* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Computational chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Inverse problem wikipedia , lookup
Expectation–maximization algorithm wikipedia , lookup
Newton's method wikipedia , lookup
Perturbation theory wikipedia , lookup
Multiple-criteria decision analysis wikipedia , lookup
Numerical continuation wikipedia , lookup
Navier–Stokes equations wikipedia , lookup
Simplex algorithm wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Least squares wikipedia , lookup
Routhian mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Signal-flow graph wikipedia , lookup
System of polynomial equations wikipedia , lookup
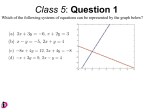
Activity 3 - 1 Business Checking Account Objectives • Solve a system of two linear equations numerically • Solve a system of two linear equations graphically • Solve a system of two linear equations using the substitution method • Recognize the connections between the three methods of solution • Interpret the solution to a system of two linear equations in terms of the problem’s content Vocabulary • System of linear equations – two equations that relate the same two variables • Numerical method – using a table of values to see with input results in the same output for the two equations • Graphical method – graph the functions and determine the coordinates of the point of intersection • Substitution method – an algebraic method using substitution to reduce the problem to one variable • Consistent – has exactly one solution (the graphs of the lines intersect) • Inconsistent – has no solutions (the graphs of the lines are parallel) Solving a System of 2 Linear Equations • Numerically – by completing a table and noting which x-value gives you the same y-value • Graphically – by graphing the equations and finding their point of intersection • Algebraically – by using properties of equality to solve the equations for one variable and then the other – Substitution method: (also known as elimination) – Addition method (the emphasis in lesson 3.3) Business Checking Account In setting up your part-time business, you have two choices for a checking account at the local bank. MONTHLY FEE TRANSACTION FEE REGULAR $11.00 $0.17 for each transaction BASIC $8.50 $0.22 for each transaction in excess of 20 If you anticipate making about 50 transactions each month, which checking account will be more economical? Basic Business Checking Account MONTHLY FEE TRANSACTION FEE REGULAR $11.00 $0.17 for each transaction BASIC $8.50 $0.22 for each transaction in excess of 20 2. Let x represent the number of transactions. Write an equation that expresses the total monthly cost, C, for the regular account. C = $11 + $0.17t 3. Let x represent the number of transactions. Write an equation that expresses the total monthly cost, C, for the basic account. This is a more complicated equation because the transaction fee does not apply to the first twenty checks. C = $8.50 for t ≤ 20 C = $8.50 + $0.22(t – 20) = $0.22t + $4.10 for t > 20 Fill in the Table • Use the two equations from the previous slide C = 11 + 0.17x and Number of Transactions 20 50 100 Cost of Regular ($) 14.40 19.50 28.00 Cost of Basic ($) 8.50 15.10 26.10 C = 4.10 + 0.22x 150 36.50 200 45.00 250 53.50 300 62.00 37.10 48.10 59.10 70.10 TI-83 Table Feature • Use the table feature of your calculator to determine the x-value that produces two identical y-values • TABLE (2nd Graph) – Put in x values of interest (independent) in table – Set Y1 = to equation of interest – Go back to table to read off dependent values TI-83 Graph • Use your calculator to graph the functions y window: Xmin: 0 Xmax: 300 Xscl: 10 Ymin = 0 Ymax = 80 Yscl = 10 Xres = 1 x Graphical Method • Step 1: Solve both equations for y = … • Step 2: Put into your calculator (y1 = for one and y2 = for the other) and graph (or graph by hand) • Step 3: If the lines intersect, then the intersection point is the solution; if the lines are parallel, then there is no solution; and if the lines are the same, then there are an infinite number of solutions • Step 4: Write the solution (intersection point) (use TRACE on your calculator to find it) Graphical Method - Solutions • Consistent Inconsistent One Solution y Solutions No Solution y x y x x Substitution Method • Step 1: Solve one or both equations for a variable (both x = … or both y = …) • Step 2: Substitute the expression that represents the variable in one equation for that variable in the other equation • Step 3: Solve the resulting equation for the remaining variable • Step 4: Substitute the value from step 3 into one of the original equations and solve for the other variable Substitution Example Given: y + x = 9 and y = 3x – 3 • Step 1: y = 9 – x and y = 3x – 3 • Step 2: 9 – x = 3x – 3 • Step 3: 9 +3 12 3 +x +x = 4x – 3 +3 = 4x = x • Step 4: y + 3 = 9 y=6 or or y = 3(3) – 3 y=9–3=6 Problem 1 Given: y = 3x – 10 and y = 5x + 14 Solve using substitution • Step 1: y = 3x – 10 and y = 5x + 14 • Step 2: 3x – 10 = 5x + 14 • Step 3: + 10 + 10 3x = 5x + 24 - 3x - 3x 0 = 2x + 24 -24 = 2x -12 = x • Step 4: y = 3(-12) – 10 = -46 Problem 2 Use the substitution method to sol the following system of checking account cost functions: C = 0.17x + 11 and C = 0.22x + 4.10 • Step 1: C = 0.17x + 11 and y = 0.22x + 4.10 • Step 2: 0.17x + 11 = 0.22x + 4.10 • Step 3: -.17x -.17x 11 = 0.05x + 4.10 - 4.1 - 4.1 6.9 = 0.05x 138 = x • Step 4: 0.17(138) + 11 = 23.46 + 11 = 34.46 Summary and Homework • Summary – The solution of a system of equations is the set of all ordered pairs that satisfy both equations. – The three standard methods for solving a system of equations are the Numerical method, Graphical method and Substitution method. – A linear system is consistent if there is at least one solution, the point of intersection of the graphs. – A linear system is inconsistent if there is no solution -that is, the lines are parallel. • Homework – 1- 4, 7, 8