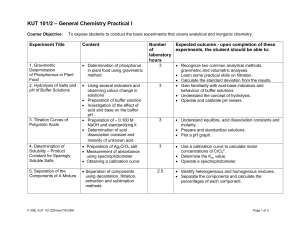
4.5: Bonding in Alcohols and Alkyl Halides
... 4.4: Classes of Alcohols and Alkyl Halides - Alcohols and alkyl halides are classified as according to the degree of substitution of the carbon bearing the halogen or -OH group OH primary (1°) : one alkyl substituent secondary (2°) : two alkyl substituents tertiary (3°) : three alkyl substituents 2- ...
... 4.4: Classes of Alcohols and Alkyl Halides - Alcohols and alkyl halides are classified as according to the degree of substitution of the carbon bearing the halogen or -OH group OH primary (1°) : one alkyl substituent secondary (2°) : two alkyl substituents tertiary (3°) : three alkyl substituents 2- ...
All of these can affect the rate at which a
... B a chemical change C both a chemical change and a physical change D neither a chemical nor a physical change 9. Other types of weathering involve the breaking down of rock by agents such as acids in rain, in groundwater, or released by certain plants. What type of change is involved in this type of ...
... B a chemical change C both a chemical change and a physical change D neither a chemical nor a physical change 9. Other types of weathering involve the breaking down of rock by agents such as acids in rain, in groundwater, or released by certain plants. What type of change is involved in this type of ...
7.2 Writing Chemical Equations
... substances change in his atomic theory. In a chemical reaction the ways in which the atoms are joined together are changed. As reactants are changed into products, bonds that hold atoms together are broken and new bonds are ...
... substances change in his atomic theory. In a chemical reaction the ways in which the atoms are joined together are changed. As reactants are changed into products, bonds that hold atoms together are broken and new bonds are ...
Chemistry B11 Chapter 4 Chemical reactions
... using chemical formulas for the reactants and products, and an arrow to indicate the direction in which the reaction proceeds. Note: It is important to show the state of each reactant and product in a chemical equation (immediately following each reactant and product). We use the symbol (g) for gas, ...
... using chemical formulas for the reactants and products, and an arrow to indicate the direction in which the reaction proceeds. Note: It is important to show the state of each reactant and product in a chemical equation (immediately following each reactant and product). We use the symbol (g) for gas, ...
Using the Molar Mass of Octane (Advanced)
... Using the Molar Mass of Octane (Advanced) Gasoline is not a simple chemical compound like water or ethanol. It is a mixture of hundreds of different compounds. The reason for this is that gasoline is made from crude oil (petroleum) which is made up of thousands of different compounds. After the oil ...
... Using the Molar Mass of Octane (Advanced) Gasoline is not a simple chemical compound like water or ethanol. It is a mixture of hundreds of different compounds. The reason for this is that gasoline is made from crude oil (petroleum) which is made up of thousands of different compounds. After the oil ...
Παρουσίαση του PowerPoint
... Chemists synthesize compounds in just about every organic chemistry laboratory in the world. Industrial chemists synthesize pharmaceuticals, polymers (plastics), pesticides, dye stuffs, food colorings and flavorings, perfumes, detergents and disinfectants. Research chemists synthesize natural produc ...
... Chemists synthesize compounds in just about every organic chemistry laboratory in the world. Industrial chemists synthesize pharmaceuticals, polymers (plastics), pesticides, dye stuffs, food colorings and flavorings, perfumes, detergents and disinfectants. Research chemists synthesize natural produc ...
Chapter 3
... Molar Mass • Use Factor-Label method to convert g <-> mole • Question: How many moles in 46.0 g water • Question: How many g in 0.76 moles of NaCl? • Question: How many molecules in 100.0 g water? ...
... Molar Mass • Use Factor-Label method to convert g <-> mole • Question: How many moles in 46.0 g water • Question: How many g in 0.76 moles of NaCl? • Question: How many molecules in 100.0 g water? ...
Biochemistry Notes
... Biochemical unity-organisms can acquire needed biochemicals by consuming other organisms. Because ...
... Biochemical unity-organisms can acquire needed biochemicals by consuming other organisms. Because ...
EXAM 3
... A 5.000 g sample of a compound known to contain only the elements phosphorous and oxygen was analyzed and found to contain 2.182 g of phosphorous. Additional experiments indicate that this compound has a molecular weight of 283.9 g/mol. How many phosphorous atoms are present in each molecule of this ...
... A 5.000 g sample of a compound known to contain only the elements phosphorous and oxygen was analyzed and found to contain 2.182 g of phosphorous. Additional experiments indicate that this compound has a molecular weight of 283.9 g/mol. How many phosphorous atoms are present in each molecule of this ...
OR 6-31G - unix.eng.ua.edu
... • Account for ‘weakly’ bound electrons (excited states, anions, lone pairs). Normally, e- density is localized near the nucleus in previous basis sets. • 6-31+G = one additional set of s and p Gaussian functions on ‘heavy’ atoms. • 6-31++G = adds one additional diffuse s function on H • Have an expo ...
... • Account for ‘weakly’ bound electrons (excited states, anions, lone pairs). Normally, e- density is localized near the nucleus in previous basis sets. • 6-31+G = one additional set of s and p Gaussian functions on ‘heavy’ atoms. • 6-31++G = adds one additional diffuse s function on H • Have an expo ...
Lipids - Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
... • unsaturated fatty acids contain one or more double bonds (usually liquid at room temp) monounsaturated – one double bond polyunsaturated – more than one double bond • about 30 different fatty acids are commonly found in triacylglycerols; most have an even number of carbons ...
... • unsaturated fatty acids contain one or more double bonds (usually liquid at room temp) monounsaturated – one double bond polyunsaturated – more than one double bond • about 30 different fatty acids are commonly found in triacylglycerols; most have an even number of carbons ...
Chapter 13 – Alcohols, Phenols, Ethers, and Thioethers
... CH3CH2O- + CH3CH2Cl → CH3CH2OCH2CH3 + Clwhere the Na+ ion is a spectator ion (see p. 214 of textbook). For ethers with different R groups bound to oxygen, all one has to do is use an alcohol with one organic group and organic chloride with a different group. Again, when the generation of an ether l ...
... CH3CH2O- + CH3CH2Cl → CH3CH2OCH2CH3 + Clwhere the Na+ ion is a spectator ion (see p. 214 of textbook). For ethers with different R groups bound to oxygen, all one has to do is use an alcohol with one organic group and organic chloride with a different group. Again, when the generation of an ether l ...
CHEM110P1_06_2015_Y_P1
... In polar covalent bonds, the two atoms involved in bond formation have different electronegativity values. ...
... In polar covalent bonds, the two atoms involved in bond formation have different electronegativity values. ...
Chapter 1
... – Hydrogen: forms one covalent bond and no unshared pairs of electrons. H – Nitrogen: normally forms three covalent bonds and has one unshared pair of electrons. ...
... – Hydrogen: forms one covalent bond and no unshared pairs of electrons. H – Nitrogen: normally forms three covalent bonds and has one unshared pair of electrons. ...
C h e m g u id e –... ACYL CHLORIDES: REACTIONS WITH WATER, ALCOHOLS AND PHENOLS
... group. Ethanoylation is a particular example of acylation where a CH3C=O group (an ethanoyl group) is substituted into another molecule. ...
... group. Ethanoylation is a particular example of acylation where a CH3C=O group (an ethanoyl group) is substituted into another molecule. ...