2.6 M - Thierry Karsenti
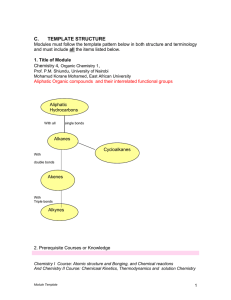
... Prof. P.M. Shiundu, University of Nairobi Mohamud Korane Mohamed, East African University Aliphatic Organic compounds and their interrelated functional groups ...
... Prof. P.M. Shiundu, University of Nairobi Mohamud Korane Mohamed, East African University Aliphatic Organic compounds and their interrelated functional groups ...
Surface electrochemistry
... Langmuir isotherm. Enthalpy of adsorption. Kinetics of catalytic reactions. The solid-state electrochemical cell. Electrode potential, cell potential. Theories for the structure of the electrochemical double layer and double layer capacitance. Nerst equation. Battery operation. Electrolysis. Fuel ce ...
... Langmuir isotherm. Enthalpy of adsorption. Kinetics of catalytic reactions. The solid-state electrochemical cell. Electrode potential, cell potential. Theories for the structure of the electrochemical double layer and double layer capacitance. Nerst equation. Battery operation. Electrolysis. Fuel ce ...
Synthesis of n-Butyl Acetate via Esterification
... acetic acid are allowed to react, at equilibrium the theoretical yield of ester is only 67%. To upset the equilibrium we can, by Le Chatelier's principle, increase the concentration of either the alcohol or acid, as noted above. If either one is doubled, the theoretical yield increases to 85%. When ...
... acetic acid are allowed to react, at equilibrium the theoretical yield of ester is only 67%. To upset the equilibrium we can, by Le Chatelier's principle, increase the concentration of either the alcohol or acid, as noted above. If either one is doubled, the theoretical yield increases to 85%. When ...
Spring 2013 Semester Exam Study Guide (Bonding, Nomenclature
... ____ 40. The concept that electrostatic repulsion between electron pairs surrounding an atom causes these pairs to be separated as far as possible is the foundation of a. VSEPR theory. c. the electron-sea model. b. the hybridization model. d. Lewis theory. ____ 41. The strong forces of attraction be ...
... ____ 40. The concept that electrostatic repulsion between electron pairs surrounding an atom causes these pairs to be separated as far as possible is the foundation of a. VSEPR theory. c. the electron-sea model. b. the hybridization model. d. Lewis theory. ____ 41. The strong forces of attraction be ...
Homework Booklet Unit 1 Feb14
... (c) Name the two pollutant gases changed by the catalyst and describe what they are changed into. 4. Explain why solid citric acid does not conduct electricity yet when it dissolves in water it does conduct. 5. Electrolysis of acids can be used to confirm the presence of hydrogen ions. (a) At which ...
... (c) Name the two pollutant gases changed by the catalyst and describe what they are changed into. 4. Explain why solid citric acid does not conduct electricity yet when it dissolves in water it does conduct. 5. Electrolysis of acids can be used to confirm the presence of hydrogen ions. (a) At which ...
Lone pairs
... charge because of the exposed positive nucleus, while the other element takes on a strong negative charge This positive hydrogen will be attracted to nearby negative atoms. It appears as though the hydrogen atom bonds to different molecules. ...
... charge because of the exposed positive nucleus, while the other element takes on a strong negative charge This positive hydrogen will be attracted to nearby negative atoms. It appears as though the hydrogen atom bonds to different molecules. ...
National 5 Unit 1 Homework Booklet
... (c) Name the two pollutant gases changed by the catalyst and describe what they are changed into. 4. Explain why solid citric acid does not conduct electricity yet when it dissolves in water it does conduct. 5. Electrolysis of acids can be used to confirm the presence of hydrogen ions. (a) At which ...
... (c) Name the two pollutant gases changed by the catalyst and describe what they are changed into. 4. Explain why solid citric acid does not conduct electricity yet when it dissolves in water it does conduct. 5. Electrolysis of acids can be used to confirm the presence of hydrogen ions. (a) At which ...
Instruction Manual, Affi-Gel® 102 and CM Bio-Gel® A Gels - Bio-Rad
... 1. Dilute the gel 1 to 1 with distilled water or appropriate solvent.* 2. With gentle stirring (end over end, do not use a stir bar), add 10-50 µ moles of ligand/ml of gel (35-40 mg protein ml gel) and adjust the pH to 4.7-5.0 with 1 N HCl. 3. Add 2-10 mg EDAC coupling reagent with continued stirrin ...
... 1. Dilute the gel 1 to 1 with distilled water or appropriate solvent.* 2. With gentle stirring (end over end, do not use a stir bar), add 10-50 µ moles of ligand/ml of gel (35-40 mg protein ml gel) and adjust the pH to 4.7-5.0 with 1 N HCl. 3. Add 2-10 mg EDAC coupling reagent with continued stirrin ...
Chapter 27
... Both constructed of coiled stainless steel/glass/Teflon, with coil diameter of 10-30 cm ...
... Both constructed of coiled stainless steel/glass/Teflon, with coil diameter of 10-30 cm ...
Chains and Rings: Organic Chemistry
... radicals are extremely reactive - electrons prefer to be in pairs! Thus, these free radicals do not last for long, but are short-lived intermediates. One of the free radicals binds to a hydrogen to form an alkane. The other must form a C=C double bond, and so becomes an alkene, since there is not en ...
... radicals are extremely reactive - electrons prefer to be in pairs! Thus, these free radicals do not last for long, but are short-lived intermediates. One of the free radicals binds to a hydrogen to form an alkane. The other must form a C=C double bond, and so becomes an alkene, since there is not en ...
(.pdf format)
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
metal-water interactions and hydrogen bond strength
... with other entities in the structure additionally modify this strength: (i) metal-water interactions (synergetic effect) [1-4 and Refs. therein]; (ii) cooperative effect ...
... with other entities in the structure additionally modify this strength: (i) metal-water interactions (synergetic effect) [1-4 and Refs. therein]; (ii) cooperative effect ...
الشريحة 1
... A double bond is formed from a sigma bond and a pi bond, and so it is stronger than a single bond. ...
... A double bond is formed from a sigma bond and a pi bond, and so it is stronger than a single bond. ...
Exam 1 Review Sheet Chapter 15 Chemistry 110b
... Acidity. Have in mind a chemically relevant definition of pKa. Make a table of the pKa’s we’ve discussed throughout the course. Review the general factors which affect acidity. [10e, 781-783; 9e, 781-783] ...
... Acidity. Have in mind a chemically relevant definition of pKa. Make a table of the pKa’s we’ve discussed throughout the course. Review the general factors which affect acidity. [10e, 781-783; 9e, 781-783] ...
Computational thermodynamics - IS MU
... 1. Introduction: Computational thermodynamics, past and present of CALPHAD technique. Thermodynamic basis: laws of thermodynamics, functions of state, equilibrium conditions, vibrational heat capacity, statistical thermodynamics. 2. Crystallography: connection of thermodynamics with crystallography, ...
... 1. Introduction: Computational thermodynamics, past and present of CALPHAD technique. Thermodynamic basis: laws of thermodynamics, functions of state, equilibrium conditions, vibrational heat capacity, statistical thermodynamics. 2. Crystallography: connection of thermodynamics with crystallography, ...
Stoichiometry Worksheet #4
... 4. Given the following equation: 2 KClO3 ---> 2 KCl + 3 O2 How many moles of O2 can be produced by letting 12.00 moles of KClO3 react? ...
... 4. Given the following equation: 2 KClO3 ---> 2 KCl + 3 O2 How many moles of O2 can be produced by letting 12.00 moles of KClO3 react? ...
File
... Functional Groups, Aldehydes, and Ketones Aldehydes and ketones contain a carbonyl group (C O), which is a carbon atom attached to an oxygen atom with a double bond. • In an aldehyde, the carbon atom of the carbonyl group is also bonded to a hydrogen atom. • In a ketone, the carbon atom of the carb ...
... Functional Groups, Aldehydes, and Ketones Aldehydes and ketones contain a carbonyl group (C O), which is a carbon atom attached to an oxygen atom with a double bond. • In an aldehyde, the carbon atom of the carbonyl group is also bonded to a hydrogen atom. • In a ketone, the carbon atom of the carb ...























