Summer Scholar Report
... tosylates as precursors to other organic compounds and as substrates in studies of organic mechanisms. Their utility derives chiefly from the properties of the tosylate group as an excellent leaving group in nucleophilic and other reactions. Methods for synthesis of primary and secondary tosylates f ...
... tosylates as precursors to other organic compounds and as substrates in studies of organic mechanisms. Their utility derives chiefly from the properties of the tosylate group as an excellent leaving group in nucleophilic and other reactions. Methods for synthesis of primary and secondary tosylates f ...
9 free IB Chem labs (sent to OCC) - VicPark-IBRoundtable-2009
... With these specifications: 20-50°C in about 8 minutes, total 12 with lead and lag time. Very easy to measure the max temperature reached ...
... With these specifications: 20-50°C in about 8 minutes, total 12 with lead and lag time. Very easy to measure the max temperature reached ...
1 This is the pre-review version of the paper published in Journal of
... acidifying effect of the H2C=CH- substituent for all vinyl chain lengths studied to less than 40% of that observed in unconstrained systems. Due to the larger delocalization of charge in phenoxide anion vs. acetaldehyde enolate, inclusion of solvation contributions stabilizes the latter much more th ...
... acidifying effect of the H2C=CH- substituent for all vinyl chain lengths studied to less than 40% of that observed in unconstrained systems. Due to the larger delocalization of charge in phenoxide anion vs. acetaldehyde enolate, inclusion of solvation contributions stabilizes the latter much more th ...
fulltext $(function(){PrimeFaces.cw("Tooltip","widget_formSmash_items_resultList_20_j_idt799_0_j_idt801",{id:"formSmash:items:resultList:20:j_idt799:0:j_idt801",widgetVar:"widget_formSmash_items_resultList_20_j_idt799_0_j_idt801",showEffect:"fade",hideEffect:"fade",target:"formSmash:items:resultList:20:j_idt799:0:fullText"});});
... been developed and applied in this transformation.16 Recent DFT calculations have provided a better understanding of the reaction pathways in some catalytic systems.17 Some catalysts have shown very high reactivities.10a, 12b, 18 However, this reaction typically requires high temperature (>100 oC) a ...
... been developed and applied in this transformation.16 Recent DFT calculations have provided a better understanding of the reaction pathways in some catalytic systems.17 Some catalysts have shown very high reactivities.10a, 12b, 18 However, this reaction typically requires high temperature (>100 oC) a ...
Enzymes: “Helper” Protein molecules
... Enzymes aren’t used up Enzymes are not changed by the reaction used only temporarily re-used again for the same reaction with other molecules very little enzyme needed to help in many reactions ...
... Enzymes aren’t used up Enzymes are not changed by the reaction used only temporarily re-used again for the same reaction with other molecules very little enzyme needed to help in many reactions ...
Document
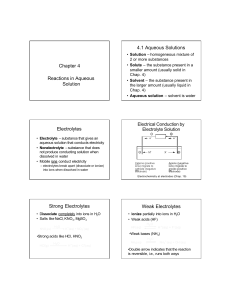
... • To form the net ionic equation, cross out anything that does not change from the left side of the equation to the right. • The ions crossed out are called spectator ions, K+ and NO3–, in this example. They play no direct role in the reaction. • The remaining ions are the reactants that form the pr ...
... • To form the net ionic equation, cross out anything that does not change from the left side of the equation to the right. • The ions crossed out are called spectator ions, K+ and NO3–, in this example. They play no direct role in the reaction. • The remaining ions are the reactants that form the pr ...
... Exciting experiments followed. Shirakawa could now control the ratio of cis/trans double bonds. Cispolyacetylene doping resulted in even higher conductivities. The iodine may first have isomerized the polymer to all-trans material, which then underwent efficient (defect-free) doping so that the degr ...
Final Exam Review Sheets
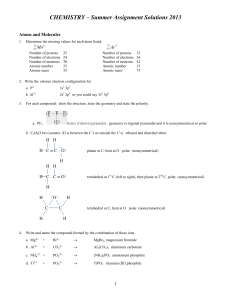
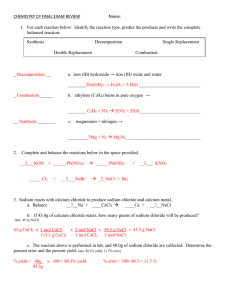
... 6. Use collision theory to explain the effect of each factor below on the rate of a chemical reaction: a. temperature: An increase in temperature results in an increase in average kinetic energy of reactants. This means there will be an increase in the number of successful collisions between reactan ...
... 6. Use collision theory to explain the effect of each factor below on the rate of a chemical reaction: a. temperature: An increase in temperature results in an increase in average kinetic energy of reactants. This means there will be an increase in the number of successful collisions between reactan ...
Step 2 - The Grange School Blogs
... Now they both have a ____ outer shell and are more _____. The formula for this molecule is H2. When two or more atoms bond by sharing electrons we call it ____________ BONDING. This type of bonding normally occurs between _______ atoms. It causes the atoms in a molecule to be held together very stro ...
... Now they both have a ____ outer shell and are more _____. The formula for this molecule is H2. When two or more atoms bond by sharing electrons we call it ____________ BONDING. This type of bonding normally occurs between _______ atoms. It causes the atoms in a molecule to be held together very stro ...
Step 2
... Now they both have a ____ outer shell and are more _____. The formula for this molecule is H2. When two or more atoms bond by sharing electrons we call it ____________ BONDING. This type of bonding normally occurs between _______ atoms. It causes the atoms in a molecule to be held together very stro ...
... Now they both have a ____ outer shell and are more _____. The formula for this molecule is H2. When two or more atoms bond by sharing electrons we call it ____________ BONDING. This type of bonding normally occurs between _______ atoms. It causes the atoms in a molecule to be held together very stro ...
Fundamentals of Chemistry
... atom is an extremely small electrically-neutral particle. It is the smallest unit involved in the chemical change of matter. Atoms can be treated as distinct particles because they behave as such chemically, but atoms themselves are composed of even smaller subparts. Understanding these atomic subpa ...
... atom is an extremely small electrically-neutral particle. It is the smallest unit involved in the chemical change of matter. Atoms can be treated as distinct particles because they behave as such chemically, but atoms themselves are composed of even smaller subparts. Understanding these atomic subpa ...
Press here to hemy 102 lab manual
... Every chemical change is accompanied by a change in energy, usually in the form of heat. The energy change of a reaction that occurs at constant pressure is termed the heat of reaction or the enthalpy change. The symbol ΔH is used to denote the enthalpy change. If heat is evolved, the reaction is ex ...
... Every chemical change is accompanied by a change in energy, usually in the form of heat. The energy change of a reaction that occurs at constant pressure is termed the heat of reaction or the enthalpy change. The symbol ΔH is used to denote the enthalpy change. If heat is evolved, the reaction is ex ...
Introduction(s)
... and a nonmetal react. Covalent (molecular) compounds are formed when two nonmetals react. ...
... and a nonmetal react. Covalent (molecular) compounds are formed when two nonmetals react. ...
134_2010_1897_MOESM1_ESM - Springer Static Content Server
... In Table 1 [1], the authors worked out apparent differences between the Stewart approach and standard physical chemistry. However, Stewart is physicochemically well grounded on proton dissociation equilibria, mass balance equations and electroneutrality condition. In particular, all acids in plasma ...
... In Table 1 [1], the authors worked out apparent differences between the Stewart approach and standard physical chemistry. However, Stewart is physicochemically well grounded on proton dissociation equilibria, mass balance equations and electroneutrality condition. In particular, all acids in plasma ...
Memorization?
... and a nonmetal react. Covalent (molecular) compounds are formed when two nonmetals react. ...
... and a nonmetal react. Covalent (molecular) compounds are formed when two nonmetals react. ...
Alcohols, acids and esters
... • To illustrate the practical importance of carboxylic acids • To demonstrate that carboxylic acids in solution show the characteristic reactions of acids • To introduce the –COOH functional group in carboxylic acids • To practise writing balanced equations to describe the reactions of carboxylic ac ...
... • To illustrate the practical importance of carboxylic acids • To demonstrate that carboxylic acids in solution show the characteristic reactions of acids • To introduce the –COOH functional group in carboxylic acids • To practise writing balanced equations to describe the reactions of carboxylic ac ...
Carbon-Carbon Bond Formation by Reductive Coupling with
... preted to conclude that the couplings proceed via two electron transfer pathways (TET) involving titanium (IV ) cyclic intermediates of the titanirene and the oxatitanacyclopropane type, respectively. ...
... preted to conclude that the couplings proceed via two electron transfer pathways (TET) involving titanium (IV ) cyclic intermediates of the titanirene and the oxatitanacyclopropane type, respectively. ...