B1 Atrial Fibrillation
... Management Strategies: Control ventricular response rate – VRR, Restore and maintain normal sinus rhythm – Cardioversion, ↓ risk of stroke 1. Controlling Ventricular Response Rate – most common way of controlling AF Which drugs? Digoxin, Beta Blockers, Calcium channel blockers : only use verapamil o ...
... Management Strategies: Control ventricular response rate – VRR, Restore and maintain normal sinus rhythm – Cardioversion, ↓ risk of stroke 1. Controlling Ventricular Response Rate – most common way of controlling AF Which drugs? Digoxin, Beta Blockers, Calcium channel blockers : only use verapamil o ...
EKG Interpretation Basics As you are well aware by now, EKG
... Changes, and 2) reciprocal ST segment depression (more on this in a moment). In other words, when you see ST segment elevation and Nonspecific T wave changes occurring together on the same EKG take it seriously. Remember that this really means an abnormal T wave axis in either the limb leads, the ch ...
... Changes, and 2) reciprocal ST segment depression (more on this in a moment). In other words, when you see ST segment elevation and Nonspecific T wave changes occurring together on the same EKG take it seriously. Remember that this really means an abnormal T wave axis in either the limb leads, the ch ...
exploring cardiovascular physiology activity
... the delivery of oxygen to actively respiring muscle cells. These include: increased respiration rate, increased heart rate, increased blood flow to muscular tissue, decreased blood flow to non-muscular tissue, increased blood pressure and increased body temperature. One risk factor for developing ca ...
... the delivery of oxygen to actively respiring muscle cells. These include: increased respiration rate, increased heart rate, increased blood flow to muscular tissue, decreased blood flow to non-muscular tissue, increased blood pressure and increased body temperature. One risk factor for developing ca ...
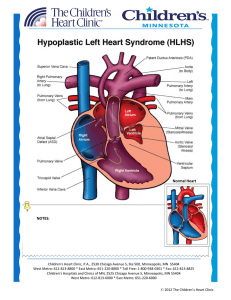
HLHS - Children`s Heart Clinic
... left atrium. It then travels from the left atrium through the mitral valve to the left ventricle. The left ventricle contracts, sending blood through the aortic valve through the aorta and out to the body. Hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS) refers to several closely related anomalies. The left v ...
... left atrium. It then travels from the left atrium through the mitral valve to the left ventricle. The left ventricle contracts, sending blood through the aortic valve through the aorta and out to the body. Hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS) refers to several closely related anomalies. The left v ...
Chapter 12 A and B questions
... How does the AV node affect the rate of AP conduction and why is this important? What is the role of Purkinje fibers? How does an action potential in a cardiac myofiber differ from that of a skeletal muscle? What is its shape, approximate duration, and which ions are responsible for the rising, plat ...
... How does the AV node affect the rate of AP conduction and why is this important? What is the role of Purkinje fibers? How does an action potential in a cardiac myofiber differ from that of a skeletal muscle? What is its shape, approximate duration, and which ions are responsible for the rising, plat ...
Name: Dr
... Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine & Therapeutics, Prince of Wales Hospital, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong Heart failure is a disease with high morbidity and mortality. It is also the commonest cause of medical ward admission in developed countries. The incidence of hear ...
... Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine & Therapeutics, Prince of Wales Hospital, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong Heart failure is a disease with high morbidity and mortality. It is also the commonest cause of medical ward admission in developed countries. The incidence of hear ...
VENTRICULAR ECTOPIC BEATS
... For the heart to work as an efficient pump it must beat in an orderly sequence with the collecting chamber (atrium) contracting before the pumping chamber (ventricle). To achieve this the heart normally follows a rhythm or beat, which begins in the atrium. Even though palpitations often produce a fe ...
... For the heart to work as an efficient pump it must beat in an orderly sequence with the collecting chamber (atrium) contracting before the pumping chamber (ventricle). To achieve this the heart normally follows a rhythm or beat, which begins in the atrium. Even though palpitations often produce a fe ...
Doc - Medtronic
... Cryoablation, which is a minimally invasive catheter approach that freezes tissue in the heart’s upper chambers, traditionally around the pulmonary veins, to block the conduction of electrical signals that trigger erratic heart rhythms. Surgical intervention, which is traditionally known as an open- ...
... Cryoablation, which is a minimally invasive catheter approach that freezes tissue in the heart’s upper chambers, traditionally around the pulmonary veins, to block the conduction of electrical signals that trigger erratic heart rhythms. Surgical intervention, which is traditionally known as an open- ...
Jake - wendyblount.com
... In clinic test to distinguish cardiac from respiratory dyspnea Validated in dogs JACVIM January 2008 <210 pmol/L – more likely respiratory disease >210 pmol/L – more likely cardiac disease Falsely elevated by increased creatinine Helpful in distinguishing cardiac from respiratory dyspnea when creati ...
... In clinic test to distinguish cardiac from respiratory dyspnea Validated in dogs JACVIM January 2008 <210 pmol/L – more likely respiratory disease >210 pmol/L – more likely cardiac disease Falsely elevated by increased creatinine Helpful in distinguishing cardiac from respiratory dyspnea when creati ...
Cardiac Conducting System AND Cardiac cycle
... 3. Bundle branches(bundle of His) a. Impulse reaches bundle branches- travels along septum, splits between L & R bundle branches b. Purkinje fibers – where the bundle branches diverge into smaller branches i. Cause ventricular contraction ii. Wave action from apex(bottom) to base(top) toward right ...
... 3. Bundle branches(bundle of His) a. Impulse reaches bundle branches- travels along septum, splits between L & R bundle branches b. Purkinje fibers – where the bundle branches diverge into smaller branches i. Cause ventricular contraction ii. Wave action from apex(bottom) to base(top) toward right ...
The Heart
... • Heart muscles contract without being stimulated by external nerves (myogenic muscles) • Heart muscle does not all contract at the same rhythm when separated • Heart rhythm is set by the sinoatrial (SA) node – specialized nerve cells • Nerve impulses travel to a second node AV node which sends the ...
... • Heart muscles contract without being stimulated by external nerves (myogenic muscles) • Heart muscle does not all contract at the same rhythm when separated • Heart rhythm is set by the sinoatrial (SA) node – specialized nerve cells • Nerve impulses travel to a second node AV node which sends the ...
EMS Cardiac Confusion By Lynn Wallis EMT
... and the PR interval are not the same thing.) The PR segment is not routinely measured, but may be commented on if it is depressed or elevated. During the PR segment, the electrical wave moves slowly through the atrioventricular (AV) node. This activity is not seen on the electrocardiogram. The PR in ...
... and the PR interval are not the same thing.) The PR segment is not routinely measured, but may be commented on if it is depressed or elevated. During the PR segment, the electrical wave moves slowly through the atrioventricular (AV) node. This activity is not seen on the electrocardiogram. The PR in ...
COM 4120 ART Computational modelling and simulation in biology
... pump; electrical activation of heart cells (the action potential) initiates contraction. Electrical properties of cells are well characterised experimentally. Mechanical properties of cardiac tissue, and coupling of electrical and mechanical properties are less well understood. ...
... pump; electrical activation of heart cells (the action potential) initiates contraction. Electrical properties of cells are well characterised experimentally. Mechanical properties of cardiac tissue, and coupling of electrical and mechanical properties are less well understood. ...
Heart
... anterior portion of each atrium of the heart, increasing slightly the atrial volume http://faculty.ucc.edu/biology-potter/Fetal_Blood_Vessels ...
... anterior portion of each atrium of the heart, increasing slightly the atrial volume http://faculty.ucc.edu/biology-potter/Fetal_Blood_Vessels ...
ECG Rhythm Interpretation December 16 & 18
... When blood flows through the heart, it follows a unidirectional pattern. There are four different valves within the myocardium and their functions are to assure blood flows from the right to left side of the myocardium and always in a “forward” direction. The two valves found between the atria and v ...
... When blood flows through the heart, it follows a unidirectional pattern. There are four different valves within the myocardium and their functions are to assure blood flows from the right to left side of the myocardium and always in a “forward” direction. The two valves found between the atria and v ...
Document
... Surface ECG shows irregular RR intervals Surface ECG shows no distinct P waves The interval between two atrial activations is usually variable and <200ms ...
... Surface ECG shows irregular RR intervals Surface ECG shows no distinct P waves The interval between two atrial activations is usually variable and <200ms ...
Treatments - Heart Rhythm Society
... For patients with heart failure, a biventricular pacemaker or defibrillator can be implanted, which paces both the left and right ventricles (lower chambers) of the heart simultaneously. This resynchronizes muscle contractions and improves the efficiency of the weakened heart. It is also referred to a ...
... For patients with heart failure, a biventricular pacemaker or defibrillator can be implanted, which paces both the left and right ventricles (lower chambers) of the heart simultaneously. This resynchronizes muscle contractions and improves the efficiency of the weakened heart. It is also referred to a ...
Cardiology Terminology Quiz by Laura King, MA, ELS
... 2. Reciprocal ST segment depressions were seen in the study patients in leads 2, 3, and AVF. ANSWER: Reciprocal ST-segment depressions were seen in the study patients in leads II, III, and aVF. Editor’s Note: Standard leads are designated with roman numerals (eg, I, II, and III). Augmented limb lead ...
... 2. Reciprocal ST segment depressions were seen in the study patients in leads 2, 3, and AVF. ANSWER: Reciprocal ST-segment depressions were seen in the study patients in leads II, III, and aVF. Editor’s Note: Standard leads are designated with roman numerals (eg, I, II, and III). Augmented limb lead ...
Second (Mobitz Type II) and Third Degree Heart Block
... Third degree heart block, also called complete AV block, happens when none of the electrical signals from the atria reach the ventricles. When complete heart block happens, the heart rate is slower. This is because back-up pacemaker cells in the AV node or ventricle control the heart rate. It is rar ...
... Third degree heart block, also called complete AV block, happens when none of the electrical signals from the atria reach the ventricles. When complete heart block happens, the heart rate is slower. This is because back-up pacemaker cells in the AV node or ventricle control the heart rate. It is rar ...
The Role of Ventricular Electrical Delay to Predict Left Ventricular
... • Subgroup analyses have identified QRS duration and QRS morphology as independent predictors of CRT outcomes • This suggests that electrical delay or electrical dyssynchrony is an important factor for predicting benefit from CRT • Identifying the electrical delay at the LV stimulation site may quan ...
... • Subgroup analyses have identified QRS duration and QRS morphology as independent predictors of CRT outcomes • This suggests that electrical delay or electrical dyssynchrony is an important factor for predicting benefit from CRT • Identifying the electrical delay at the LV stimulation site may quan ...
Electrocardiography
Electrocardiography (ECG or EKG*) is the process of recording the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time using electrodes placed on a patient's body. These electrodes detect the tiny electrical changes on the skin that arise from the heart muscle depolarizing during each heartbeat.In a conventional 12 lead ECG, ten electrodes are placed on the patient's limbs and on the surface of the chest. The overall magnitude of the heart's electrical potential is then measured from twelve different angles (""leads"") and is recorded over a period of time (usually 10 seconds). In this way, the overall magnitude and direction of the heart's electrical depolarization is captured at each moment throughout the cardiac cycle. The graph of voltage versus time produced by this noninvasive medical procedure is referred to as an electrocardiogram (abbreviated ECG or EKG).During each heartbeat, a healthy heart will have an orderly progression of depolarization that starts with pacemaker cells in the sinoatrial node, spreads out through the atrium, passes through the atrioventricular node down into the bundle of His and into the Purkinje fibers spreading down and to the left throughout the ventricles. This orderly pattern of depolarization gives rise to the characteristic ECG tracing. To the trained clinician, an ECG conveys a large amount of information about the structure of the heart and the function of its electrical conduction system. Among other things, an ECG can be used to measure the rate and rhythm of heartbeats, the size and position of the heart chambers, the presence of any damage to the heart's muscle cells or conduction system, the effects of cardiac drugs, and the function of implanted pacemakers.