Assessment in Action
... 11. Compare the pathophysiology, assessment, and management of type 1 diabetes with that of type 2 diabetes. (pp 1223-1225) 12. Discuss the role of glucose as a major source of energy for the body, and explain the relationship of glucose to insulin. (pp 1221-1223) 13. Compare hyperglycemic and hypog ...
... 11. Compare the pathophysiology, assessment, and management of type 1 diabetes with that of type 2 diabetes. (pp 1223-1225) 12. Discuss the role of glucose as a major source of energy for the body, and explain the relationship of glucose to insulin. (pp 1221-1223) 13. Compare hyperglycemic and hypog ...
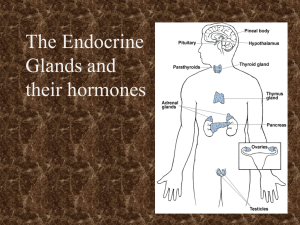
Hormones of the Body
... • This gland has both endocrine and exocrine functions… we’ll only cover the endocrine portion now (exocrine is for digestion) ...
... • This gland has both endocrine and exocrine functions… we’ll only cover the endocrine portion now (exocrine is for digestion) ...
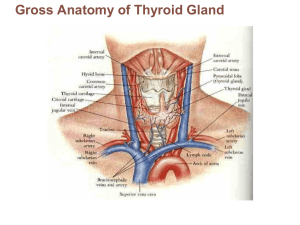
2. Thyroid Gland T 4 and T 3
... results in high BMR, sweating, rapid heart rate, weight loss, restlessness, mood shifts, fatigues easily, limited energy; also toxic goiter – exophthalmos - protrusion of eyeballs, fibrous tissue become edematous (swollen) • treatments - removal of thyroid gland or irradiation ...
... results in high BMR, sweating, rapid heart rate, weight loss, restlessness, mood shifts, fatigues easily, limited energy; also toxic goiter – exophthalmos - protrusion of eyeballs, fibrous tissue become edematous (swollen) • treatments - removal of thyroid gland or irradiation ...
Endocrine System Anatomy
... • Acromegaly = enlargement of the extremities, from excessive amounts of growth hormone. • Adrenalitis = inflammation of the adrenal gland. • Hypercalcemia = excessive calcium in the blood. • Hyperglycemia = excessive sugar in the blood. • Hyperkalemia = excessive potassium in blood. • Hyperthyroidi ...
... • Acromegaly = enlargement of the extremities, from excessive amounts of growth hormone. • Adrenalitis = inflammation of the adrenal gland. • Hypercalcemia = excessive calcium in the blood. • Hyperglycemia = excessive sugar in the blood. • Hyperkalemia = excessive potassium in blood. • Hyperthyroidi ...
Endocrine, powerpoint notes
... condition. It is sometimes defined as an adult height of less than 4 feet 10 inches (147 cm),[2] although this definition is problematic because short stature in itself is not a disorder. b. Dwarfism can be caused by about 200 distinct medical conditions,[3] such that the symptoms and characteristic ...
... condition. It is sometimes defined as an adult height of less than 4 feet 10 inches (147 cm),[2] although this definition is problematic because short stature in itself is not a disorder. b. Dwarfism can be caused by about 200 distinct medical conditions,[3] such that the symptoms and characteristic ...
Thyroid Hormone
... – Due to hyposecretion (type 1) or hypoactivity (type 2) of insulin – Blood glucose levels remain high nausea higher blood glucose levels (fight or flight response) – Glycosuria – glucose spilled into urine – Fats used for cellular fuel lipidemia; if severe ketones (ketone bodies) from fatty ...
... – Due to hyposecretion (type 1) or hypoactivity (type 2) of insulin – Blood glucose levels remain high nausea higher blood glucose levels (fight or flight response) – Glycosuria – glucose spilled into urine – Fats used for cellular fuel lipidemia; if severe ketones (ketone bodies) from fatty ...
Physiology is an Integrated Science
... several others learning goals for each hormone – know: it’s effects , functions what stim its release where is it made its target organs types of hormones direct hormones tropic hormones pre-hormone ...
... several others learning goals for each hormone – know: it’s effects , functions what stim its release where is it made its target organs types of hormones direct hormones tropic hormones pre-hormone ...
Hormones
... There are also coordination that involve both nervous and endocrine system e.g when a person is being attacked by a dog ...
... There are also coordination that involve both nervous and endocrine system e.g when a person is being attacked by a dog ...
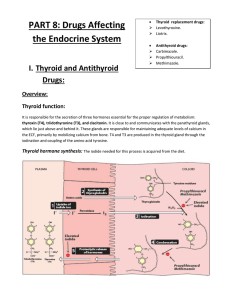
PART 8: Drugs Affecting the Endocrine System Thyroid and
... commonly used oral drug for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Metformin is decreasing glucose production by the liver. It may also decrease intestinal absorption of glucose and improve insulin receptor sensitivity. This results in increased peripheral glucose uptake and use. ...
... commonly used oral drug for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Metformin is decreasing glucose production by the liver. It may also decrease intestinal absorption of glucose and improve insulin receptor sensitivity. This results in increased peripheral glucose uptake and use. ...
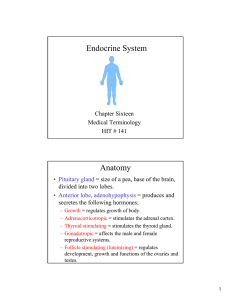
Chapter 16
... 2. Increased blood pressure Catecholamines 3. Liver converts glycogen to glucose (epinephrine and releases glucose to blood and norepinephrine) 4. Dilation of bronchioles 5. Changes in blood flow patterns leading to decreased digestive system activity and reduced urine output 6. Increased metabolic ...
... 2. Increased blood pressure Catecholamines 3. Liver converts glycogen to glucose (epinephrine and releases glucose to blood and norepinephrine) 4. Dilation of bronchioles 5. Changes in blood flow patterns leading to decreased digestive system activity and reduced urine output 6. Increased metabolic ...
Endocrine System
... • Insulin level is low because the person’s immune system destroys the pancreatic beta cells that make the insulin • People with this must have daily doses of insulin to prevent death • Develops in people younger than age 20 • If not treated properly can lead to blindness and kidney disease ...
... • Insulin level is low because the person’s immune system destroys the pancreatic beta cells that make the insulin • People with this must have daily doses of insulin to prevent death • Develops in people younger than age 20 • If not treated properly can lead to blindness and kidney disease ...
Unit One – Concept Two - Calgary Christian School
... cortisol – associated with blood glucose levels. An increase in cortisol increases amino acid levels in the blood to relieve stress, amino acids are converted to glucose in the liver, thus raising blood sugar levels aldosterone – increase sodium retention and water reabsorption in kidneys and helps ...
... cortisol – associated with blood glucose levels. An increase in cortisol increases amino acid levels in the blood to relieve stress, amino acids are converted to glucose in the liver, thus raising blood sugar levels aldosterone – increase sodium retention and water reabsorption in kidneys and helps ...
endocrine system - Natural science Tree
... Endocrine system consist of different endocrine glands in the body. Endocrine glands are ductless . And produce and secrete hormones. That are transported through the blood in the blood vessels of the body. Towards a specific target organ where it has a specific function. The target cells only respo ...
... Endocrine system consist of different endocrine glands in the body. Endocrine glands are ductless . And produce and secrete hormones. That are transported through the blood in the blood vessels of the body. Towards a specific target organ where it has a specific function. The target cells only respo ...
Endocrinology - You Can Do It! | Physical Therapy Students
... • The patients also have purple abdominal striae, the look like stretch marks but they are wider and purple in color • Hirsutism: a side effect of the stimulation of ACTH is the stimulation of the androgens production, and that’s why growth of excessive hair happens ...
... • The patients also have purple abdominal striae, the look like stretch marks but they are wider and purple in color • Hirsutism: a side effect of the stimulation of ACTH is the stimulation of the androgens production, and that’s why growth of excessive hair happens ...
SCF Class 2
... These starchy foods and fiber take longer to digest and fill us up. It may or may not be nutrient dense. When we decrease the amount of sugar we eat, the blood glucose becomes balanced, not too high or too low. Consuming too many acids , like alcohol ,which metabolizes into vinegar, vinegar itself a ...
... These starchy foods and fiber take longer to digest and fill us up. It may or may not be nutrient dense. When we decrease the amount of sugar we eat, the blood glucose becomes balanced, not too high or too low. Consuming too many acids , like alcohol ,which metabolizes into vinegar, vinegar itself a ...
Endocrine Review
... Complete the table below about hormones. HINT-‐ some glands secrete more than one hormone. (use glands chart on class webpage) ...
... Complete the table below about hormones. HINT-‐ some glands secrete more than one hormone. (use glands chart on class webpage) ...
Document
... • Also contain beta cells: secrete insulin b. Glucagon and insulin: hormones that regulate blood glucose levels c. Glucose: primary source of energy for nervous system • Blood glucose levels too low: NS does not function properly • Blood glucose levels too high: kidneys produce large quantities of u ...
... • Also contain beta cells: secrete insulin b. Glucagon and insulin: hormones that regulate blood glucose levels c. Glucose: primary source of energy for nervous system • Blood glucose levels too low: NS does not function properly • Blood glucose levels too high: kidneys produce large quantities of u ...
SCF Class 2
... These starchy foods and fiber take longer to digest and fill us up. It may or may not be nutrient dense. When we decrease the amount of sugar we eat, the blood glucose becomes balanced, not too high or too low. Consuming too many acids , like alcohol ,which metabolizes into vinegar, vinegar itself a ...
... These starchy foods and fiber take longer to digest and fill us up. It may or may not be nutrient dense. When we decrease the amount of sugar we eat, the blood glucose becomes balanced, not too high or too low. Consuming too many acids , like alcohol ,which metabolizes into vinegar, vinegar itself a ...
Hormones
... – More liver glycogen utilized – Muscle glucose uptake liver glucose release – As glycogen stores , glucagon levels ...
... – More liver glycogen utilized – Muscle glucose uptake liver glucose release – As glycogen stores , glucagon levels ...
Glucose Regulation in Diabetes
... the immune system destroys the β-cells of the pancreas. As a result, the person’s ability to produce insulin is greatly inhibited. Diagnosis usually occurs in early childhood and is treated with insulin injections. Type II Diabetes (insulin-independent diabetes) is caused by a deficiency of insulin ...
... the immune system destroys the β-cells of the pancreas. As a result, the person’s ability to produce insulin is greatly inhibited. Diagnosis usually occurs in early childhood and is treated with insulin injections. Type II Diabetes (insulin-independent diabetes) is caused by a deficiency of insulin ...
18-1 COMPONENTS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM FIGURE 17.1
... untreated, or poorly treated, Grave's disease. In severe cases, shock, coma, and death can result. Which of the following symptoms would you expect to observe during thyroid storm? High fever Dehydration (resulting from sweating) Tachycardia (above normal heart rate) 2. Iodine deficiency in the diet ...
... untreated, or poorly treated, Grave's disease. In severe cases, shock, coma, and death can result. Which of the following symptoms would you expect to observe during thyroid storm? High fever Dehydration (resulting from sweating) Tachycardia (above normal heart rate) 2. Iodine deficiency in the diet ...
The Endocrine System
... These signs are very useful, but many other signs and symptoms related to endocrine disorders are less definitive. For example, the condition of polyuria, or increased urine production, may be the result of hyposecretion of ADH (diabetes insipidus) or a form of diabetes mellitus, and a symptom such ...
... These signs are very useful, but many other signs and symptoms related to endocrine disorders are less definitive. For example, the condition of polyuria, or increased urine production, may be the result of hyposecretion of ADH (diabetes insipidus) or a form of diabetes mellitus, and a symptom such ...
Endocrine System
... Cause – Decreased secretion of insulin Symptoms – Polyuria, polyphagia, polydipsia, weight loss, blurred vision, and possible diabetic muscles. If not treated, excess glucose in blood (hyperglycemia) and secreted in urine (glycosuria) If too much insulin given, blood sugar can get too low (hypoglyce ...
... Cause – Decreased secretion of insulin Symptoms – Polyuria, polyphagia, polydipsia, weight loss, blurred vision, and possible diabetic muscles. If not treated, excess glucose in blood (hyperglycemia) and secreted in urine (glycosuria) If too much insulin given, blood sugar can get too low (hypoglyce ...
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM STUDY GUIDE
... 10. What is the importance of mineralocorticoids? What is the main hormone in this subcategory? What is the target organ of these hormones? 11. How do the kidneys respond when aldosterone levels rise? What triggers the release of aldosterone to the blood? 12. What is renin and what does it do? 13. W ...
... 10. What is the importance of mineralocorticoids? What is the main hormone in this subcategory? What is the target organ of these hormones? 11. How do the kidneys respond when aldosterone levels rise? What triggers the release of aldosterone to the blood? 12. What is renin and what does it do? 13. W ...
Glycemic index

The glycemic index or glycaemic index (GI) is a number associated with a particular type of food that indicates the food's effect on a person's blood glucose (also called blood sugar) level. A value of 100 represents the standard, an equivalent amount of pure glucose.The GI represents the total rise in a person's blood sugar level following consumption of the food; it may or may not represent the rapidity of the rise in blood sugar. The steepness of the rise can be influenced by a number of other factors, such as the quantity of fat eaten with the food. The GI is useful for understanding how the body breaks down carbohydrates and only takes into account the available carbohydrate (total carbohydrate minus fiber) in a food. Although the food may contain fats and other components that contribute to the total rise in blood sugar, these effects are not reflected in the GI.The glycemic index is usually applied in the context of the quantity of the food and the amount of carbohydrate in the food that is actually consumed. A related measure, the glycemic load (GL), factors this in by multiplying the glycemic index of the food in question by the carbohydrate content of the actual serving. Watermelon has a high glycemic index, but a low glycemic load for the quantity typically consumed. Fructose, by contrast, has a low glycemic index, but can have a high glycemic load if a large quantity is consumed.GI tables are available that list many types of foods and their GIs. Some tables also include the serving size and the glycemic load of the food per serving.A practical limitation of the glycemic index is that it does not measure insulin production due to rises in blood sugar. As a result, two foods could have the same glycemic index, but produce different amounts of insulin. Likewise, two foods could have the same glycemic load, but cause different insulin responses. Furthermore, both the glycemic index and glycemic load measurements are defined by the carbohydrate content of food. For example when eating steak, which has no carbohydrate content but provides a high protein intake, up to 50% of that protein can be converted to glucose when there is little to no carbohydrate consumed with it. But because it contains no carbohydrate itself, steak cannot have a glycemic index. For some food comparisons, the ""insulin index"" may be more useful.