Document
... plants.(liquid to gas) • Condensation- gas to liquid in form of precipitation. • Transpiration- loss of water vapor from plants. • Respiration- gaseous exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between organisms and environment. (Organisms also lose water through excretion.) • After an organism dies, de ...
... plants.(liquid to gas) • Condensation- gas to liquid in form of precipitation. • Transpiration- loss of water vapor from plants. • Respiration- gaseous exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between organisms and environment. (Organisms also lose water through excretion.) • After an organism dies, de ...
Micro-organisms and humans - questions
... 30 Micro-organisms and humans 1 List the main types of organism included under the heading of 'Micro-organisms' Bacteria 2 Which of the following are not found in bacteria? cytoplasm, cell wall, nuclear membrane, DNA, chromosome, glycogen, cellulose 3 Saprophytic bacteria release ….. A ….. into thei ...
... 30 Micro-organisms and humans 1 List the main types of organism included under the heading of 'Micro-organisms' Bacteria 2 Which of the following are not found in bacteria? cytoplasm, cell wall, nuclear membrane, DNA, chromosome, glycogen, cellulose 3 Saprophytic bacteria release ….. A ….. into thei ...
Chapters 3, 4, 5, 6 Test Review
... 36. The wearing away of surface soil by water and wind is known as soil erosion. 37. The sulfur and nitrogen compounds in smog combine with water to form Acid rain. 38. As DDT moves up the trophic levels in food chains, or food webs, its concentration increases 39. What are the factors that affect t ...
... 36. The wearing away of surface soil by water and wind is known as soil erosion. 37. The sulfur and nitrogen compounds in smog combine with water to form Acid rain. 38. As DDT moves up the trophic levels in food chains, or food webs, its concentration increases 39. What are the factors that affect t ...
What Is Behind Antibiotic Resistance?
... What Is Behind Antibiotic Resistance? What then, accounts for the seemingly rapid ...
... What Is Behind Antibiotic Resistance? What then, accounts for the seemingly rapid ...
Chapter 1: Introduction
... • conversion of atmospheric nitrogen (N2) into “bio-available” ammonia and nitrate compounds • makes nitrogen available for plants and, indirectly, all other organisms (necessary for proteins, etc) ...
... • conversion of atmospheric nitrogen (N2) into “bio-available” ammonia and nitrate compounds • makes nitrogen available for plants and, indirectly, all other organisms (necessary for proteins, etc) ...
1. Overview of the Microbial World
... • conversion of atmospheric nitrogen (N2) into “bio-available” ammonia and nitrate compounds • makes nitrogen available for plants and, indirectly, all other organisms (necessary for proteins, etc) ...
... • conversion of atmospheric nitrogen (N2) into “bio-available” ammonia and nitrate compounds • makes nitrogen available for plants and, indirectly, all other organisms (necessary for proteins, etc) ...
Ecosystems of Aquifers and Springs
... A. Most aquifers do not support traditional aquatic ecosystems. 1. No light, no photosynthesis (for plants) 2. No nutrients 3. No dissolved O2 to support aerobic life. 4. Survivors include: bacteria, protozoans, and other unicellular organisms. ...
... A. Most aquifers do not support traditional aquatic ecosystems. 1. No light, no photosynthesis (for plants) 2. No nutrients 3. No dissolved O2 to support aerobic life. 4. Survivors include: bacteria, protozoans, and other unicellular organisms. ...
Antimicrobial Agents
... a. The antimicrobial agent must resemble the chemical structure of an essential ______________________ used by the cell for a particular metabolic reaction. b. Because of this similarity in structure the antimicrobial agent reacts with the __________ ____________ on the specific ____________________ ...
... a. The antimicrobial agent must resemble the chemical structure of an essential ______________________ used by the cell for a particular metabolic reaction. b. Because of this similarity in structure the antimicrobial agent reacts with the __________ ____________ on the specific ____________________ ...
Chapter 2 - Jenksps.org
... they receive nitrogen fertilizer. This is because most plants cannot use the nitrogen in the air! They use nitrogen in the _________ that has been converted into more usable forms. Certain ________________ convert the nitrogen from the air into these more usable forms. ------------------------------ ...
... they receive nitrogen fertilizer. This is because most plants cannot use the nitrogen in the air! They use nitrogen in the _________ that has been converted into more usable forms. Certain ________________ convert the nitrogen from the air into these more usable forms. ------------------------------ ...
Family Enterobacteriaceae
... Members of the Enterobacteriaceae are rod-shaped, and are typically 1-5 μm in length. Like other Proteobacteria they have Gram-negative stains,[1] and they are facultative anaerobes, fermenting sugars to produce lactic acid and various other end products. Most also reduce nitrate to nitrite, althoug ...
... Members of the Enterobacteriaceae are rod-shaped, and are typically 1-5 μm in length. Like other Proteobacteria they have Gram-negative stains,[1] and they are facultative anaerobes, fermenting sugars to produce lactic acid and various other end products. Most also reduce nitrate to nitrite, althoug ...
Bacteria
... Do not use oxygen gas for energy production Oxygen gas is not a poison for them however E. Coli is an example of this ...
... Do not use oxygen gas for energy production Oxygen gas is not a poison for them however E. Coli is an example of this ...
Oppgave 5.
... Ethylacetate Dimethylformamide (DMF), HCON(CH3)2 Acetaldehyde Ethanol Trans-methyl methylacrylate, CH3CH=CHCOOCH3 3-aminoanisole, (1-methoxy-4-amino-benzene) 3-oxobutanenitrile, NCCH2COCH3 ...
... Ethylacetate Dimethylformamide (DMF), HCON(CH3)2 Acetaldehyde Ethanol Trans-methyl methylacrylate, CH3CH=CHCOOCH3 3-aminoanisole, (1-methoxy-4-amino-benzene) 3-oxobutanenitrile, NCCH2COCH3 ...
221_exam_1_2003
... Describe how thioglycolate medium is used to determine the relationship of an organism to oxygen. Explain the function of the various key ingredients of the thioglycolate medium. Describe the growth pattern you would expect to observe for a strict aerobe, strict anaerobe, facultative and microaerop ...
... Describe how thioglycolate medium is used to determine the relationship of an organism to oxygen. Explain the function of the various key ingredients of the thioglycolate medium. Describe the growth pattern you would expect to observe for a strict aerobe, strict anaerobe, facultative and microaerop ...
슬라이드 1
... - breaks down sphingomyelin and other membrane phospholipids, resulting in cell lysis ...
... - breaks down sphingomyelin and other membrane phospholipids, resulting in cell lysis ...
Ecology Unit UPCO
... Climax communities have populations that remain the same because they are in balance with one another and the environment. ...
... Climax communities have populations that remain the same because they are in balance with one another and the environment. ...
Ecologists study . Ecology is the study of is an individual living thing
... (stays stable) after a period of exponential growth once resources become less available. The number at which the environment can support this population is known as the carrying capacity. ...
... (stays stable) after a period of exponential growth once resources become less available. The number at which the environment can support this population is known as the carrying capacity. ...
The Land Ethic Aldo Leopold
... – Keep populations below the carrying capacity – The less violent the man made changes, the greater the probability of successful readjustment in the pyramid. – Violence, in turn, varies with human population ...
... – Keep populations below the carrying capacity – The less violent the man made changes, the greater the probability of successful readjustment in the pyramid. – Violence, in turn, varies with human population ...
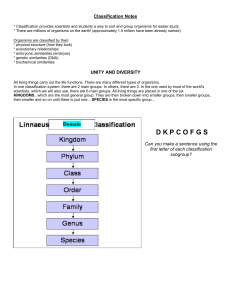
2013 Taxonomy Notes ppt
... All living things carry out the life functions. There are many different types of organisms. In one classification system, there are 2 main groups. In others, there are 3. In the one used by most of the world's scientists, which we will also use, there are 6 main groups. All living things are placed ...
... All living things carry out the life functions. There are many different types of organisms. In one classification system, there are 2 main groups. In others, there are 3. In the one used by most of the world's scientists, which we will also use, there are 6 main groups. All living things are placed ...
Antibiotics - dr chohan`s ent day surgery
... – Increasing incidence of treatment failure secondary to resistant organisms as well as compliance issues (taste/length of course) have some recommending 2nd ...
... – Increasing incidence of treatment failure secondary to resistant organisms as well as compliance issues (taste/length of course) have some recommending 2nd ...
Unit 2: Multi-cellular organisms
... Those individuals best ADAPTED to a changing environment pass on the genes that confer a selective ADVANTAGE to their offspring. The less well adapted members die. This weeding out process is called NATURAL selection. ...
... Those individuals best ADAPTED to a changing environment pass on the genes that confer a selective ADVANTAGE to their offspring. The less well adapted members die. This weeding out process is called NATURAL selection. ...
Ecology - Warren County Schools
... among the young, but then shows that death rates decline for those few individuals that have survived to a ...
... among the young, but then shows that death rates decline for those few individuals that have survived to a ...
Extreme Life
... High Temps: So What? • What’s the Big Deal about life at high temperatures? • Experience says that putting living creatures in boiling hot water kills them • Mmmmm … lobster! • How? • Denaturing of the proteins • High heat causes proteins to lose some of their structural/chemical properties • Break ...
... High Temps: So What? • What’s the Big Deal about life at high temperatures? • Experience says that putting living creatures in boiling hot water kills them • Mmmmm … lobster! • How? • Denaturing of the proteins • High heat causes proteins to lose some of their structural/chemical properties • Break ...
Ecological impacts of metal pollution in the Fal and Hayle estuaries
... Grossly contaminated estuaries in Cornwall provide excellent systems for the study of the ecological effects of metal pollution. They also allow us to compare the sensitivity of different monitoring methods. I will review the published literature on the Fal and the Hayle estuaries, and a number of p ...
... Grossly contaminated estuaries in Cornwall provide excellent systems for the study of the ecological effects of metal pollution. They also allow us to compare the sensitivity of different monitoring methods. I will review the published literature on the Fal and the Hayle estuaries, and a number of p ...
The take home message: The burden of infectious disease in the
... human host • Some need us; some don’t • They differ in the complexity of their life cycles – Some live entirely in a human host – Some have complex cycles that go from us to the environment and back to us ...
... human host • Some need us; some don’t • They differ in the complexity of their life cycles – Some live entirely in a human host – Some have complex cycles that go from us to the environment and back to us ...
Triclocarban

Triclocarban is an antibacterial agent common in personal care products like soaps and lotions as well as in the medical field, for which it was originally developed. Studies on its antibacterial qualities and mechanisms are growing. Research suggests that it is similar in its mechanism to triclosan and is effective in fighting infections by targeting the growth of bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus. Additional research seeks to understand its potential for causing antibacterial resistance and its effects on organismal and environmental health.