Inorganic Reaction Mechanisms at the Molecular Level Oxford
... these types of reactions are not amenable to selective generation of primary oxidation products such as alcohols from alkanes. For these types of oxidation reactions, due to the low homolytic bond strength of the CH bonds of the alcohol product compared to the starting alkane, transition states or i ...
... these types of reactions are not amenable to selective generation of primary oxidation products such as alcohols from alkanes. For these types of oxidation reactions, due to the low homolytic bond strength of the CH bonds of the alcohol product compared to the starting alkane, transition states or i ...
EXPERIMENT 3: The Grignard Reaction: Synthesis of
... The reactions involved in the synthesis of complex organic molecules can commonly be categorized into either functional group interconversions or skeleton building reactions. The latter category, primarily those involving carbon-carbon bond formations, is most important in anabolic organic synthesis ...
... The reactions involved in the synthesis of complex organic molecules can commonly be categorized into either functional group interconversions or skeleton building reactions. The latter category, primarily those involving carbon-carbon bond formations, is most important in anabolic organic synthesis ...
Print PDF
... This course provides students who plan future studies in forensic science technology, chemical sciences or chemical engineering a firm grounding in the quantum mechanical description of molecules, as well as a critical set of insights into thermochemical reasoning. The quantum mechanical focus will ...
... This course provides students who plan future studies in forensic science technology, chemical sciences or chemical engineering a firm grounding in the quantum mechanical description of molecules, as well as a critical set of insights into thermochemical reasoning. The quantum mechanical focus will ...
sn2 reactions of alkyl halides
... 1-chlorobutane? Explain how the nature of the leaving group affects the rate of an SN 2 reaction. Would 1-iodobutane react faster or slower than the other halides? How would we know that the ...
... 1-chlorobutane? Explain how the nature of the leaving group affects the rate of an SN 2 reaction. Would 1-iodobutane react faster or slower than the other halides? How would we know that the ...
CHM 253L Organic Chemistry Laboratory I
... be for the entire series of compounds. You'll need to consider the contributions of polarity AND hydrogen bonding. Compare with literature solubility data for each compound in water. Be sure to cite your source!!! 9. Describe how the modeled ions demonstrate the hybrid structure or weighted average ...
... be for the entire series of compounds. You'll need to consider the contributions of polarity AND hydrogen bonding. Compare with literature solubility data for each compound in water. Be sure to cite your source!!! 9. Describe how the modeled ions demonstrate the hybrid structure or weighted average ...
0_specific - ugc-inno
... Geometry Optimization starting with Zwitterion form can happen unhindered even in presence of water even if water does not seem to be significantly faciliting what happens without its presence. Geometrical Variations At this juncture the question of greater concern seems to be to find ways for proto ...
... Geometry Optimization starting with Zwitterion form can happen unhindered even in presence of water even if water does not seem to be significantly faciliting what happens without its presence. Geometrical Variations At this juncture the question of greater concern seems to be to find ways for proto ...
Quiz 3 – Aldehydes and Ketones 1 Which of the following reactions
... 7 You have two C6H10O ketones, I and II. Both are optically active, but I is racemized by treatment with base and II is not. Wolff-Kishner reduction of both ketones gives the same achiral hydrocarbon, formula C6H12. What reasonable structures may be assigned to I and II? A) I is 3-methyl-4-penten-2- ...
... 7 You have two C6H10O ketones, I and II. Both are optically active, but I is racemized by treatment with base and II is not. Wolff-Kishner reduction of both ketones gives the same achiral hydrocarbon, formula C6H12. What reasonable structures may be assigned to I and II? A) I is 3-methyl-4-penten-2- ...
chapter 4 carbon and the molecular diversity of life
... 2. Carbon atoms are the most versatile building blocks of molecules • With a total of 6 electrons, a carbon atom has 2 in the first shell and 4 in the second shell. – Carbon has little tendency to form ionic bonds by loosing or gaining 4 electrons. – Instead, carbon usually completes its valence sh ...
... 2. Carbon atoms are the most versatile building blocks of molecules • With a total of 6 electrons, a carbon atom has 2 in the first shell and 4 in the second shell. – Carbon has little tendency to form ionic bonds by loosing or gaining 4 electrons. – Instead, carbon usually completes its valence sh ...
BJ - Faculty Web Pages
... (c) Which of the following molecules may show a rotational Raman spectrum: H2, NO, N2O, CH4 H2, NO, N2O (d) Say you wish to study the anti-Stokes portion of the Raman spectrum of a sample, but you are having difficulty because the peaks barely rise above the baseline. What could you do to the sample ...
... (c) Which of the following molecules may show a rotational Raman spectrum: H2, NO, N2O, CH4 H2, NO, N2O (d) Say you wish to study the anti-Stokes portion of the Raman spectrum of a sample, but you are having difficulty because the peaks barely rise above the baseline. What could you do to the sample ...
document
... Relative numbers of reactant and product molecules that are required. Can be used to determine masses of reactants used and products that can be made. ...
... Relative numbers of reactant and product molecules that are required. Can be used to determine masses of reactants used and products that can be made. ...
MSc Applied Chemistry Syllabus
... Basic quantum mechanics-Functions and operations postulates of quantum mechanicsSchordinger equation-physical significance of wave function-Radial dependence curves-Radial probability distribution curves and their significance-Angular functions. Applications of Schordinger’s equation to a particle i ...
... Basic quantum mechanics-Functions and operations postulates of quantum mechanicsSchordinger equation-physical significance of wave function-Radial dependence curves-Radial probability distribution curves and their significance-Angular functions. Applications of Schordinger’s equation to a particle i ...
Example - cloudfront.net
... a) Balance elements that appear in more than one compound __________ (NH4)2CO3 NH3 + CO2 + H2O b) Balance __________________ as though they are one item as long as the ion stays together as a group on each side of the arrow. Al + CuSO4 Al2(SO4)3 + Cu c) If you can’t seem to get it balanced, ____ ...
... a) Balance elements that appear in more than one compound __________ (NH4)2CO3 NH3 + CO2 + H2O b) Balance __________________ as though they are one item as long as the ion stays together as a group on each side of the arrow. Al + CuSO4 Al2(SO4)3 + Cu c) If you can’t seem to get it balanced, ____ ...
M.Sc.Course - Department of Chemistry, IIT Bombay
... Basic concepts of quantitative analysis, methods of sampling, errors in chemical analysis of data, general theory of neutralisation, redox, precipitation and complexometric titrations. Solubility product and precipitation, organic precipitants and extractants. A brief survey of separation methods: s ...
... Basic concepts of quantitative analysis, methods of sampling, errors in chemical analysis of data, general theory of neutralisation, redox, precipitation and complexometric titrations. Solubility product and precipitation, organic precipitants and extractants. A brief survey of separation methods: s ...
esters - wellswaysciences
... © Pearson Education Ltd 2009 This document may have been altered from the original ...
... © Pearson Education Ltd 2009 This document may have been altered from the original ...
chapter twenty-two organic and biological molecules
... a. Addition polymer: Polymer that forms by adding monomer units together (usually by reacting double bonds). Teflon, polyvinyl chloride and polyethylene are examples of addition polymers. b. Condensation polymer: Polymer that forms when two monomers combine by eliminating a small molecule (usually H ...
... a. Addition polymer: Polymer that forms by adding monomer units together (usually by reacting double bonds). Teflon, polyvinyl chloride and polyethylene are examples of addition polymers. b. Condensation polymer: Polymer that forms when two monomers combine by eliminating a small molecule (usually H ...
UV Spectroscopy
... Principle: Colorimetry analysis method is useful in determining the concentration of coloured solutions using the visible region (400nm–750nm) of electromagnetic spectrum and Beer Lambert’s law. If the test solution is colourless then a suitable complexing agent can be added to test solution to get ...
... Principle: Colorimetry analysis method is useful in determining the concentration of coloured solutions using the visible region (400nm–750nm) of electromagnetic spectrum and Beer Lambert’s law. If the test solution is colourless then a suitable complexing agent can be added to test solution to get ...
Lewis Structure Activity
... http://www.stolaf.edu/depts/chemistry/courses/toolkits/121/js/lewis Check your electron tally answer with total required valence electrons in the table on the bottom of the paper. Then try to create the Lewis structure. Once you are satisfied with your structure, check it. Write the correct structur ...
... http://www.stolaf.edu/depts/chemistry/courses/toolkits/121/js/lewis Check your electron tally answer with total required valence electrons in the table on the bottom of the paper. Then try to create the Lewis structure. Once you are satisfied with your structure, check it. Write the correct structur ...
Higher Chemistry Learning Outcomes
... The first ionisation energy is the energy required to remove one mole of electrons from one mole of gaseous atoms. The second and subsequent ionisation energies refer to the energies required to remove further moles of electrons. The trends in first ionisation energy across periods and down gr ...
... The first ionisation energy is the energy required to remove one mole of electrons from one mole of gaseous atoms. The second and subsequent ionisation energies refer to the energies required to remove further moles of electrons. The trends in first ionisation energy across periods and down gr ...
Final Exam SG Part 1 (Unit 5).
... c. How many moles are produced from the moles of the reactants? d. If you double the amount of white molecules (so now you have 8 pairs) but keep the same amount of black molecules, how many molecules can you produce? 4. Percent Yield a. ___Sb4O6 + ____C → ____Sb + ____CO Determine the percent yield ...
... c. How many moles are produced from the moles of the reactants? d. If you double the amount of white molecules (so now you have 8 pairs) but keep the same amount of black molecules, how many molecules can you produce? 4. Percent Yield a. ___Sb4O6 + ____C → ____Sb + ____CO Determine the percent yield ...
Mr. Hauptman Organic Chemistry
... This compound is classified as (1) an aldehyde (3) an amine (2) an amide (4) a ketone 32) Given the structural formula: This structural formula represents a molecule of (1) an aldehyde (3) a ketone (2) an ester (4) an amino acid Base your answers to questions 33 and 34 on the information below. Give ...
... This compound is classified as (1) an aldehyde (3) an amine (2) an amide (4) a ketone 32) Given the structural formula: This structural formula represents a molecule of (1) an aldehyde (3) a ketone (2) an ester (4) an amino acid Base your answers to questions 33 and 34 on the information below. Give ...
Document
... • Water is split and electrons transferred with H+ from water to CO2, reducing it to sugar. ...
... • Water is split and electrons transferred with H+ from water to CO2, reducing it to sugar. ...
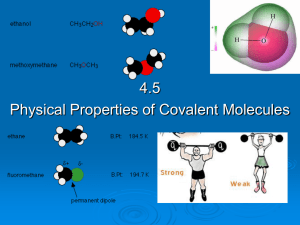
4.5 Physical properties of molecular covalent
... decreases. E.g. Individual amino acids are soluble in water but large protein polymers are generally insoluble. As the non-polar hydrocarbon chain of a polar molecule increases, the solubility of the molecule decreases because the non-polar carbon chain outweighs the polar part. E.g. ethanol (CH3CH2 ...
... decreases. E.g. Individual amino acids are soluble in water but large protein polymers are generally insoluble. As the non-polar hydrocarbon chain of a polar molecule increases, the solubility of the molecule decreases because the non-polar carbon chain outweighs the polar part. E.g. ethanol (CH3CH2 ...
Describing Matter
... observed without changing a substance into another. - Chemical properties can be observed only by changing substances into other substances. * The scissors are physically hard, they chemically rusted. 4. A metal melts at 450 degrees C. Is this a physical or chemical property – explain? - Melting is ...
... observed without changing a substance into another. - Chemical properties can be observed only by changing substances into other substances. * The scissors are physically hard, they chemically rusted. 4. A metal melts at 450 degrees C. Is this a physical or chemical property – explain? - Melting is ...