yield? When a teacher gives an exam to the class, every student could get a grade of 100 percent. However, this outcome generally does not occur. Instead, the performance of the class is usually spread over a range of grades. Your exam grade, expressed as a percentage, i ...
... How do you calculate percent yield? When a teacher gives an exam to the class, every student could get a grade of 100 percent. However, this outcome generally does not occur. Instead, the performance of the class is usually spread over a range of grades. Your exam grade, expressed as a percentage, i ...
Chapter 3 Stoichiometry: Ratios of Combination
... • Empirical- simplest whole-number ratio of atoms in a formula • Molecular - the “true” ratio of atoms in a formula; often a whole-number multiple of the empirical formula • We can determine empirical formulas from % composition data; a good ...
... • Empirical- simplest whole-number ratio of atoms in a formula • Molecular - the “true” ratio of atoms in a formula; often a whole-number multiple of the empirical formula • We can determine empirical formulas from % composition data; a good ...
Conjugate addition_Clayden
... The reason that α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds react differently is conjugation, the phenomenon we discussed in Chapter 7. There we introduced you to the idea that bringing two π systems (two C=C bonds, for example, or a C=C bond and a C=O bond) close together leads to a stabilizing interaction. ...
... The reason that α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds react differently is conjugation, the phenomenon we discussed in Chapter 7. There we introduced you to the idea that bringing two π systems (two C=C bonds, for example, or a C=C bond and a C=O bond) close together leads to a stabilizing interaction. ...
Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Chemical Reactions
... The calculation of either weight is straightforward; it is the sum of the individual atomic weights of all atoms or ions present in one particle of the substance. The average atomic weight of an ...
... The calculation of either weight is straightforward; it is the sum of the individual atomic weights of all atoms or ions present in one particle of the substance. The average atomic weight of an ...