MARK CROUCH D.O. CROUCH CLINIC ANGELICA CLARK, PA
... How to take Thyroid Hormone Replacement Take your thyroid hormone on an empty stomach: 30-60 minutes before a meal or 1-2 hours after a meal. Do not take thyroid hormone within 4 hours of vitamins or minerals (calcium, iron, magnesium). Take your thyroid hormone every day. Do not miss any doses even ...
... How to take Thyroid Hormone Replacement Take your thyroid hormone on an empty stomach: 30-60 minutes before a meal or 1-2 hours after a meal. Do not take thyroid hormone within 4 hours of vitamins or minerals (calcium, iron, magnesium). Take your thyroid hormone every day. Do not miss any doses even ...
The Thyroid Gland
... Biosynthesis of Thyroid Hormones Iodine: - Distribution: the sea - Source: food (and drink), in the form of I-. The international recommended intake of iodine:150 mg/day (1/3 is absorbed in the thyroid) The total iodine in the thyroid: 8-10 mg (90% of the total iodine in body) ...
... Biosynthesis of Thyroid Hormones Iodine: - Distribution: the sea - Source: food (and drink), in the form of I-. The international recommended intake of iodine:150 mg/day (1/3 is absorbed in the thyroid) The total iodine in the thyroid: 8-10 mg (90% of the total iodine in body) ...
The Endocrine System
... major endocrine glands and several other organs, such as the heart and kidneys, that have other important functions. The hormones secreted by these endocrine organs are distributed by the circulatory system to target tissues throughout the body. Each hormone affects a specific set of target tissues ...
... major endocrine glands and several other organs, such as the heart and kidneys, that have other important functions. The hormones secreted by these endocrine organs are distributed by the circulatory system to target tissues throughout the body. Each hormone affects a specific set of target tissues ...
the thyroid gland
... Thyroglobulin Iodination Thyronine Thyroglobulin pinocytosis • Hormone release ...
... Thyroglobulin Iodination Thyronine Thyroglobulin pinocytosis • Hormone release ...
13 lecture
... The endocrine system traditionally consists of seven glands located throughout the body. Three additional structures are also considered endocrine glands, although for the following reasons they are not usually included. The functions of thepineal body (epiphysis cerebri), which is located in the c ...
... The endocrine system traditionally consists of seven glands located throughout the body. Three additional structures are also considered endocrine glands, although for the following reasons they are not usually included. The functions of thepineal body (epiphysis cerebri), which is located in the c ...
Histology Ch 21 755-762 [4-20
... 7. Release of T4 and T3 – majority of T3/4 liberated by lysosomal pathway in a T4:3 ratio of 20:1, and they cross basal membrane and enter blood/lymph capillaries -most hormones immediately bound to thyroxin-binding protein or nonspecific albumin leaving small amounts of unbound circulating hormone ...
... 7. Release of T4 and T3 – majority of T3/4 liberated by lysosomal pathway in a T4:3 ratio of 20:1, and they cross basal membrane and enter blood/lymph capillaries -most hormones immediately bound to thyroxin-binding protein or nonspecific albumin leaving small amounts of unbound circulating hormone ...
Tài liệu PDF
... In the bloodstream, less than one percent of the circulating T3 and T4 remains unbound. This free T3 and T4 can cross the lipid bilayer of cell membranes and be taken up by cells. The remaining 99 percent of circulating T3 and T4 is bound to specialized transport proteins called thyroxine-binding gl ...
... In the bloodstream, less than one percent of the circulating T3 and T4 remains unbound. This free T3 and T4 can cross the lipid bilayer of cell membranes and be taken up by cells. The remaining 99 percent of circulating T3 and T4 is bound to specialized transport proteins called thyroxine-binding gl ...
Hormonal preparations
... by intracellular metabolism of glucose. Therefore derivatives of sulfonilurea imitate signal of increased concentration of sugar in blood. ...
... by intracellular metabolism of glucose. Therefore derivatives of sulfonilurea imitate signal of increased concentration of sugar in blood. ...
What is the Endocrine System
... Catecholamines are a group of similar hormones produced in the adrenal medulla, the interior portion of the adrenal glands. Adrenal glands are small, triangular organs located on top of each kidney. The primary catecholamines are dopamine, epinephrine (adrenaline), and norepinephrine. These hormones ...
... Catecholamines are a group of similar hormones produced in the adrenal medulla, the interior portion of the adrenal glands. Adrenal glands are small, triangular organs located on top of each kidney. The primary catecholamines are dopamine, epinephrine (adrenaline), and norepinephrine. These hormones ...
Document
... gonadotropin-releasing hormone( GnRH), thyrotropin-releasing hormone(TRH),somatostatin, and vasopressin;3)large proteins such as insulin and thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH);4) steroid hormones such as estradiol, testosterone and cortisol, 5)vitamin derivatives such as retinoids(vitamin A) and vita ...
... gonadotropin-releasing hormone( GnRH), thyrotropin-releasing hormone(TRH),somatostatin, and vasopressin;3)large proteins such as insulin and thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH);4) steroid hormones such as estradiol, testosterone and cortisol, 5)vitamin derivatives such as retinoids(vitamin A) and vita ...
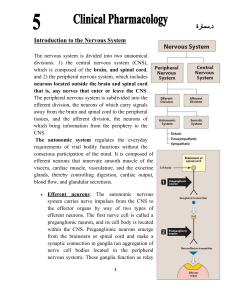
Introduction to the Nervous System
... tissues receive dual innervations, some effector organs, such as the adrenal medulla, kidney, pilomotor muscles, and sweat glands, receive innervations only from the sympathetic system. The control of blood pressure is also mainly a sympathetic activity, with essentially no participation by the para ...
... tissues receive dual innervations, some effector organs, such as the adrenal medulla, kidney, pilomotor muscles, and sweat glands, receive innervations only from the sympathetic system. The control of blood pressure is also mainly a sympathetic activity, with essentially no participation by the para ...
File
... secreted into the circulatory system and communicate regulatory messages within the body. • Hormones reach all parts of the body, but only target cells are equipped to respond. • Insect metamorphosis and many other processes are regulated by hormones. • P.S. – Plants have hormones too ...
... secreted into the circulatory system and communicate regulatory messages within the body. • Hormones reach all parts of the body, but only target cells are equipped to respond. • Insect metamorphosis and many other processes are regulated by hormones. • P.S. – Plants have hormones too ...
Novel cyclic AMP signalling avenues in learning and memory
... showed that AKAP150 is widely distributed throughout the mouse brain. The highest AKAP150 expression levels were observed in striatum, cerebral cortex and several other forebrain regions (e.g. olfactory tubercle), relatively high expression was found in hippocampus and olfactory bulb and low/no expr ...
... showed that AKAP150 is widely distributed throughout the mouse brain. The highest AKAP150 expression levels were observed in striatum, cerebral cortex and several other forebrain regions (e.g. olfactory tubercle), relatively high expression was found in hippocampus and olfactory bulb and low/no expr ...
Endocrine Flashcards
... children) is more serious. It is caused by destruction of pancreatic islets by autoimmune disorders. They must have insulin injections daily throughout life. It is a consequence of obesity. They produce insulin, but their cells are less sensitive to the effects of insulin Diet and exercise Progester ...
... children) is more serious. It is caused by destruction of pancreatic islets by autoimmune disorders. They must have insulin injections daily throughout life. It is a consequence of obesity. They produce insulin, but their cells are less sensitive to the effects of insulin Diet and exercise Progester ...
Effects of thyroid dysfunction and nitric oxide on - biomed
... and nitric oxide on insulin sensitive cells A study revealing that thyroid hormones alone or in combination with insulin modulate NOX levels, expression of IL-6 and activation of NF-KB in insulin sensitive cells in a cell type specific manner. Thyroid Dysfunction The thyroid gland is one of the mo ...
... and nitric oxide on insulin sensitive cells A study revealing that thyroid hormones alone or in combination with insulin modulate NOX levels, expression of IL-6 and activation of NF-KB in insulin sensitive cells in a cell type specific manner. Thyroid Dysfunction The thyroid gland is one of the mo ...
central hypothyroidism: a diagnosis overlooked?
... the TSH molecule and affects glycosylation, which changes the biological activity of TSH. and release. The main hormone secreted by the thyroid is T4 which reaches the peripheral organs and is converted to T3 by deiodinisation. T3 enters the cell nuclei and binds to thyroid hormones receptors α and ...
... the TSH molecule and affects glycosylation, which changes the biological activity of TSH. and release. The main hormone secreted by the thyroid is T4 which reaches the peripheral organs and is converted to T3 by deiodinisation. T3 enters the cell nuclei and binds to thyroid hormones receptors α and ...
Iodination of Tyrosine and Formation of the Thyroid Hormones
... • Glucose absorption from GIT is increased • Glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis & glucose oxidation • lipolysis • protein synthesis & catabolism (overall catabolic effect) ...
... • Glucose absorption from GIT is increased • Glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis & glucose oxidation • lipolysis • protein synthesis & catabolism (overall catabolic effect) ...
Heart-brain communication Veen, Frederik Martin van der
... posterior to the facial nucleus and extending caudally to the first cervical level (C1) of the spinal cord. The DMV lies in the dorsomedial portion of the caudal medulla oblongata close to the floor of the fourth ventricle and it also extends caudally to C1 in the spinal cord. The NA receives affere ...
... posterior to the facial nucleus and extending caudally to the first cervical level (C1) of the spinal cord. The DMV lies in the dorsomedial portion of the caudal medulla oblongata close to the floor of the fourth ventricle and it also extends caudally to C1 in the spinal cord. The NA receives affere ...
Endocrine Glands
... Endocrine Glands Pituitary gland: releases human growth hormone which regulates body growth; releases other hormones that control most of the other endocrine glands; controlled by the brain (hypothalamus) Thyroid gland: releases the hormone thyroxin which regulates the body’s metabolism and activity ...
... Endocrine Glands Pituitary gland: releases human growth hormone which regulates body growth; releases other hormones that control most of the other endocrine glands; controlled by the brain (hypothalamus) Thyroid gland: releases the hormone thyroxin which regulates the body’s metabolism and activity ...
Ch41_Endocrine Function - University of Perpetual Help System
... levels and have an opposite effect. In some cells, binding of hormones or neurotransmitters to surface receptors acts directly rather than through a second messenger to open ion channels in the cell membrane. The influx of ions serves as an intracellular signal to convey the hormonal message to the c ...
... levels and have an opposite effect. In some cells, binding of hormones or neurotransmitters to surface receptors acts directly rather than through a second messenger to open ion channels in the cell membrane. The influx of ions serves as an intracellular signal to convey the hormonal message to the c ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.