“No Score” from Exam 1??
... and Molecular Geometry (MG) 1. Draw the Lewis structure of the molecule 2. Count the number of electron domains in the Lewis structure: one bond (single, double, or triple) counts as ______ domain! And one lone pair counts as ______ domain!) 3. The electron domain geometry corresponds to the number ...
... and Molecular Geometry (MG) 1. Draw the Lewis structure of the molecule 2. Count the number of electron domains in the Lewis structure: one bond (single, double, or triple) counts as ______ domain! And one lone pair counts as ______ domain!) 3. The electron domain geometry corresponds to the number ...
W(CO)
... were also varied. According to the thermodynamic data from NIST,[10] ΔHf(CO) = −110.53 kJ/mole, ΔH(W) = 851.03 kJ/mole, and ΔHf[W(CO)6] = −882.9 kJ/mole, which gives a thermodynamic mean BDE(W–CO) value of 1.85 eV3 that is consistent with the value calculated here for t1 = 0 (1.84 eV). All the other ...
... were also varied. According to the thermodynamic data from NIST,[10] ΔHf(CO) = −110.53 kJ/mole, ΔH(W) = 851.03 kJ/mole, and ΔHf[W(CO)6] = −882.9 kJ/mole, which gives a thermodynamic mean BDE(W–CO) value of 1.85 eV3 that is consistent with the value calculated here for t1 = 0 (1.84 eV). All the other ...
Kinetics of the Gas-Phase Reactions of C1
... HCl reacting with niobium and tantalum oxide (and oxyhydroxide) anions. Interestingly, these reactions bear analogy to condensed-phase acid-base interactions along the line of NaOH and HCl reacting to give NaCl and H20. For the transition metal oxide anions, C1 of HCl replaces an OH unit on the meta ...
... HCl reacting with niobium and tantalum oxide (and oxyhydroxide) anions. Interestingly, these reactions bear analogy to condensed-phase acid-base interactions along the line of NaOH and HCl reacting to give NaCl and H20. For the transition metal oxide anions, C1 of HCl replaces an OH unit on the meta ...
Pre-lab Questions - HCC Learning Web
... Molecular State- Straight-chain alcohols with up to 12 carbon atoms are liquids. Solubility- Alcohols with a small organic part such as methanol or ethanol are much like water , thus miscible with water. Alcohols with a larger organic radical are more like alkanes and less like water. Alcohols with ...
... Molecular State- Straight-chain alcohols with up to 12 carbon atoms are liquids. Solubility- Alcohols with a small organic part such as methanol or ethanol are much like water , thus miscible with water. Alcohols with a larger organic radical are more like alkanes and less like water. Alcohols with ...
Document
... proton to another species in a proton-transfer reaction Brønsted–Lowry Base The species (molecule or ion) that accepts a proton from another species in a proton-transfer reaction ...
... proton to another species in a proton-transfer reaction Brønsted–Lowry Base The species (molecule or ion) that accepts a proton from another species in a proton-transfer reaction ...
Prelab Assignment: The lodination of Acetone
... of both acetone and H+ remain essentially at their initial values in the reaction mixture. Having found the reaction rate for one composition of the system, it might be well to think for a moment about what changes in composition you might make to decrease the time and hence increase the rate of rea ...
... of both acetone and H+ remain essentially at their initial values in the reaction mixture. Having found the reaction rate for one composition of the system, it might be well to think for a moment about what changes in composition you might make to decrease the time and hence increase the rate of rea ...
Discussion 9, Mahaffy et al., Chapter 15
... a. Oxidation is loss of electrons (acts as a reducing agent) b.Reduction is gain of electrons (acts as a oxidizing agent) Assigning Oxidation numbers c. Oxidation number is 0 for atoms in an element. d.The sum of all oxidation numbers in a molecule or ion must add up to the total charge. e. In compo ...
... a. Oxidation is loss of electrons (acts as a reducing agent) b.Reduction is gain of electrons (acts as a oxidizing agent) Assigning Oxidation numbers c. Oxidation number is 0 for atoms in an element. d.The sum of all oxidation numbers in a molecule or ion must add up to the total charge. e. In compo ...
Effect of nucleophile on reaction
... • Nucleophile not involved in RDS of SN1 so does not effect the reaction ...
... • Nucleophile not involved in RDS of SN1 so does not effect the reaction ...
Organic Compounds - 2012 Book Archive
... the most complex chemical structures known are those of the organic molecules found in living organisms. (For more information on biopolymers, see Chapter 12 "Solids", Section 12.8 "Polymeric Solids".) In spite of their size and complexity, these biological molecules obey the same chemical principle ...
... the most complex chemical structures known are those of the organic molecules found in living organisms. (For more information on biopolymers, see Chapter 12 "Solids", Section 12.8 "Polymeric Solids".) In spite of their size and complexity, these biological molecules obey the same chemical principle ...
SUGGESTED TIMELINE: 4 Weeks - Hazlet Township Public Schools
... HS-PS1-2. Construct and revise an explanation for the outcome of a simple chemical reaction based on the outermost electron states of atoms, trends in the periodic table, and knowledge of the patterns of chemical properties HS-PS1-3. Plan and conduct an investigation to gather evidence to compare th ...
... HS-PS1-2. Construct and revise an explanation for the outcome of a simple chemical reaction based on the outermost electron states of atoms, trends in the periodic table, and knowledge of the patterns of chemical properties HS-PS1-3. Plan and conduct an investigation to gather evidence to compare th ...
The Gibbs Function of a Chemical Reaction*
... of elementary steps comprising a mechanism. Stoichiometric equations are helpful for accounting purposes only as required in stoichiometric calculations. This is much the same as using symbols of the elements and their standard atomic weights. For instance, we know that only in exceptional cases wil ...
... of elementary steps comprising a mechanism. Stoichiometric equations are helpful for accounting purposes only as required in stoichiometric calculations. This is much the same as using symbols of the elements and their standard atomic weights. For instance, we know that only in exceptional cases wil ...
the powerpoint
... • When a substance changes color, the chemical composition of the substance may have changed (for example, iron turns to a reddish-brown when it rusts, clothes change color when bleach is added, apples turn brown when they react with oxygen in the air, or marshmallows turn black when burned). • It i ...
... • When a substance changes color, the chemical composition of the substance may have changed (for example, iron turns to a reddish-brown when it rusts, clothes change color when bleach is added, apples turn brown when they react with oxygen in the air, or marshmallows turn black when burned). • It i ...
Zinc of unsuspected worth
... are typically milder and more selective than the popular magnesium-based Grignard reagents, and in recent years more and more complex functionalized organozinc reagents have been prepared6. An unusual example of selectivity in organozinc chemistry is the Soai reaction, described in 19957. Dialkylzin ...
... are typically milder and more selective than the popular magnesium-based Grignard reagents, and in recent years more and more complex functionalized organozinc reagents have been prepared6. An unusual example of selectivity in organozinc chemistry is the Soai reaction, described in 19957. Dialkylzin ...
Thermochemistry
... First Law of Thermodynamics Energy can be converted from one form to another but energy cannot be created or destroyed. Second Law of Thermodynamics The entropy of the universe increases in a spontaneous process and remains unchanged in an equilibrium process. ...
... First Law of Thermodynamics Energy can be converted from one form to another but energy cannot be created or destroyed. Second Law of Thermodynamics The entropy of the universe increases in a spontaneous process and remains unchanged in an equilibrium process. ...
Slide 1
... Analyze In part (a) we must predict the value for relative to that for on the basis of the balanced equation for the reaction. In part (b) we must calculate the value for and compare this value with our qualitative prediction. Plan The free–energy change incorporates both the change in enthalpy and ...
... Analyze In part (a) we must predict the value for relative to that for on the basis of the balanced equation for the reaction. In part (b) we must calculate the value for and compare this value with our qualitative prediction. Plan The free–energy change incorporates both the change in enthalpy and ...
alcohols ws 1 - Chesterhouse School
... (d) Lactic acid is chiral. Draw displayed formulae of the two optical isomers of lactic acid clearly showing their three-dimensional structures. Indicate with an asterisk (*) the chiral carbon atom in each. ...
... (d) Lactic acid is chiral. Draw displayed formulae of the two optical isomers of lactic acid clearly showing their three-dimensional structures. Indicate with an asterisk (*) the chiral carbon atom in each. ...
Thermobest for Chem1
... First Law of Thermodynamics Energy can be converted from one form to another but energy cannot be created or destroyed. Second Law of Thermodynamics The entropy of the universe increases in a spontaneous process and remains unchanged in an equilibrium process. ...
... First Law of Thermodynamics Energy can be converted from one form to another but energy cannot be created or destroyed. Second Law of Thermodynamics The entropy of the universe increases in a spontaneous process and remains unchanged in an equilibrium process. ...
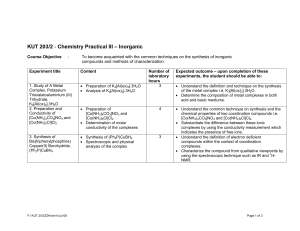
KUT 203/2 - Chemistry Practical III (Inorganic Chemistry)
... • Understand the concept on lingkage isomerism in coordination compounds and the technique used in the synthesis and isolation of these complex ions i.e. [(NH3)5CoNO2]Cl2 and [(NH3)5CoONO]Cl2. • Substantiate the functional group present in the isomers using the spectroscopic technique such as IR. • ...
... • Understand the concept on lingkage isomerism in coordination compounds and the technique used in the synthesis and isolation of these complex ions i.e. [(NH3)5CoNO2]Cl2 and [(NH3)5CoONO]Cl2. • Substantiate the functional group present in the isomers using the spectroscopic technique such as IR. • ...
Final Review
... c. Definite volume; shape of container; no intermolecular attractions d. Volume and shape of container; no intermolecular attractions e. Volume and shape of container; strong intermolecular attractions 102. Which transformation is evaporation? a. liquid ---> solid d. solid ---> gas b. liquid ---> ga ...
... c. Definite volume; shape of container; no intermolecular attractions d. Volume and shape of container; no intermolecular attractions e. Volume and shape of container; strong intermolecular attractions 102. Which transformation is evaporation? a. liquid ---> solid d. solid ---> gas b. liquid ---> ga ...