Accelerated idioventricular rhythm observed under total intravenous
... severe when their doses were decreased (+1), because the surgery 1 year prior had no episode of an AIVR with balanced anesthesia using sevoflurane, remifentanil, and propofol, the doses of which were lower than those at this time. The arrhythmias were objectively recorded on an ECG trace (+1). Most ...
... severe when their doses were decreased (+1), because the surgery 1 year prior had no episode of an AIVR with balanced anesthesia using sevoflurane, remifentanil, and propofol, the doses of which were lower than those at this time. The arrhythmias were objectively recorded on an ECG trace (+1). Most ...
Acute Care Ultrasound Echo - Society for Acute Medicine
... (vs. left in Abdo-US! ) Probes with small footprints (ribs!) ideal, hold them like a pen, use enough gel ...
... (vs. left in Abdo-US! ) Probes with small footprints (ribs!) ideal, hold them like a pen, use enough gel ...
PowerPoint
... tires (gets tired). •It beats itself without the brain having to control it. •It started beating before you were born and will continue until death. •The size of a human heart is similar to your clenched fist. • It is protected by the ribs. ...
... tires (gets tired). •It beats itself without the brain having to control it. •It started beating before you were born and will continue until death. •The size of a human heart is similar to your clenched fist. • It is protected by the ribs. ...
Part 1: EKG
... c. In heart block, the atrial rate is (normal, high or low?) ______________ but the ventricular rate is (normal, high or low?) __________________. ...
... c. In heart block, the atrial rate is (normal, high or low?) ______________ but the ventricular rate is (normal, high or low?) __________________. ...
Atrial fibrillation
... Two trials in 2002, the American AFFIRM trial and a second European study demonstrated that there was no longer term difference in mortality and morbidity between rate control and anticoagulation and rhythm control with anticoagulation in patients with persistent or chronic AF. 2, 3 So whilst it ma ...
... Two trials in 2002, the American AFFIRM trial and a second European study demonstrated that there was no longer term difference in mortality and morbidity between rate control and anticoagulation and rhythm control with anticoagulation in patients with persistent or chronic AF. 2, 3 So whilst it ma ...
Properties of Cardiac muscle MCQ
... B. Nuclei are in the periphery. C. Rich in blood supply and mitochondria. D. They form branching network connected by intercalated discs. 3. The excitability of the cardiac muscle is increased by the following factor except: A. Hypokalemia. B. Sympathetic stimulation. C. Mild ischemia. D. Catecholam ...
... B. Nuclei are in the periphery. C. Rich in blood supply and mitochondria. D. They form branching network connected by intercalated discs. 3. The excitability of the cardiac muscle is increased by the following factor except: A. Hypokalemia. B. Sympathetic stimulation. C. Mild ischemia. D. Catecholam ...
managing disease together
... ejection fraction less than or equal to 35% and a prolonged QRS duration to maintain synchrony of the left and right ventricles in patients who have undergone an AV nodal ablation for chronic (permanent) atrial fibrillation and have NYHA Class II or III heart failure. Contraindications: Contraindica ...
... ejection fraction less than or equal to 35% and a prolonged QRS duration to maintain synchrony of the left and right ventricles in patients who have undergone an AV nodal ablation for chronic (permanent) atrial fibrillation and have NYHA Class II or III heart failure. Contraindications: Contraindica ...
AP Biology CardioVascular System Study Guide
... 27. Explain the “lubb dub” sound the heart makes with it it working. 28. Trace the path of the blood from the time it enters the heart, to the lungs, out of the heart and back again. http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/biocoach/cardio1/intro.html ...
... 27. Explain the “lubb dub” sound the heart makes with it it working. 28. Trace the path of the blood from the time it enters the heart, to the lungs, out of the heart and back again. http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/biocoach/cardio1/intro.html ...
... Classification consists of two steps: training and validation. In the training phase, SVM receives features as input. In this investigation, features extracted from heartbeat are represented by 2, 3 and 4 dimensional row vectors. The system under investigation is configured as follows. The dataset i ...
Human Body Systems
... distort in shape in order to squeeze through extremely tiny capillaries. When they aren’t elongated they are moving in a single file line in order to get through small vessels. ...
... distort in shape in order to squeeze through extremely tiny capillaries. When they aren’t elongated they are moving in a single file line in order to get through small vessels. ...
Heart Intro SJW
... The amount of blood pumped can be calculated: Heart Rate x Stroke Volume = Cardiac Output. Heart rate: The number of heart beats per minute. Stroke volume: The volume of blood pumped from heart with each beat. Cardiac output: The amount of blood pumped by heart in one minute. ...
... The amount of blood pumped can be calculated: Heart Rate x Stroke Volume = Cardiac Output. Heart rate: The number of heart beats per minute. Stroke volume: The volume of blood pumped from heart with each beat. Cardiac output: The amount of blood pumped by heart in one minute. ...
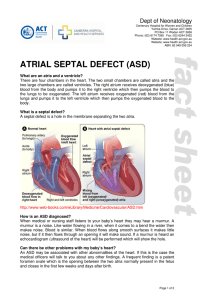
atrial septal defect (asd)
... In most children ASDs will rarely cause a problem. However, if the defect is large it may cause heart failure. Symptoms of heart failure include fast breathing, fast heart rate and poor growth. These symptoms are often controlled with medications until the hole decreases in size or closes. The major ...
... In most children ASDs will rarely cause a problem. However, if the defect is large it may cause heart failure. Symptoms of heart failure include fast breathing, fast heart rate and poor growth. These symptoms are often controlled with medications until the hole decreases in size or closes. The major ...
Spiral Waves and the Heart: Spatiotemporal
... 2. Multiple small electrical shocks that have lower energy and synchronize the tissue to allow resumption of sinus rhythm. 3. Anti-arrhythmic drugs, which can make the rhythm more regular. When we understand how spiral waves behave, we might provide better treatments for arrhythmias. For example, in ...
... 2. Multiple small electrical shocks that have lower energy and synchronize the tissue to allow resumption of sinus rhythm. 3. Anti-arrhythmic drugs, which can make the rhythm more regular. When we understand how spiral waves behave, we might provide better treatments for arrhythmias. For example, in ...
Location of the heart
... Atrial stretch receptors stimulated by venous return Heart rate increases SA and AV nodes stimulated by venous return Heart rate increases ...
... Atrial stretch receptors stimulated by venous return Heart rate increases SA and AV nodes stimulated by venous return Heart rate increases ...
EMS_April_2016 - S. Blake Wachter, MD, PhD Advanced Heart
... 37% were witnessed by bystander 33% of these got bystander CPR – Survival was 11.2% compared to those who did not get CPR 7% ...
... 37% were witnessed by bystander 33% of these got bystander CPR – Survival was 11.2% compared to those who did not get CPR 7% ...
Clinical Anatomy Series – Cardiac Anatomy
... autoimmune. Clinical features include sharp central chest pain exacerbated by movement and lying down and relieved by sitting forward. Pain may be referred to the shoulder or neck. Auscultation may reveal a pericardial friction rub, typically at the left lower sternal edge on e ...
... autoimmune. Clinical features include sharp central chest pain exacerbated by movement and lying down and relieved by sitting forward. Pain may be referred to the shoulder or neck. Auscultation may reveal a pericardial friction rub, typically at the left lower sternal edge on e ...
Heart Quiz Revamp
... a. decreased heart rate but increased force of contraction b. increased heart rate but decreased force of contraction c. increased heart rate and force of contraction d. decreased heart rate and force of contraction 9. The heart wall a. has an inner layer called the epicardium, which is fused with t ...
... a. decreased heart rate but increased force of contraction b. increased heart rate but decreased force of contraction c. increased heart rate and force of contraction d. decreased heart rate and force of contraction 9. The heart wall a. has an inner layer called the epicardium, which is fused with t ...
Document
... provide a simple and safe approach to the acute management of heart rhythm problems. They are directed at junior doctors who may have to deal with these at times complex problems whilst on call, when direction from more senior colleagues may not be immediately available. It is hoped that they will s ...
... provide a simple and safe approach to the acute management of heart rhythm problems. They are directed at junior doctors who may have to deal with these at times complex problems whilst on call, when direction from more senior colleagues may not be immediately available. It is hoped that they will s ...
Cardiac Emergencies
... rhinorrhea, no ill contacts. PMH: unremarkable. vigorous feeder (2530oz/d) until the last couple of days. FHx: father had a “leaky valve” but was cleared to join the Marines ...
... rhinorrhea, no ill contacts. PMH: unremarkable. vigorous feeder (2530oz/d) until the last couple of days. FHx: father had a “leaky valve” but was cleared to join the Marines ...
Cardiovascular System PPT
... 2. Atrioventricular (AV) node delays the impulse approximately 0.1 second ...
... 2. Atrioventricular (AV) node delays the impulse approximately 0.1 second ...
Circulation support part 1 dr. Horáček
... failure to provide transport and regulatory functions • heart failure: failure to pump the amount of blood necessary to satisfy metabolic needs of tissues – injury of : myocardium, valves, arrhythmias, support tissues – myocardial failure: injury due to ischaemia/reperfusion, inflammation, trauma, m ...
... failure to provide transport and regulatory functions • heart failure: failure to pump the amount of blood necessary to satisfy metabolic needs of tissues – injury of : myocardium, valves, arrhythmias, support tissues – myocardial failure: injury due to ischaemia/reperfusion, inflammation, trauma, m ...
H.5 - HL transport-system
... begins at the apex. d) The impulse travels on emerging into the heart muscle higher up the ventricle wall in this way the contraction spreads upwards. •Note that this direction of contraction pushes the blood towards the semi-lunar valve and also not that the transmission time down the Purkinje tiss ...
... begins at the apex. d) The impulse travels on emerging into the heart muscle higher up the ventricle wall in this way the contraction spreads upwards. •Note that this direction of contraction pushes the blood towards the semi-lunar valve and also not that the transmission time down the Purkinje tiss ...
The Heart - WordPress.com
... organ located between the lungs in the centre of the chest (thorax), and is about the size of a fist. ...
... organ located between the lungs in the centre of the chest (thorax), and is about the size of a fist. ...
Electrocardiography
Electrocardiography (ECG or EKG*) is the process of recording the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time using electrodes placed on a patient's body. These electrodes detect the tiny electrical changes on the skin that arise from the heart muscle depolarizing during each heartbeat.In a conventional 12 lead ECG, ten electrodes are placed on the patient's limbs and on the surface of the chest. The overall magnitude of the heart's electrical potential is then measured from twelve different angles (""leads"") and is recorded over a period of time (usually 10 seconds). In this way, the overall magnitude and direction of the heart's electrical depolarization is captured at each moment throughout the cardiac cycle. The graph of voltage versus time produced by this noninvasive medical procedure is referred to as an electrocardiogram (abbreviated ECG or EKG).During each heartbeat, a healthy heart will have an orderly progression of depolarization that starts with pacemaker cells in the sinoatrial node, spreads out through the atrium, passes through the atrioventricular node down into the bundle of His and into the Purkinje fibers spreading down and to the left throughout the ventricles. This orderly pattern of depolarization gives rise to the characteristic ECG tracing. To the trained clinician, an ECG conveys a large amount of information about the structure of the heart and the function of its electrical conduction system. Among other things, an ECG can be used to measure the rate and rhythm of heartbeats, the size and position of the heart chambers, the presence of any damage to the heart's muscle cells or conduction system, the effects of cardiac drugs, and the function of implanted pacemakers.