Chemistry - Volusia County Schools
... more than a single step or thought process. The student is expected to decide what to do—using formal methods of reasoning and problem-solving strategies—and to bring together skill and knowledge from various domains. ...
... more than a single step or thought process. The student is expected to decide what to do—using formal methods of reasoning and problem-solving strategies—and to bring together skill and knowledge from various domains. ...
File
... Matter is classified as a pure substance or as a mixture of substances. (3.1q) The three phases of matter (solids, liquids, and gases) have different properties. (3.1kk) A pure substance (element or compound) has a constant composition and constant properties throughout a given sample, and from sam ...
... Matter is classified as a pure substance or as a mixture of substances. (3.1q) The three phases of matter (solids, liquids, and gases) have different properties. (3.1kk) A pure substance (element or compound) has a constant composition and constant properties throughout a given sample, and from sam ...
chemistry in the 8th grade
... chemical change is involved in changing physical state. A chemical change only occurs when chemical bonds are broken, formed, or both. When matter is in the solid state, the particles (atoms or molecules) that make up the matter are very close together. These particles can vibrate around fixed posit ...
... chemical change is involved in changing physical state. A chemical change only occurs when chemical bonds are broken, formed, or both. When matter is in the solid state, the particles (atoms or molecules) that make up the matter are very close together. These particles can vibrate around fixed posit ...
Topic guide 9.3: Drug discovery and design
... be used to deduce the likely structure of the pharmacophore – the part of the ligand molecule that enables it to be recognised at the binding site. Quantitative structure-activity relationship models can be used to predict the most effective ligands based on our knowledge of the pharmacophore and, a ...
... be used to deduce the likely structure of the pharmacophore – the part of the ligand molecule that enables it to be recognised at the binding site. Quantitative structure-activity relationship models can be used to predict the most effective ligands based on our knowledge of the pharmacophore and, a ...
Introduction Modeling of subsurface flow processes is important for
... (2013) noticed that the cells in which the pressure affects the flux are only the neighboring four cells. This implies that one could design the testing pressure field in which the cells where the pressure is one alternate every two cells. In other words, the testing pressure fields are generated on ...
... (2013) noticed that the cells in which the pressure affects the flux are only the neighboring four cells. This implies that one could design the testing pressure field in which the cells where the pressure is one alternate every two cells. In other words, the testing pressure fields are generated on ...
Numerical Solution of Hyperbolic Telegraph Equation Using Method
... used. For the collocation method the residual is then collocated at equally space point and equated to zero while for the partition method, the domain is subdivided into subdomain and the residual are integrated over these subdomain and equated to zero. The resulting system of equations are then sol ...
... used. For the collocation method the residual is then collocated at equally space point and equated to zero while for the partition method, the domain is subdivided into subdomain and the residual are integrated over these subdomain and equated to zero. The resulting system of equations are then sol ...
PRE AP CHEMISTRY REVIEW PROBLEMS NON COLLEGE
... The following are problems that students entering AP Chemistry are expected to solve and answer without difficulty. You may use a scientific calculator. A periodic table and other helpful information are provided on the last page. If you are finding the need to refer to a textbook or other resources ...
... The following are problems that students entering AP Chemistry are expected to solve and answer without difficulty. You may use a scientific calculator. A periodic table and other helpful information are provided on the last page. If you are finding the need to refer to a textbook or other resources ...
File
... Alex’s hypothesis was that the rate will be affected by changing the concentrations of the propanone and the iodine, as the reaction can happen without a catalyst. Hannah’s hypothesis was that as the catalyst is involved in the reaction, the concentrations of the propanone, iodine and the hydrogen i ...
... Alex’s hypothesis was that the rate will be affected by changing the concentrations of the propanone and the iodine, as the reaction can happen without a catalyst. Hannah’s hypothesis was that as the catalyst is involved in the reaction, the concentrations of the propanone, iodine and the hydrogen i ...
Under Choice Based Credit System Proposed syllabus and Scheme of Examination
... Course Chemistry IVChemistry of s- 2 and ...
... Course Chemistry IVChemistry of s- 2 and ...
CHEMISTRY 103 – Practice Problems #3 Chapters 8 – 10 http
... 34. Answer the questions below about the structure and bonding in this molecule. a. Draw in any lone pairs needed to complete octets. b. What is the bond order for the bond marked “a”? c. What is the hybridization on the C atom marked “b”? d. What is the molecular geometry around the C atom marked “ ...
... 34. Answer the questions below about the structure and bonding in this molecule. a. Draw in any lone pairs needed to complete octets. b. What is the bond order for the bond marked “a”? c. What is the hybridization on the C atom marked “b”? d. What is the molecular geometry around the C atom marked “ ...
File
... Increases across a period; increases down a group. b. Increases across a period; decreases down a group. c. Decreases across a period; increases down a group. d. Decreases across a period; decreases down a group. ...
... Increases across a period; increases down a group. b. Increases across a period; decreases down a group. c. Decreases across a period; increases down a group. d. Decreases across a period; decreases down a group. ...
Structure of Molecules and Compounds | Principles of Biology from
... How can we describe or illustrate molecules? They have a physical form derived from the specific spatial relationships of multiple chemical elements. Knowing what those elements are is one thing, but knowing how they are arranged, and in what proportions, is the basis for creating molecular ...
... How can we describe or illustrate molecules? They have a physical form derived from the specific spatial relationships of multiple chemical elements. Knowing what those elements are is one thing, but knowing how they are arranged, and in what proportions, is the basis for creating molecular ...
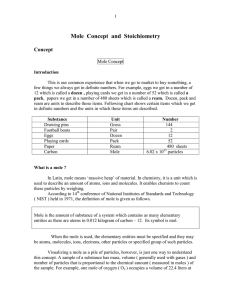
Mole Concept and Stoichiometry
... and contains about 6.022 x 1023 molecules of oxygen. Measuring one of these quantities allows the calculation of the others and this is frequently done in stoichiometry. One interpretation : A specific number of particles When a quantity of particles is to be described, mole is a grouping unit analo ...
... and contains about 6.022 x 1023 molecules of oxygen. Measuring one of these quantities allows the calculation of the others and this is frequently done in stoichiometry. One interpretation : A specific number of particles When a quantity of particles is to be described, mole is a grouping unit analo ...
in Peptide Synthesis, Molecular Recognition
... building block in peptides and proteins, we have explored its particular role in a variety of biological processes by tuning its intrinsic structural and functional properties using readily accessible proline mimetics ('pseudoprolines', 'PPro). In enhancing and extending well-known Pro effects, i.e. ...
... building block in peptides and proteins, we have explored its particular role in a variety of biological processes by tuning its intrinsic structural and functional properties using readily accessible proline mimetics ('pseudoprolines', 'PPro). In enhancing and extending well-known Pro effects, i.e. ...
Gas-Phase Basicity of (CH3)3N
... being somewhat depleted relative to that of a true Boltzmann.5 For SORI-CAD low and high collision energy data, the effective temperature is 548 and 643 K, respectively. The branching ratio for the protonated dimer of o-TMAB and one of the bases (1,5,7triazabicyclo[4.4.0]dec-5-ene) inverts with ion ...
... being somewhat depleted relative to that of a true Boltzmann.5 For SORI-CAD low and high collision energy data, the effective temperature is 548 and 643 K, respectively. The branching ratio for the protonated dimer of o-TMAB and one of the bases (1,5,7triazabicyclo[4.4.0]dec-5-ene) inverts with ion ...
Quantum Computing - University of Washington
... For the last fifty years computers have grown faster, smaller, and more powerful — transforming and benefiting our society in ways too numerous to count. But like any exponential explosion of resources, this growth — known as Moore's law — must soon come to an end. Research has already begun on what ...
... For the last fifty years computers have grown faster, smaller, and more powerful — transforming and benefiting our society in ways too numerous to count. But like any exponential explosion of resources, this growth — known as Moore's law — must soon come to an end. Research has already begun on what ...
Unit 3. Stoichiometry
... When 10.0 g of octane (C8H18) is burned in the presence of 25.0 g of oxygen, 7.36 g of H2O is produced (carbon dioxide is the other product). a) What is the excess reactant and how much is left? b) What is the percent yield of this reaction? ...
... When 10.0 g of octane (C8H18) is burned in the presence of 25.0 g of oxygen, 7.36 g of H2O is produced (carbon dioxide is the other product). a) What is the excess reactant and how much is left? b) What is the percent yield of this reaction? ...