Final Review
... c. Definite volume; shape of container; no intermolecular attractions d. Volume and shape of container; no intermolecular attractions e. Volume and shape of container; strong intermolecular attractions 102. Which transformation is evaporation? a. liquid ---> solid d. solid ---> gas b. liquid ---> ga ...
... c. Definite volume; shape of container; no intermolecular attractions d. Volume and shape of container; no intermolecular attractions e. Volume and shape of container; strong intermolecular attractions 102. Which transformation is evaporation? a. liquid ---> solid d. solid ---> gas b. liquid ---> ga ...
NNIN Nanotechnology Open Textbook, Chapter 2
... photosynthesis and polymerized into more complex polysaccharides such as starch, glycogen and cellulose. The simplest carbohydrates are monosaccharides. These simple sugars contain three to nine carbon atoms and are classified as aldoses or ketoses depending on whether their carbonyl group is an ald ...
... photosynthesis and polymerized into more complex polysaccharides such as starch, glycogen and cellulose. The simplest carbohydrates are monosaccharides. These simple sugars contain three to nine carbon atoms and are classified as aldoses or ketoses depending on whether their carbonyl group is an ald ...
Molecular Geometry and Electron Domain Theory
... This model accounts for the comparative bond angles observed experimentally in these molecules. The valence shell electron pairs repel one another, establishing the geometry in which the energy of their interaction is minimized. Lone pair electrons apparently generate a greater repulsion, thus sligh ...
... This model accounts for the comparative bond angles observed experimentally in these molecules. The valence shell electron pairs repel one another, establishing the geometry in which the energy of their interaction is minimized. Lone pair electrons apparently generate a greater repulsion, thus sligh ...
AP Chem Stoichiometry Notes Table of Contents Atomic Masses
... 1. Determine what reaction is occurring. What are the reactants, the products, and the physical states involved? 2. Write an unbalanced equation that summarizes the reaction described in step 1. 3. Balance the equation by inspection, starting with the most complicated molecule(s). Determine what coe ...
... 1. Determine what reaction is occurring. What are the reactants, the products, and the physical states involved? 2. Write an unbalanced equation that summarizes the reaction described in step 1. 3. Balance the equation by inspection, starting with the most complicated molecule(s). Determine what coe ...
Molecular Geometry and Electron Domain Theory
... This model accounts for the comparative bond angles observed experimentally in these molecules. The valence shell electron pairs repel one another, establishing the geometry in which the energy of their interaction is minimized. Lone pair electrons apparently generate a greater repulsion, thus sligh ...
... This model accounts for the comparative bond angles observed experimentally in these molecules. The valence shell electron pairs repel one another, establishing the geometry in which the energy of their interaction is minimized. Lone pair electrons apparently generate a greater repulsion, thus sligh ...
Chapter 9 – Reaction Energetics
... Reactions involve breaking and forming bonds, and the heat generated or absorbed during a reaction is the net result. If we knew the energies of all of the interactions involved, we could determine the enthalpy of reaction by determining how much energy must be supplied to break all of the interacti ...
... Reactions involve breaking and forming bonds, and the heat generated or absorbed during a reaction is the net result. If we knew the energies of all of the interactions involved, we could determine the enthalpy of reaction by determining how much energy must be supplied to break all of the interacti ...
Regents Review Questions
... forms of solid carbon. Diamond is one of the hardest substances known, while graphite is a very soft substance. Diamond has a rigid network of bonded atoms. Graphite has atoms bonded in thin layers that are held together by weak forces. Recent experiments have produced new forms of solid carbon call ...
... forms of solid carbon. Diamond is one of the hardest substances known, while graphite is a very soft substance. Diamond has a rigid network of bonded atoms. Graphite has atoms bonded in thin layers that are held together by weak forces. Recent experiments have produced new forms of solid carbon call ...
Analysing a protein structure
... Save the so obtained image (choose File | Save As, give a name and choose Image File). You can save in the same manner every active screen. You can see the H-bond network with 1-5 interaction: for example the carbonylic oxygen of Ser109 is H-bonded to the peptidic hydrogen of Val 113. The β sheet ( ...
... Save the so obtained image (choose File | Save As, give a name and choose Image File). You can save in the same manner every active screen. You can see the H-bond network with 1-5 interaction: for example the carbonylic oxygen of Ser109 is H-bonded to the peptidic hydrogen of Val 113. The β sheet ( ...
BSc Honours chemistry CBCS Syllabus 2016-17
... reduction (catalytic and chemical), syn and anti-hydroxylation (oxidation). 1,2-and 1,4-addition reactions in conjugated dienes and, Diels-Alder reaction; Allylic and benzylicbromination and mechanism, e.g. propene, 1-butene, toluene, ethyl benzene. Reactions of alkynes: Acidity, Electrophilic and N ...
... reduction (catalytic and chemical), syn and anti-hydroxylation (oxidation). 1,2-and 1,4-addition reactions in conjugated dienes and, Diels-Alder reaction; Allylic and benzylicbromination and mechanism, e.g. propene, 1-butene, toluene, ethyl benzene. Reactions of alkynes: Acidity, Electrophilic and N ...
Triple resonance for a three-level system of a chiral molecule
... transitions of molecules. We have, however, many examples of C1 chiral molecules in the literatures, for which all a-, b-, and c-types of rotational transitions were observed and reported. Thus the observations on these chiral molecules remained a puzzle for us for a long time. We may wonder how we ...
... transitions of molecules. We have, however, many examples of C1 chiral molecules in the literatures, for which all a-, b-, and c-types of rotational transitions were observed and reported. Thus the observations on these chiral molecules remained a puzzle for us for a long time. We may wonder how we ...
Homework,1 Atoms, molecules, and ions
... e) none of these 7- You are setting up a reaction between two chemicals that react according to the equation 3 A + 4 B products. If you start with 1.00 mole each of both A and B, which chemical will be in excess at the end, and by how much (assuming the reaction goes to completion)? a) A is in exc ...
... e) none of these 7- You are setting up a reaction between two chemicals that react according to the equation 3 A + 4 B products. If you start with 1.00 mole each of both A and B, which chemical will be in excess at the end, and by how much (assuming the reaction goes to completion)? a) A is in exc ...
Stoichiometry of Ozonation of Environmentally
... give OH radicals in fairly high yields (17). It is often assumed that ozone reacts with unsaturated organics in a well-defined stoichiometric ratio, with one carbon-carbon double bond consumed per ozone molecule reacted. However, this work demonstrates that a single ozone molecule can effectively de ...
... give OH radicals in fairly high yields (17). It is often assumed that ozone reacts with unsaturated organics in a well-defined stoichiometric ratio, with one carbon-carbon double bond consumed per ozone molecule reacted. However, this work demonstrates that a single ozone molecule can effectively de ...
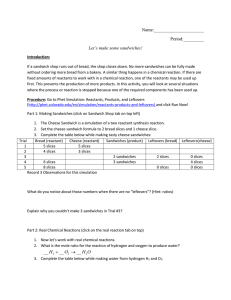
Name: Period:______ Let`s make some sandwiches! Introduction: If
... 4. Notice that the labels changed from molecules to moles. This does not change the mole ratio, as a mole is simply a large number of molecules. How many molecules are in a mole? 5. In Trial #6, what reactant limits you from making more water molecules? Which reactant was present in excess and remai ...
... 4. Notice that the labels changed from molecules to moles. This does not change the mole ratio, as a mole is simply a large number of molecules. How many molecules are in a mole? 5. In Trial #6, what reactant limits you from making more water molecules? Which reactant was present in excess and remai ...
STUDY GUIDE
... MAIN IDEA: An alkene is a hydrocarbon that has at least one double bond between two carbon atoms. The carbon chain is numbered using the lowest number for the double bond. The root name ends in -ene. An alkyne is a hydrocarbon that has at least one triple bond between two carbon atoms. Naming alkyn ...
... MAIN IDEA: An alkene is a hydrocarbon that has at least one double bond between two carbon atoms. The carbon chain is numbered using the lowest number for the double bond. The root name ends in -ene. An alkyne is a hydrocarbon that has at least one triple bond between two carbon atoms. Naming alkyn ...
Macromolecules,Carbs - Ms. Nakamura`s Biology Class Wiki
... Why study Functional Groups? These are the building blocks for biological molecules …and that comes next! ...
... Why study Functional Groups? These are the building blocks for biological molecules …and that comes next! ...
3.5 The Alcohols
... The crude cyclohexene will contain water soluble impurities that need separating from the alkene. The cyclohexene is transferred to a separating funnel. Water is added to the separating funnel and shaken to remove water soluble impurities from the cyclohexene and transfer them to the water. Allow to ...
... The crude cyclohexene will contain water soluble impurities that need separating from the alkene. The cyclohexene is transferred to a separating funnel. Water is added to the separating funnel and shaken to remove water soluble impurities from the cyclohexene and transfer them to the water. Allow to ...
$doc.title
... • Alkanes: Compounds with C-‐C single bonds and C-‐H bonds only (no func)onal groups), non-‐polar molecule • Easy to rotate around C-‐C single bonds • Connec)ng carbons can lead to large or small mole ...
... • Alkanes: Compounds with C-‐C single bonds and C-‐H bonds only (no func)onal groups), non-‐polar molecule • Easy to rotate around C-‐C single bonds • Connec)ng carbons can lead to large or small mole ...
Document
... Pre-steady-state kinetics vs steady-state kinetics 1. The order of binding of substrates and release of product serves to define the reactants present at the active site during catalysis: it does not establish the kinetically preferred order of substrate addition and product release or allow conclu ...
... Pre-steady-state kinetics vs steady-state kinetics 1. The order of binding of substrates and release of product serves to define the reactants present at the active site during catalysis: it does not establish the kinetically preferred order of substrate addition and product release or allow conclu ...
Gibbs Free Energy - nchsdduncanchem2
... Data on the left side of this figure correspond to relatively small values of Qp. They therefore describe systems in which there is far more reactant than product. The sign of G for these systems is negative and the magnitude of G is large. The system is therefore relatively far from equilibrium an ...
... Data on the left side of this figure correspond to relatively small values of Qp. They therefore describe systems in which there is far more reactant than product. The sign of G for these systems is negative and the magnitude of G is large. The system is therefore relatively far from equilibrium an ...
Chemical Reactions - thsicp-23
... Products in combustion are ALWAYS carbon dioxide and water. (although incomplete burning does cause some byproducts like carbon monoxide) Combustion is used to heat homes and run automobiles (octane, as in gasoline, is C8H18) ...
... Products in combustion are ALWAYS carbon dioxide and water. (although incomplete burning does cause some byproducts like carbon monoxide) Combustion is used to heat homes and run automobiles (octane, as in gasoline, is C8H18) ...
Writing Net Ionic Equations
... to go to completion. Unionized or partially ionized molecules give solutions that are known as nonelectrolytes or weak electrolytes. The best known nonelectrolyte is water formed in acid-base neutralization reactions. Acetic acid is an example of an acid that is primarily molecular (weak electrolyt ...
... to go to completion. Unionized or partially ionized molecules give solutions that are known as nonelectrolytes or weak electrolytes. The best known nonelectrolyte is water formed in acid-base neutralization reactions. Acetic acid is an example of an acid that is primarily molecular (weak electrolyt ...
A-level Paper 3 Practice Paper 3 - A
... Give one essential condition and name the type of mechanism in this reaction of ...
... Give one essential condition and name the type of mechanism in this reaction of ...