Endocrine System - Dr. Diamond`s Website
... • Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood • Hormones control several major processes – Reproduction – Growth and development – Mobilization of body defenses – Maintenance of much of homeostasis – Regulation of metabolism ...
... • Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood • Hormones control several major processes – Reproduction – Growth and development – Mobilization of body defenses – Maintenance of much of homeostasis – Regulation of metabolism ...
Chapter 13 The Endocrine System • Endocrine System Produces
... – Secretes eight different hormones that regulate other endocrine organs – Two lobes: posterior and anterior ...
... – Secretes eight different hormones that regulate other endocrine organs – Two lobes: posterior and anterior ...
Target cells
... • The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, & organs that secrete hormones into the blood • Hormone – an organic substance secreted by a cell that has an effect on the metabolic activity of another cell or tissue • Target cells – cells that are affected by the hormone – Have specific receptor ...
... • The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, & organs that secrete hormones into the blood • Hormone – an organic substance secreted by a cell that has an effect on the metabolic activity of another cell or tissue • Target cells – cells that are affected by the hormone – Have specific receptor ...
Chapter 17
... Increase body temperature (calorigenic effect) Stimulate protein synthesis Increase the use of glucose and fatty acids for ATP production Stimulate lipolysis Enhance some actions of catecholamines Regulate development and growth of nervous tissue and bones ...
... Increase body temperature (calorigenic effect) Stimulate protein synthesis Increase the use of glucose and fatty acids for ATP production Stimulate lipolysis Enhance some actions of catecholamines Regulate development and growth of nervous tissue and bones ...
THE ENDROCINE SYSTEM
... that are secreted by the cells to the extracellular fluid and regulate the metabolic functions of other cells – Most hormones are amino acid bases, but gonadal and adrenocortical hormones are steroids, derived from cholesterol ...
... that are secreted by the cells to the extracellular fluid and regulate the metabolic functions of other cells – Most hormones are amino acid bases, but gonadal and adrenocortical hormones are steroids, derived from cholesterol ...
Chapter 9 The Endocrine System
... Hormones are flowing… Hormones are chemical substances secreted into extracellular fluid that regulate activity of other cells Hormones circulate to all organs but affect ONLY certain tissue cells/organs referred to as its TARGET CELLS/ORGANS Target MUST have specific protein receptors on its plasm ...
... Hormones are flowing… Hormones are chemical substances secreted into extracellular fluid that regulate activity of other cells Hormones circulate to all organs but affect ONLY certain tissue cells/organs referred to as its TARGET CELLS/ORGANS Target MUST have specific protein receptors on its plasm ...
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 9 Review Sheet
... A tropic hormone is a hormone that comes from an endocrine gland and has action upon another gland to release another hormone to exert effects on other body organs and tissues. 6. Explain how a negative feedback system works. How does this illustrate actions of the endocrine system? In the endocrine ...
... A tropic hormone is a hormone that comes from an endocrine gland and has action upon another gland to release another hormone to exert effects on other body organs and tissues. 6. Explain how a negative feedback system works. How does this illustrate actions of the endocrine system? In the endocrine ...
Chapter 13
... • Works with nervous system to control and coordinate all other body systems • Effects body systems by chemical stimuli ...
... • Works with nervous system to control and coordinate all other body systems • Effects body systems by chemical stimuli ...
ANP 201 Dr Smith - University of Agriculture Abeokuta
... (E) Adrenal Medulla Hormones The principal hormone of the adrenal medulla is epinephrine. Norepinephrine is also present in smaller amounts but functions mainly as neurotransmitters in the sympathetic nervous system. These two hormones (norepinephrine and epinephrine) along with their precursor, dop ...
... (E) Adrenal Medulla Hormones The principal hormone of the adrenal medulla is epinephrine. Norepinephrine is also present in smaller amounts but functions mainly as neurotransmitters in the sympathetic nervous system. These two hormones (norepinephrine and epinephrine) along with their precursor, dop ...
Endocrine and Reproductive Systems
... • Hormones bind to target cells, which are cells that have specific receptors for a hormone either in the cell membrane or inside the cell. • A hormone will not affect a cell that does not have receptors for the hormone. ▶ Glands are organs that release secretions. The body has two types of glands. ...
... • Hormones bind to target cells, which are cells that have specific receptors for a hormone either in the cell membrane or inside the cell. • A hormone will not affect a cell that does not have receptors for the hormone. ▶ Glands are organs that release secretions. The body has two types of glands. ...
chemical signals in animals
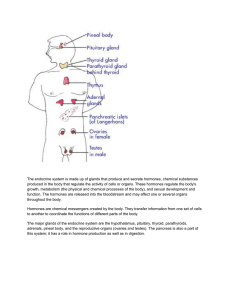
... a) Endocrine glands: are ductless organs that secret hormones either into the bloodstream or the fluid around cells. • The endocrine glands can be found through out the body and are collectively known as the endocrine system. • Endocrine glands, such as the pancreas, can also be exocrine glands. b) ...
... a) Endocrine glands: are ductless organs that secret hormones either into the bloodstream or the fluid around cells. • The endocrine glands can be found through out the body and are collectively known as the endocrine system. • Endocrine glands, such as the pancreas, can also be exocrine glands. b) ...
Chapter 16 Raging Hormones: The Endocrine System
... ⻬ Lactogenic hormone, or prolactin (PRL): Promotes milk production in mammary glands, which are considered nonendocrine targets. ⻬ Interstitial-cell stimulating hormone (ICSH): Stimulates formation and secretion of testosterone. ⻬ Thyrotropic hormone, or thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH): Controls t ...
... ⻬ Lactogenic hormone, or prolactin (PRL): Promotes milk production in mammary glands, which are considered nonendocrine targets. ⻬ Interstitial-cell stimulating hormone (ICSH): Stimulates formation and secretion of testosterone. ⻬ Thyrotropic hormone, or thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH): Controls t ...
Study Guide for Endocrine
... Study Guide for Endocrine 1. Create a notecard for every hormone discussed. Include the organ that produces it, effector organs, and action 2. What is a gland? 3. How do paracrine, endocrine, and exocrine glands differ from one another? 4. List some of the functions that are regulated by hormones 5. ...
... Study Guide for Endocrine 1. Create a notecard for every hormone discussed. Include the organ that produces it, effector organs, and action 2. What is a gland? 3. How do paracrine, endocrine, and exocrine glands differ from one another? 4. List some of the functions that are regulated by hormones 5. ...
6. The Importance of the Endocrine System
... Ex/ von Mering and Minkowski’s experiment with the pancreas in dogs These techniques helped uncover the effect of many hormones, but they were limited because most hormones do not work independently Some glands also produce several hormones, so their removal cannot be linked to one hormone Ex/ attem ...
... Ex/ von Mering and Minkowski’s experiment with the pancreas in dogs These techniques helped uncover the effect of many hormones, but they were limited because most hormones do not work independently Some glands also produce several hormones, so their removal cannot be linked to one hormone Ex/ attem ...
File
... hormones. If there is insufficient iodine in the diet, thyroxine cannot be made, and there will be no signal to stop TSH secretion. Constant stimulation of the thyroid gland by TSH causes a goitre, which is an enlargement of the thyroid gland. In Canada, it is uncommon for people to have goitres bec ...
... hormones. If there is insufficient iodine in the diet, thyroxine cannot be made, and there will be no signal to stop TSH secretion. Constant stimulation of the thyroid gland by TSH causes a goitre, which is an enlargement of the thyroid gland. In Canada, it is uncommon for people to have goitres bec ...
Endocrine System
... effects and targets: 1) amino acid uptake and protein synthesis are stimulated; 2) long bone extension (height growth) is stimulated indirectly, by stimulating the release of growth factors from the liver. Overproduction leads to giantism – height, but also pronounced brow ridges and other effects. ...
... effects and targets: 1) amino acid uptake and protein synthesis are stimulated; 2) long bone extension (height growth) is stimulated indirectly, by stimulating the release of growth factors from the liver. Overproduction leads to giantism – height, but also pronounced brow ridges and other effects. ...
ANATOMY OF THE PITUITARY GLAND
... anterior lobe of pituitary gland (hypophyseal portal system). Inferior hypophyseal: supplies posterior lobe of pituitary gland. ...
... anterior lobe of pituitary gland (hypophyseal portal system). Inferior hypophyseal: supplies posterior lobe of pituitary gland. ...
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 9 Review Sheet
... A tropic hormone is a hormone that comes from an endocrine gland and has action upon another gland to release another hormone to exert effects on other body organs and tissues. 6. Explain how a negative feedback system works. How does this illustrate actions of the endocrine system? In the endocrine ...
... A tropic hormone is a hormone that comes from an endocrine gland and has action upon another gland to release another hormone to exert effects on other body organs and tissues. 6. Explain how a negative feedback system works. How does this illustrate actions of the endocrine system? In the endocrine ...
Chapter 11
... Where is the pancreas located? Its endocrine portions are the islets of _____________________________ that include two cell types--________ cells that secrete glucagon, and ______________ cells that secrete insulin. Glucagon _______________________ the blood levels of glucose by stimulating the brea ...
... Where is the pancreas located? Its endocrine portions are the islets of _____________________________ that include two cell types--________ cells that secrete glucagon, and ______________ cells that secrete insulin. Glucagon _______________________ the blood levels of glucose by stimulating the brea ...
Pituitary Gland
... Luteinizing hormone (LH): Acts with FSH to stimulate estrogen secretion and follicle growth to maturity; causes ovulation; causes interstitial cells in the testes to secrete testosterone in the male Growth hormone (GH): Stimulates growth by accelerating protein anabolism; also accelerates fat catabo ...
... Luteinizing hormone (LH): Acts with FSH to stimulate estrogen secretion and follicle growth to maturity; causes ovulation; causes interstitial cells in the testes to secrete testosterone in the male Growth hormone (GH): Stimulates growth by accelerating protein anabolism; also accelerates fat catabo ...
Endocrine System
... Each adrenal gland is actually two endocrine organs. The outer portion is called the adrenal cortex. The inner portion is called the adrenal medulla. The hormones of the adrenal cortex are essential for life. The types of hormones secreted by the adrenal medulla are not. The adrenal cortex produces ...
... Each adrenal gland is actually two endocrine organs. The outer portion is called the adrenal cortex. The inner portion is called the adrenal medulla. The hormones of the adrenal cortex are essential for life. The types of hormones secreted by the adrenal medulla are not. The adrenal cortex produces ...
Anterior Pituitary: Growth Hormone (GH)
... adrenaline mobilizes the body for peak physical response. Flooding the bloodstream at up to 300 times the normal concentration, the adrenaline interacts with receptors on cells in various organs, increasing the heart rate and blood pressure and prompting the release from the liver of extra sugar to ...
... adrenaline mobilizes the body for peak physical response. Flooding the bloodstream at up to 300 times the normal concentration, the adrenaline interacts with receptors on cells in various organs, increasing the heart rate and blood pressure and prompting the release from the liver of extra sugar to ...
Mammary gland

A mammary gland is an organ in female mammals that produces milk to feed young offspring. Mammals get their name from the word ""mammary."" In humans, the mammary glands are situated in the breasts. In ruminants such as cows, goats, and deer, the mammary glands are contained in the udders. The mammary glands of mammals other than primates, such as dogs and cats, are sometimes called dugs.