Hormones and the Endocrine System
... Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) – plays an important role in the menstrual cycle. In males, it causes the testes to produce a hormone that regulates sperm production. ...
... Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) – plays an important role in the menstrual cycle. In males, it causes the testes to produce a hormone that regulates sperm production. ...
Answers to Mastering Concepts Questions
... 3. What prevents a hormone from affecting all body cells equally? A hormone exerts a physiological effect only on target cells that have specific receptors for the hormone. 4. Many dairy operators inject their cows with bovine growth hormone to stimulate milk production. Cite two reasons that bovin ...
... 3. What prevents a hormone from affecting all body cells equally? A hormone exerts a physiological effect only on target cells that have specific receptors for the hormone. 4. Many dairy operators inject their cows with bovine growth hormone to stimulate milk production. Cite two reasons that bovin ...
Endocrine system: physiological peculiarities, symptoms and
... Deficiency of luteinizing hormone (LH) and folliclestimulating hormone (FSH), together referred to as the gonadotropins, leads to different symptoms in men and women. Women experience oligo- or amenorrhea (infrequent/light or absent menstrual periods respectively) and infertility. Men lose facial, s ...
... Deficiency of luteinizing hormone (LH) and folliclestimulating hormone (FSH), together referred to as the gonadotropins, leads to different symptoms in men and women. Women experience oligo- or amenorrhea (infrequent/light or absent menstrual periods respectively) and infertility. Men lose facial, s ...
Hypothalamic Control of Pituitary Function
... innervate the posterior pituitary gland, which is responsible for ADH and oxytocin production. The arcuate nucleus is the chief hypothalamic structure which secretes releasing factors to the anterior pituitary. It does this by a unique blood supply called the hypophysial portal system which transpor ...
... innervate the posterior pituitary gland, which is responsible for ADH and oxytocin production. The arcuate nucleus is the chief hypothalamic structure which secretes releasing factors to the anterior pituitary. It does this by a unique blood supply called the hypophysial portal system which transpor ...
Answers to WHAT DID YOU LEARN questions
... gonadotropins (FSH and LH), thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), growth hormone (GH), prolactin (PRL), and melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH). ACTH stimulates the adrenal cortex to produce and secrete some corticosteroid hormones. FSH and LH influence reproductive system activities by regulating hor ...
... gonadotropins (FSH and LH), thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), growth hormone (GH), prolactin (PRL), and melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH). ACTH stimulates the adrenal cortex to produce and secrete some corticosteroid hormones. FSH and LH influence reproductive system activities by regulating hor ...
Anatomy chapter 11 (Endocrine system)
... • Releasing hormones from the hypothalamus control the secretions of the anterior pituitary. •A small gland located in the brain that is important for puberty and sexual cycles. •Growth hormone (GH) stimulates body cells to grow and reproduce; it also speeds the rate at which cells use carbohydrates ...
... • Releasing hormones from the hypothalamus control the secretions of the anterior pituitary. •A small gland located in the brain that is important for puberty and sexual cycles. •Growth hormone (GH) stimulates body cells to grow and reproduce; it also speeds the rate at which cells use carbohydrates ...
Basic Human Anatomy Lesson 10: Endocrine System
... b. This internal secretion results from the fact that these glands have no ducts. Thus, they are often referred to as the ductless glands. c. The secretions produced by the endocrine glands are called hormones. d. Hormones are carried by the bloodstream to specific organs or tissues, which are then ...
... b. This internal secretion results from the fact that these glands have no ducts. Thus, they are often referred to as the ductless glands. c. The secretions produced by the endocrine glands are called hormones. d. Hormones are carried by the bloodstream to specific organs or tissues, which are then ...
chapt11answers
... The hormone-receptor complex binds with the _DNA__ and activates specific __genes___ that, in turn, direct the synthesis of specific ___proteins__. __non-steroid__ hormones combine with receptors in target cell __membranes__; the receptors have a ___binding_____ site and a/an __activity_______ site. ...
... The hormone-receptor complex binds with the _DNA__ and activates specific __genes___ that, in turn, direct the synthesis of specific ___proteins__. __non-steroid__ hormones combine with receptors in target cell __membranes__; the receptors have a ___binding_____ site and a/an __activity_______ site. ...
The Endocrine System
... •Hormone levels in the blood are mostly maintained by negative feedback •A stimulus or low hormone levels in the blood triggers the release of more hormone •Hormone release stops once an appropriate level in the blood is reached ...
... •Hormone levels in the blood are mostly maintained by negative feedback •A stimulus or low hormone levels in the blood triggers the release of more hormone •Hormone release stops once an appropriate level in the blood is reached ...
Hormones (secretion, regulation, function complete)
... Controls Ca2+ balance in the blood in bone to release Ca and phosphates into blood; in kidneys to enhance reabsorption of Ca; in the intestine to increase absorption of Ca; causes conversion of Vit. D into its active form, ...
... Controls Ca2+ balance in the blood in bone to release Ca and phosphates into blood; in kidneys to enhance reabsorption of Ca; in the intestine to increase absorption of Ca; causes conversion of Vit. D into its active form, ...
Chapter 23
... 3. The endocrine system controls homeostasis by secreting hormones, i.e., messenger molecules, into the bloodstream for delivery to virtually all body cells. 4. The nervous and endocrine systems act as a coordinated supersystem called the neuroendocrine system: some neurons stimulate or inhibit the ...
... 3. The endocrine system controls homeostasis by secreting hormones, i.e., messenger molecules, into the bloodstream for delivery to virtually all body cells. 4. The nervous and endocrine systems act as a coordinated supersystem called the neuroendocrine system: some neurons stimulate or inhibit the ...
Endocrinology - NCORD Healthcare LLC
... scrotum below the penis in males, secrete androgens, mainly testosterone, that control sexual development,puberty, facial hair, sexual behavior, libido, erectile function, and the formation of spermatozoa (spermatogenesis). Pancreas - located in the abdomen. The pancreas is both an endocrine gland a ...
... scrotum below the penis in males, secrete androgens, mainly testosterone, that control sexual development,puberty, facial hair, sexual behavior, libido, erectile function, and the formation of spermatozoa (spermatogenesis). Pancreas - located in the abdomen. The pancreas is both an endocrine gland a ...
Semester 2 Study Guide
... ____________________________________________________________________________________________ 7. The secretion of GH is controlled by ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ 8. Actions of ...
... ____________________________________________________________________________________________ 7. The secretion of GH is controlled by ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ 8. Actions of ...
The Endocrine System - Highland 4U Biology with Mr. Byrnes
... • Use cue cards and markers to illustrate which components of the system each person represents • Be sure to include details such as what each hormone does and which component is stimulating which ...
... • Use cue cards and markers to illustrate which components of the system each person represents • Be sure to include details such as what each hormone does and which component is stimulating which ...
Hormone - WordPress.com
... corticosteroids: aldosterone and cortisol FSH stimulates follicle growth and ovarian estrogen production; stimulates sperm production and androgen-binding protein LH has a role in ovulation and the growth of the corpus luteum; stimulates androgen secretion by interstitial cells in testes ...
... corticosteroids: aldosterone and cortisol FSH stimulates follicle growth and ovarian estrogen production; stimulates sperm production and androgen-binding protein LH has a role in ovulation and the growth of the corpus luteum; stimulates androgen secretion by interstitial cells in testes ...
Endocrine System - Mr. Ford`s Class
... • Most hormonal secretions are controlled by negative feedback • Some positive feedback loops can be found in the reproductive system ...
... • Most hormonal secretions are controlled by negative feedback • Some positive feedback loops can be found in the reproductive system ...
The Endocrine System
... •Hormone levels in the blood are mostly maintained by negative feedback •A stimulus or low hormone levels in the blood triggers the release of more hormone •Hormone release stops once an appropriate level in the blood is reached ...
... •Hormone levels in the blood are mostly maintained by negative feedback •A stimulus or low hormone levels in the blood triggers the release of more hormone •Hormone release stops once an appropriate level in the blood is reached ...
Chapter 9 Outline
... The endocrine system is arguably the most elegant and mysterious of all the body systems. Considered to be the second great homeostatic system of the body (after the faster-acting nervous system), the endocrine system controls reproduction, growth and development, body defenses, metabolic processes, ...
... The endocrine system is arguably the most elegant and mysterious of all the body systems. Considered to be the second great homeostatic system of the body (after the faster-acting nervous system), the endocrine system controls reproduction, growth and development, body defenses, metabolic processes, ...
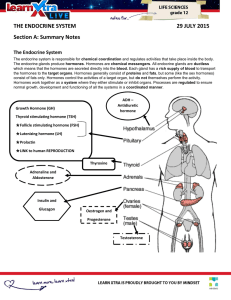
Get Notes - Mindset Learn
... Progesterone prepares the endometrium of the uterus for Undersecretion: during pregnancy, implantation once fertilisation of the egg cell has occurred will cause a spontaneous ...
... Progesterone prepares the endometrium of the uterus for Undersecretion: during pregnancy, implantation once fertilisation of the egg cell has occurred will cause a spontaneous ...
The Endocrine System
... The endocrine glands include the hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, thymus, and pancreas. ...
... The endocrine glands include the hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, thymus, and pancreas. ...
CHAPTER 13: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... PTH targets bone cells (activates osteoclasts to resorb bone), proximal convoluted tubules (causes PCT’s to reabsorb calcium back into bloodstream), and small intestine (promotes calcium absorption, See Fig 13.26, page 490). ...
... PTH targets bone cells (activates osteoclasts to resorb bone), proximal convoluted tubules (causes PCT’s to reabsorb calcium back into bloodstream), and small intestine (promotes calcium absorption, See Fig 13.26, page 490). ...
File - Mr. Downing Biology 30
... Endocrine glands are different from exocrine glands in that they release hormones and secrete these substances directly into the blood Exocrine glands produce secretions released via tubular ducts (ex: mammary glands secrete milk through ducts and therefore they are considered exocrine) ...
... Endocrine glands are different from exocrine glands in that they release hormones and secrete these substances directly into the blood Exocrine glands produce secretions released via tubular ducts (ex: mammary glands secrete milk through ducts and therefore they are considered exocrine) ...
The Endocrine System
... • Humans have an adrenal gland located above each kidney. Each adrenal gland has an inner core, the medulla, and an outer core, also called the cortex. • The medulla and the cortex function as separate endocrine glands. – The medulla is controlled by the nervous system, and the cortex is controlled ...
... • Humans have an adrenal gland located above each kidney. Each adrenal gland has an inner core, the medulla, and an outer core, also called the cortex. • The medulla and the cortex function as separate endocrine glands. – The medulla is controlled by the nervous system, and the cortex is controlled ...
Mammary gland

A mammary gland is an organ in female mammals that produces milk to feed young offspring. Mammals get their name from the word ""mammary."" In humans, the mammary glands are situated in the breasts. In ruminants such as cows, goats, and deer, the mammary glands are contained in the udders. The mammary glands of mammals other than primates, such as dogs and cats, are sometimes called dugs.