OEV I04 General Chemistry_1 - The Open University of Tanzania
... the concept of reaction mechanism in the context of key reactions of organic and inorganic chemistry, and the principles governing chemical processes in terms of thermodynamic properties, kinetics and thermo-chemistry. The text also summarizes the key functional groups in organic chemistry. The mate ...
... the concept of reaction mechanism in the context of key reactions of organic and inorganic chemistry, and the principles governing chemical processes in terms of thermodynamic properties, kinetics and thermo-chemistry. The text also summarizes the key functional groups in organic chemistry. The mate ...
GENERAL CHEMISTRY REVIEW
... b) At a particular instant, the activities (concentrations) of H3O+, HOCl and OCl- in solution are 10-7, 10-3 and 10-4, respectively. Determine whether the reaction above is at equilibrium and if not, predict wheter the concentration of HOCl will increase or decrease as the reaction proceeds. ...
... b) At a particular instant, the activities (concentrations) of H3O+, HOCl and OCl- in solution are 10-7, 10-3 and 10-4, respectively. Determine whether the reaction above is at equilibrium and if not, predict wheter the concentration of HOCl will increase or decrease as the reaction proceeds. ...
2.5 THE NAMES AND FORMULAS OF COMPOUNDS
... explain many of the properties of ionic compounds, but they aren’t sufficient to explain the physical state of molecular compounds. If covalent bonds were the only forces at work, molecular compounds would all be gases, as there would be no attraction between the molecules strong enough to order the ...
... explain many of the properties of ionic compounds, but they aren’t sufficient to explain the physical state of molecular compounds. If covalent bonds were the only forces at work, molecular compounds would all be gases, as there would be no attraction between the molecules strong enough to order the ...
Period 4 - cloudfront.net
... 3. which is true about intramolecular forces and intermolecular forces A. intramolecular are in the same molecule while intermolecular forces are between neighboring molecules B. intermolecular forces have 3 types: ionic, covalent, metallic C. intramolecular forcers are weak D. intramolecular force ...
... 3. which is true about intramolecular forces and intermolecular forces A. intramolecular are in the same molecule while intermolecular forces are between neighboring molecules B. intermolecular forces have 3 types: ionic, covalent, metallic C. intramolecular forcers are weak D. intramolecular force ...
Computational Study of protonation of ozone
... confirmed experimentally by several researchers [5, 6]. However, for the calculation were used outdated methods. This is not allowed reliably reason about thermodynamic stability of protonated ozone. The purpose of this issue is the thermodynamic estimation of protonation reaction of ozone. Experime ...
... confirmed experimentally by several researchers [5, 6]. However, for the calculation were used outdated methods. This is not allowed reliably reason about thermodynamic stability of protonated ozone. The purpose of this issue is the thermodynamic estimation of protonation reaction of ozone. Experime ...
chapter 1 - Revsworld
... Which of the following statements is/are correct? I. When heat energy flows from a system to the surroundings, we know that the temperature of the system is greater than that of the surroundings. II. Given the thermochemical equation 4NH3(g) + 5O2(g) ------> 4 NO(g) + 6H2O(g) H = -906 kJ, the therm ...
... Which of the following statements is/are correct? I. When heat energy flows from a system to the surroundings, we know that the temperature of the system is greater than that of the surroundings. II. Given the thermochemical equation 4NH3(g) + 5O2(g) ------> 4 NO(g) + 6H2O(g) H = -906 kJ, the therm ...
Section 2 Hydrocarbons Chapter 22
... Unsaturated Hydrocarbons • Hydrocarbons that do not contain the maximum amount of hydrogen are referred to as unsaturated. • Unsaturated hydrocarbons are hydrocarbons in which not all carbon atoms have four single covalent bonds. • An unsaturated hydrocarbon has one or more double bonds or triple bo ...
... Unsaturated Hydrocarbons • Hydrocarbons that do not contain the maximum amount of hydrogen are referred to as unsaturated. • Unsaturated hydrocarbons are hydrocarbons in which not all carbon atoms have four single covalent bonds. • An unsaturated hydrocarbon has one or more double bonds or triple bo ...
Oxidation and Reduction
... Silver tarnishes when it comes in contact with sulfur compounds in the air. Copper gets coated in beautiful green patina as it ages. Metals rust or corrode in the presence of air and water. Minerals (ionic compounds) found in ore can be decomposed with the use of electricity to produce pure metals a ...
... Silver tarnishes when it comes in contact with sulfur compounds in the air. Copper gets coated in beautiful green patina as it ages. Metals rust or corrode in the presence of air and water. Minerals (ionic compounds) found in ore can be decomposed with the use of electricity to produce pure metals a ...
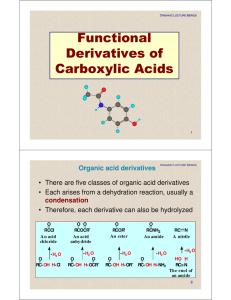
Functional Derivatives of Carboxylic Acids
... • Step 3: Make a new bond between a nucleophile and an electrophile. The ketone reacts with a second mole of Grignard reagent to give a second tetrahedral carbonyl addition intermediate. ...
... • Step 3: Make a new bond between a nucleophile and an electrophile. The ketone reacts with a second mole of Grignard reagent to give a second tetrahedral carbonyl addition intermediate. ...
Progression of Learning in Secondary School Chemistry Secondary
... Associates a characteristic property of a substance or material with its use (e.g. metal is used to make pots because it is a good conductor of heat) Physical Changes Recognizes different physical changes Molecule Describes a molecule using Dalton's atomic model (combination of atoms linked by chemi ...
... Associates a characteristic property of a substance or material with its use (e.g. metal is used to make pots because it is a good conductor of heat) Physical Changes Recognizes different physical changes Molecule Describes a molecule using Dalton's atomic model (combination of atoms linked by chemi ...
AP Chemistry - Freehold Regional High School District
... 1. There are six main types of chemical reactions; 2. The products of a chemical reaction can be predicted using a set of rules. 3. Stoichiometry is a method of problem solving using balanced equations. Solution concentration can be expressed in several ways. Chemical compounds can be acids, bases o ...
... 1. There are six main types of chemical reactions; 2. The products of a chemical reaction can be predicted using a set of rules. 3. Stoichiometry is a method of problem solving using balanced equations. Solution concentration can be expressed in several ways. Chemical compounds can be acids, bases o ...
Grignard Reaction - OpenBU
... the pressure after each inversion by gently removing the cap). Remove the lower aqueous phase and place in another beaker (this time it should be saved). Repeat with a second and third portion of 5% NaOH (aq.), collecting the bottom layer each time in the same beaker as the material to be saved. For ...
... the pressure after each inversion by gently removing the cap). Remove the lower aqueous phase and place in another beaker (this time it should be saved). Repeat with a second and third portion of 5% NaOH (aq.), collecting the bottom layer each time in the same beaker as the material to be saved. For ...
Supporting Information - Royal Society of Chemistry
... where Λ 0 is the molar conductivity at infinite dilution and K is a coefficient related to the electrolyte theory. A linear decrease in molar conductivity was observed up to [SDS] = 7.8×10–3 M, corresponding to the CMC value. Light scattering: Aggregation of surfactant monomers is also revealed by a ...
... where Λ 0 is the molar conductivity at infinite dilution and K is a coefficient related to the electrolyte theory. A linear decrease in molar conductivity was observed up to [SDS] = 7.8×10–3 M, corresponding to the CMC value. Light scattering: Aggregation of surfactant monomers is also revealed by a ...
Grignard Reaction - OpenBU
... the pressure after each inversion by gently removing the cap). Remove the lower aqueous phase and place in another beaker (this time it should be saved). Repeat with a second and third portion of 5% NaOH (aq.), collecting the bottom layer each time in the same beaker as the material to be saved. For ...
... the pressure after each inversion by gently removing the cap). Remove the lower aqueous phase and place in another beaker (this time it should be saved). Repeat with a second and third portion of 5% NaOH (aq.), collecting the bottom layer each time in the same beaker as the material to be saved. For ...
Grignard Reaction - Synthesis of Substituted Benzoic Acids
... the pressure after each inversion by gently removing the cap). Remove the lower aqueous phase and place in another beaker (this time it should be saved). Repeat with a second and third portion of 5% NaOH (aq.), collecting the bottom layer each time in the same beaker as the material to be saved. For ...
... the pressure after each inversion by gently removing the cap). Remove the lower aqueous phase and place in another beaker (this time it should be saved). Repeat with a second and third portion of 5% NaOH (aq.), collecting the bottom layer each time in the same beaker as the material to be saved. For ...
Chemistry STAAR Review File
... Compiled a Periodic Table of 56 elements based on the periodicity of properties such as molar volume when arranged in order of atomic weight. He wrote out the properties of each element on a different card and spent a great deal of time arranging and rearranging them. He was looking for patterns or ...
... Compiled a Periodic Table of 56 elements based on the periodicity of properties such as molar volume when arranged in order of atomic weight. He wrote out the properties of each element on a different card and spent a great deal of time arranging and rearranging them. He was looking for patterns or ...
Topic 6 Kinetics File
... increase of number of moles of gaseous molecules; 2) change of state from solid to liquid or liquid to gas; 3) increase of temperature Exothermic: A reaction in which energy is evolved. ΔH is –. Products more stable than reactants. Gibb’s free energy: Must be negative for reaction to be spontaneous. ...
... increase of number of moles of gaseous molecules; 2) change of state from solid to liquid or liquid to gas; 3) increase of temperature Exothermic: A reaction in which energy is evolved. ΔH is –. Products more stable than reactants. Gibb’s free energy: Must be negative for reaction to be spontaneous. ...
Chapter 4: Solution Chemistry and the Hydrosphere
... products based on the charges of the ions! 2. Use the Solubility Rules to determine if each product is soluble or insoluble. – If at least one product is insoluble, a precipitation reaction has occurred. Write the formulas for both products, indicating the precipitate as (s), then balance the equati ...
... products based on the charges of the ions! 2. Use the Solubility Rules to determine if each product is soluble or insoluble. – If at least one product is insoluble, a precipitation reaction has occurred. Write the formulas for both products, indicating the precipitate as (s), then balance the equati ...
Chemical Reactions (L1)
... Single replacement reactions occur when one chemical takes the place of another in a reaction. In the typical single replacement reaction, an element trades places with one of the ions in a compound. ...
... Single replacement reactions occur when one chemical takes the place of another in a reaction. In the typical single replacement reaction, an element trades places with one of the ions in a compound. ...
On the Evolution of Chemical Organizations
... Chemical evolution (i.e., prebiotic evolution) is concerned with the period of life’s history that precedes the arrival of the first living organism [17]. Since Miller’s pioneering work [19, 20], prebiotic chemistry has been studied in various laboratory experiments [16]. On the other hand, there ar ...
... Chemical evolution (i.e., prebiotic evolution) is concerned with the period of life’s history that precedes the arrival of the first living organism [17]. Since Miller’s pioneering work [19, 20], prebiotic chemistry has been studied in various laboratory experiments [16]. On the other hand, there ar ...