Ecology
... A. When water vapor cools in the atmosphere, it condenses and falls to earth as rain. Gravity draws the water back to earth in the form of rain, sleet, and snow. B. Water is absorbed by the roots of the trees and used in photosynthesis, but it is also lost from their leaves through the process of tr ...
... A. When water vapor cools in the atmosphere, it condenses and falls to earth as rain. Gravity draws the water back to earth in the form of rain, sleet, and snow. B. Water is absorbed by the roots of the trees and used in photosynthesis, but it is also lost from their leaves through the process of tr ...
Glossary of terms
... Simple chemicals required by plants and animals to live. For example: nitrogen, carbon and phosphorus. ...
... Simple chemicals required by plants and animals to live. For example: nitrogen, carbon and phosphorus. ...
Dewey Notes 09 Life in the Ocean
... tuna (large fish) production. Whales have figured out, that for their massive needs, it is inefficient to pass the food through intermediate trophic levels, so the largest beasts on Earth eat some of the smallest (zooplankton). ...
... tuna (large fish) production. Whales have figured out, that for their massive needs, it is inefficient to pass the food through intermediate trophic levels, so the largest beasts on Earth eat some of the smallest (zooplankton). ...
Ecology ppt
... • All of the relationships between an organism and its environment – both living and nonliving- make up its niche • Think of an organisms niche as its lifestyle ...
... • All of the relationships between an organism and its environment – both living and nonliving- make up its niche • Think of an organisms niche as its lifestyle ...
Ecology Study Guide 2
... 2. Discuss biotic and abiotic factors that affect land and aquatic biomes. 3. Discuss the role of beneficial bacteria (e.g. in the recycling of nutrients) 4. Explain how energy flows through ecosystems in one direction, from photosynthetic organisms to herbivores to carnivores and decomposers. 5. Ex ...
... 2. Discuss biotic and abiotic factors that affect land and aquatic biomes. 3. Discuss the role of beneficial bacteria (e.g. in the recycling of nutrients) 4. Explain how energy flows through ecosystems in one direction, from photosynthetic organisms to herbivores to carnivores and decomposers. 5. Ex ...
Microbial Diseases Of Skin And eyes - Wikispaces
... – List the cutaneous fungal infections. – Discuss microbial diseases of the eye and list the microbes that cause them. ...
... – List the cutaneous fungal infections. – Discuss microbial diseases of the eye and list the microbes that cause them. ...
SYNTHETIC ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS
... Mechanism of action: They are chemical analogues of p-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) → they competitively inhibit bacterial enzyme, which is responsible for the synthesis of folic acid → inhibit bacterial folic acid, which is the most important factor of microbial life. In environments containing large ...
... Mechanism of action: They are chemical analogues of p-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) → they competitively inhibit bacterial enzyme, which is responsible for the synthesis of folic acid → inhibit bacterial folic acid, which is the most important factor of microbial life. In environments containing large ...
UbD-viruses and survey of kingdoms - Glenbard High School District
... 12B Students who meet the standard know and apply concepts that describe how living things interact with each other and with their environment Understanding(s): Students will understand that… Essential Question(s): What provocative questions will foster -‐Virus ...
... 12B Students who meet the standard know and apply concepts that describe how living things interact with each other and with their environment Understanding(s): Students will understand that… Essential Question(s): What provocative questions will foster -‐Virus ...
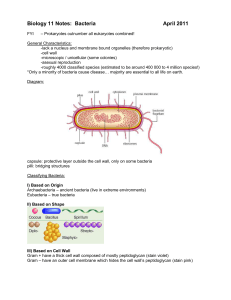
Biology 11 Notes: Kingdom Monera
... -lack a nucleus and membrane bound organelles (therefore prokaryotic) -cell wall -microscopic / unicellular (some colonies) -asexual reproduction -roughly 4000 classified species (estimated to be around 400 000 to 4 million species!) *Only a minority of bacteria cause disease… majority are essential ...
... -lack a nucleus and membrane bound organelles (therefore prokaryotic) -cell wall -microscopic / unicellular (some colonies) -asexual reproduction -roughly 4000 classified species (estimated to be around 400 000 to 4 million species!) *Only a minority of bacteria cause disease… majority are essential ...
Ecology Ecology is the study of the relationships of organisms to
... Nitrates in the soil are broken down by these organisms, and the nitrogen is released into the atmosphere. ...
... Nitrates in the soil are broken down by these organisms, and the nitrogen is released into the atmosphere. ...
Chapter 6 Study Guide
... sulfur—to survive, grow, and reproduce. Nutrients are transported into microorganisms by two kinds of processes: active transport that expends energy and passive transport that does not need energy input. The environmental factors that control microbial growth are temperature; gases; pH; osmotic, hy ...
... sulfur—to survive, grow, and reproduce. Nutrients are transported into microorganisms by two kinds of processes: active transport that expends energy and passive transport that does not need energy input. The environmental factors that control microbial growth are temperature; gases; pH; osmotic, hy ...
8-1 “Components of an Ecosystem”
... Most living things require oxygen to carry out their life processes. Some organisms obtain oxygen from the air, which is about 20% oxygen. Fish and other water organisms obtain dissolved oxygen from the water around them. ...
... Most living things require oxygen to carry out their life processes. Some organisms obtain oxygen from the air, which is about 20% oxygen. Fish and other water organisms obtain dissolved oxygen from the water around them. ...
8-1 “Components of an Ecosystem”
... Most living things require oxygen to carry out their life processes. Some organisms obtain oxygen from the air, which is about 20% oxygen. Fish and other water organisms obtain dissolved oxygen from the water around them. ...
... Most living things require oxygen to carry out their life processes. Some organisms obtain oxygen from the air, which is about 20% oxygen. Fish and other water organisms obtain dissolved oxygen from the water around them. ...
Lethal Effects of Temperature
... The former is the lowest temperature at which a suspension of bacteria is killed in 10 minutes; while the later is the time required to kill a finite number of cells or spores at a given temperature. Wet heat is often used as a means of killing bacteria. How effective this is as a means of destroyin ...
... The former is the lowest temperature at which a suspension of bacteria is killed in 10 minutes; while the later is the time required to kill a finite number of cells or spores at a given temperature. Wet heat is often used as a means of killing bacteria. How effective this is as a means of destroyin ...
Ecology: Study Guide
... greenhouse effect. Because we burn fossil fuels we have an excess build up of greenhouse gases, especially CO2 . ...
... greenhouse effect. Because we burn fossil fuels we have an excess build up of greenhouse gases, especially CO2 . ...
Plant Biotechnology
... environment – poses no threat to groundwater – breaks down under UV light of the sun ...
... environment – poses no threat to groundwater – breaks down under UV light of the sun ...
Fast Facts About Pathogens
... method of replication, and size, among other factors, are different from those of bacteria. While bacteria can multiply almost anywhere, given the right conditions, a virus must get inside other living cells in order to do so. ...
... method of replication, and size, among other factors, are different from those of bacteria. While bacteria can multiply almost anywhere, given the right conditions, a virus must get inside other living cells in order to do so. ...
Title - Iowa State University
... Many are found in human intestines. We have a mutualistic relationship with these bacteria and depend on them to help digest some foods we eat. 2. __Exotoxins___ are poisonous illness-causing proteins secreted by bacteria and other organisms. An example of this type of toxin is _cholera_. 3. _Endoto ...
... Many are found in human intestines. We have a mutualistic relationship with these bacteria and depend on them to help digest some foods we eat. 2. __Exotoxins___ are poisonous illness-causing proteins secreted by bacteria and other organisms. An example of this type of toxin is _cholera_. 3. _Endoto ...
Keywords Biology B1 Metabolism All the chemical reactions going
... environmental conditions e.g. thermophiles can withstand extreme temperatures. ...
... environmental conditions e.g. thermophiles can withstand extreme temperatures. ...
ecology web page
... Biodiversity = measures how much Species differ within the same Ecosystem. Ex. Some trees are resistant to a Disease and others die off. ...
... Biodiversity = measures how much Species differ within the same Ecosystem. Ex. Some trees are resistant to a Disease and others die off. ...
Ecology is study of interactions between
... Light – how much light is available for the organism. What about caves? ...
... Light – how much light is available for the organism. What about caves? ...
WHAT IS ECOLOGY?
... and yet animals and plants cannot use nitrogen gas as a nutrient. So what’s an animal or plant to do? How do animals get nitrogen? They eat protein! How do plants get nitrogen? From bacteria that are in the soil or in the roots of some plants. Plants can only use nitrogen when it is in the form of n ...
... and yet animals and plants cannot use nitrogen gas as a nutrient. So what’s an animal or plant to do? How do animals get nitrogen? They eat protein! How do plants get nitrogen? From bacteria that are in the soil or in the roots of some plants. Plants can only use nitrogen when it is in the form of n ...
Electron Sources
... 2. Heterotrophs - microorganisms that use reduced, preformed (made by other organisms) organic molecule as carbon sources a. chemoheterotroph (chemoorganotrophic heterotroph) use organic compounds for energy, hydrogen, electrons, and carbon (nonphotosynthetic) b. photoheterotroph (photoorganotrophic ...
... 2. Heterotrophs - microorganisms that use reduced, preformed (made by other organisms) organic molecule as carbon sources a. chemoheterotroph (chemoorganotrophic heterotroph) use organic compounds for energy, hydrogen, electrons, and carbon (nonphotosynthetic) b. photoheterotroph (photoorganotrophic ...
Beta-Lactamase Threat in Respiratory Tract Infections
... Bacteria responsible for Healthcare Associated and Hospital Acquired PneumoniaStreptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), Pseudomonas aeruginosa, E. coli, ...
... Bacteria responsible for Healthcare Associated and Hospital Acquired PneumoniaStreptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), Pseudomonas aeruginosa, E. coli, ...
Triclocarban

Triclocarban is an antibacterial agent common in personal care products like soaps and lotions as well as in the medical field, for which it was originally developed. Studies on its antibacterial qualities and mechanisms are growing. Research suggests that it is similar in its mechanism to triclosan and is effective in fighting infections by targeting the growth of bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus. Additional research seeks to understand its potential for causing antibacterial resistance and its effects on organismal and environmental health.