Study Guide for Final #1
... 1.) Know who the important contributors were who helped to derive the different models of the atom. Know what their contributions were. 2.) Be able to describe Dalton’s atomic theory. 3.) Know where the three different subatomic particles are located, their charges, and their relative sizes. 4.) Kno ...
... 1.) Know who the important contributors were who helped to derive the different models of the atom. Know what their contributions were. 2.) Be able to describe Dalton’s atomic theory. 3.) Know where the three different subatomic particles are located, their charges, and their relative sizes. 4.) Kno ...
Geophysics
... Statistics for the Physical and Environmental Sciences Statistics for the Physical Sciences (no longer offered) Probability and Statistics for Engineers ...
... Statistics for the Physical and Environmental Sciences Statistics for the Physical Sciences (no longer offered) Probability and Statistics for Engineers ...
Lecture 5
... To balance the equation, we must find the coefficients that will lead to a balanced equation. ...
... To balance the equation, we must find the coefficients that will lead to a balanced equation. ...
for Professional Electives ONLY
... This is a comprehensive list of courses that will count towards your electives, but it is not a guarantee that they will be offered every year/quarter or that you will be able to enroll as prerequisites must be completed prior to enrolling. Enrollment and offering of courses depend on respective dep ...
... This is a comprehensive list of courses that will count towards your electives, but it is not a guarantee that they will be offered every year/quarter or that you will be able to enroll as prerequisites must be completed prior to enrolling. Enrollment and offering of courses depend on respective dep ...
Atomic Mass - HCC Learning Web
... Balancing Chemical Equations 1. Write the correct formula(s) for the reactants on the left side and the correct formula(s) for the product(s) on the right side of the equation. Ethane reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide & water: C2H6 + O2 ...
... Balancing Chemical Equations 1. Write the correct formula(s) for the reactants on the left side and the correct formula(s) for the product(s) on the right side of the equation. Ethane reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide & water: C2H6 + O2 ...
BASIC CHEMICAL CONCEPTS
... whose atoms are alike in having the same positive charge on the nucleus”. This plunges beginners immediately into the world of atoms and atomic structure. As Alex Johnstone (1999, 2000) has explained, this goes against the psychology of learning. Chemistry is only fully intelligible to beginners if ...
... whose atoms are alike in having the same positive charge on the nucleus”. This plunges beginners immediately into the world of atoms and atomic structure. As Alex Johnstone (1999, 2000) has explained, this goes against the psychology of learning. Chemistry is only fully intelligible to beginners if ...
AP Chemistry - West Bloomfield School District
... a. Write a balanced equation for the reaction that occurs (remember oxygen is O 2). b. How many grams of P2O5 are formed if 3.40 g of P4 react? c. How many grams of oxygen would be consumed using 16.00 g of P 4? 65. When a mixture of silver metal and sulfur is heated, silver sulfide is formed: 16 Ag ...
... a. Write a balanced equation for the reaction that occurs (remember oxygen is O 2). b. How many grams of P2O5 are formed if 3.40 g of P4 react? c. How many grams of oxygen would be consumed using 16.00 g of P 4? 65. When a mixture of silver metal and sulfur is heated, silver sulfide is formed: 16 Ag ...
H3AsO4 + 3 I- + 2 H3O+ H3AsO3 + I3- + H2O
... bond and one bond and a triple bond consists of one and two bonds. Sometimes a bond can be placed in more than one location. In such situations, we describe the molecule by using two or more resonance structures. The molecule is envisioned as a blend of these multiple resonance structures a ...
... bond and one bond and a triple bond consists of one and two bonds. Sometimes a bond can be placed in more than one location. In such situations, we describe the molecule by using two or more resonance structures. The molecule is envisioned as a blend of these multiple resonance structures a ...
chemical reactions
... Many equations are balanced by trial and error; but it must be remembered that coefficients can be changed in order to balance an equation, but not subscripts of a correct formula. ...
... Many equations are balanced by trial and error; but it must be remembered that coefficients can be changed in order to balance an equation, but not subscripts of a correct formula. ...
g - Porterville College Home
... b. For cations, subtract one electron for each charge. Use this number of electrons exactly for bonding and non-bonding in the structure. These electrons must be distributed to all atoms such that each has an octet except hydrogen (“duet”). 2. Place atoms around a central atom (lone atom, or the ato ...
... b. For cations, subtract one electron for each charge. Use this number of electrons exactly for bonding and non-bonding in the structure. These electrons must be distributed to all atoms such that each has an octet except hydrogen (“duet”). 2. Place atoms around a central atom (lone atom, or the ato ...
30. Which set of ionic compounds?
... the systematic procedure you devised to identify the solid, and describe how well it worked in practice. After the presentation, be prepared to accept and answer questions and to discuss what you did with the rest of the class. ...
... the systematic procedure you devised to identify the solid, and describe how well it worked in practice. After the presentation, be prepared to accept and answer questions and to discuss what you did with the rest of the class. ...
BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES – (For Professional Electives
... This is a comprehensive list of courses that will count towards your electives, but it is not a guarantee that they will be offered every year/quarter or that you will be able to enroll as prerequisites must be completed prior to enrolling. Enrollment and offering of courses depend on respective dep ...
... This is a comprehensive list of courses that will count towards your electives, but it is not a guarantee that they will be offered every year/quarter or that you will be able to enroll as prerequisites must be completed prior to enrolling. Enrollment and offering of courses depend on respective dep ...
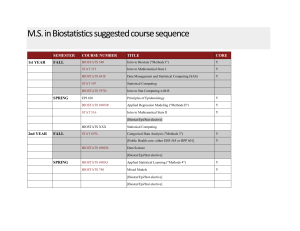
M.S. in Biostatistics suggested course sequence
... M.S. in Biostatistics suggested course sequence 1st YEAR ...
... M.S. in Biostatistics suggested course sequence 1st YEAR ...
August 2007
... The ice finishes melting at 2 minutes and heat enters the container. The ice finishes melting at 2 minutes and heat leaves the container. The ice finishes melting at 5 minutes and heat enters the container. The ice finishes melting at 5 minutes and heat leaves the container. ...
... The ice finishes melting at 2 minutes and heat enters the container. The ice finishes melting at 2 minutes and heat leaves the container. The ice finishes melting at 5 minutes and heat enters the container. The ice finishes melting at 5 minutes and heat leaves the container. ...
General Chemistry Stoichiometry Notes
... 1. Leader- Keeps all on task and makes sure directions are followed. 2. Scientist- Follows directions and is in charge of making sure no mistakes occur. 3. Mathematician- insures calculations are correct. I will pick one lab per group to grade-- you get whatever score they get…make sure everyone in ...
... 1. Leader- Keeps all on task and makes sure directions are followed. 2. Scientist- Follows directions and is in charge of making sure no mistakes occur. 3. Mathematician- insures calculations are correct. I will pick one lab per group to grade-- you get whatever score they get…make sure everyone in ...
AP CHEMISTRY
... 2. Which of the following pairs of compounds have the same empirical formula? a. Acetylene, C2H2, and benzene, C6H6 b. Ethane, C2H6, and benzene, C6H6 c. Nitrogen dioxide, NO2 , and dinitrogen tetroxide, N2O4 3. D. Diphenyl ether, C12H8O, and phenol, C6H5OHIn an experiment, a 2.514-g sample of calci ...
... 2. Which of the following pairs of compounds have the same empirical formula? a. Acetylene, C2H2, and benzene, C6H6 b. Ethane, C2H6, and benzene, C6H6 c. Nitrogen dioxide, NO2 , and dinitrogen tetroxide, N2O4 3. D. Diphenyl ether, C12H8O, and phenol, C6H5OHIn an experiment, a 2.514-g sample of calci ...
Chemistry 11 – Course Review
... ___________________________ devised the Scattering Experiment, which showed that all atoms had a small dense __________________________. ...
... ___________________________ devised the Scattering Experiment, which showed that all atoms had a small dense __________________________. ...