Menopause is Not an Estrogen Deficiency Problem
... the inner lining of the uterus that was lost during the menstrual cycle. Progesterone causes the uterine lining and the breast to further develop to prepare for a possible pregnancy. Estrogen and progesterone also effect other organs like the brain, the endocrine system, the immune system, etc. When ...
... the inner lining of the uterus that was lost during the menstrual cycle. Progesterone causes the uterine lining and the breast to further develop to prepare for a possible pregnancy. Estrogen and progesterone also effect other organs like the brain, the endocrine system, the immune system, etc. When ...
1 BIOL 2401 CHAPTER 15: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
... IX. Autonomic Reflexes – play a key role in blood pressure, digestion, defecation & urination. X. Autonomic Control – _________________ is the major control & integration center. Posterior & lateral region control sympathetic division. Anterior & medial control parasympathetic. A. Sensory input – ol ...
... IX. Autonomic Reflexes – play a key role in blood pressure, digestion, defecation & urination. X. Autonomic Control – _________________ is the major control & integration center. Posterior & lateral region control sympathetic division. Anterior & medial control parasympathetic. A. Sensory input – ol ...
Target cells
... The Male Reproductive System – Sperm are produced in the seminiferous tubules of the testes (spermatogenesis) – Sperm are stored in the epidymus, then transported through the vas deferens, and leave the body through the urethra – Seminal fluids (semen) are added to the sperm by the seminal vesicles ...
... The Male Reproductive System – Sperm are produced in the seminiferous tubules of the testes (spermatogenesis) – Sperm are stored in the epidymus, then transported through the vas deferens, and leave the body through the urethra – Seminal fluids (semen) are added to the sperm by the seminal vesicles ...
Menopause Is Not an Estrogen Deficiency Problem
... the inner lining of the uterus that was lost during the menstrual cycle. Progesterone causes the uterine lining and the breast to further develop to prepare for a possible pregnancy. Estrogen and progesterone also effect other organs like the brain, the endocrine system , the immune system, etc. Whe ...
... the inner lining of the uterus that was lost during the menstrual cycle. Progesterone causes the uterine lining and the breast to further develop to prepare for a possible pregnancy. Estrogen and progesterone also effect other organs like the brain, the endocrine system , the immune system, etc. Whe ...
Trigeminal V, Abducent VI, Facial VII and Vestibulocochlear VIII
... middle and oral region of spindle tract of trigeminal nerve V nucleus in Camel is location and cell type is resemble that studying in other animal (10), Cat (5) . 2. Abducent nerve VI nucleus : The location and cells contain this nucleus in Camel is similar in Pig , Rabbit, Dog, Guinea Pig (9), (10) ...
... middle and oral region of spindle tract of trigeminal nerve V nucleus in Camel is location and cell type is resemble that studying in other animal (10), Cat (5) . 2. Abducent nerve VI nucleus : The location and cells contain this nucleus in Camel is similar in Pig , Rabbit, Dog, Guinea Pig (9), (10) ...
Slide 1 - Elsevier Store
... nucleus (DMH). From the DMH arise distinct projections critical for the circadian regulation of the hypothalamicpituitary-adrenal axis, sleep/wake and feeding; the next anatomical site along each of these pathways is indicated. The DMH is also critical for regulation of locomotor activity rhythms, b ...
... nucleus (DMH). From the DMH arise distinct projections critical for the circadian regulation of the hypothalamicpituitary-adrenal axis, sleep/wake and feeding; the next anatomical site along each of these pathways is indicated. The DMH is also critical for regulation of locomotor activity rhythms, b ...
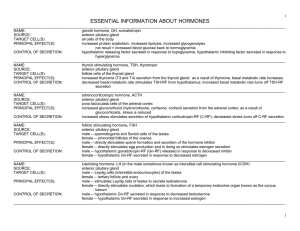
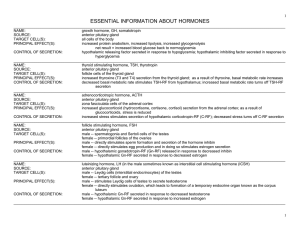
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION ABOUT HORMONES
... parafollicular cells (C cells) of the thyroid gland osteoblasts of bone, kidney tubule cell increased bone formation and ossification; prevent calcium reabsorption by kidneys hypercalcemia (too much calcium in blood) directly stimulates parafollicular cells to secrete CT; when blood falls back into ...
... parafollicular cells (C cells) of the thyroid gland osteoblasts of bone, kidney tubule cell increased bone formation and ossification; prevent calcium reabsorption by kidneys hypercalcemia (too much calcium in blood) directly stimulates parafollicular cells to secrete CT; when blood falls back into ...
Handout 10-Endocrine - People Server at UNCW
... parafollicular cells (C cells) of the thyroid gland osteoblasts of bone, kidney tubule cell increased bone formation and ossification; prevent calcium reabsorption by kidneys hypercalcemia (too much calcium in blood) directly stimulates parafollicular cells to secrete CT; when blood falls back into ...
... parafollicular cells (C cells) of the thyroid gland osteoblasts of bone, kidney tubule cell increased bone formation and ossification; prevent calcium reabsorption by kidneys hypercalcemia (too much calcium in blood) directly stimulates parafollicular cells to secrete CT; when blood falls back into ...
Neuroanatomy - TechnionMed
... b. NOT touch, hearing, sight or taste cell bodies of taste fibers are found in a. geniculate ganglion b. glossopharyngeal ganglion c. vagal/jugular ganglion d. NOT semilunar ganglion ADH and oxytocin are secreted from the hypothalamus by the following nucleus a. Paraventricular and supraoptic b. NOT ...
... b. NOT touch, hearing, sight or taste cell bodies of taste fibers are found in a. geniculate ganglion b. glossopharyngeal ganglion c. vagal/jugular ganglion d. NOT semilunar ganglion ADH and oxytocin are secreted from the hypothalamus by the following nucleus a. Paraventricular and supraoptic b. NOT ...
13 Anterior Pituitary Hormones
... GH release, and SRIF appears to be the primary regulator of GH pulses in response to physiologic stimuli. GHRH stimulates GH synthesis and secretion, whereas SRIF, as well as IGF-1, inhibits GH secretion (Fig. 4). Ghrelin, a recently discovered orexigenic factor, is a potent GH secretagogue produced ...
... GH release, and SRIF appears to be the primary regulator of GH pulses in response to physiologic stimuli. GHRH stimulates GH synthesis and secretion, whereas SRIF, as well as IGF-1, inhibits GH secretion (Fig. 4). Ghrelin, a recently discovered orexigenic factor, is a potent GH secretagogue produced ...
Q1: What happens at the synapse between two neurons? Answer
... 1. Roots move in the direction of gravity (positive +ve getropism) 2. Shoots move (up) against direction of gravity (negative -v geotropism) Q19: Why do mammals like humans need an endocrinal system? or Q: What are the limitations of nervous system in human body? How it is overcome? Answer: Nervous ...
... 1. Roots move in the direction of gravity (positive +ve getropism) 2. Shoots move (up) against direction of gravity (negative -v geotropism) Q19: Why do mammals like humans need an endocrinal system? or Q: What are the limitations of nervous system in human body? How it is overcome? Answer: Nervous ...
Timing of Impulses From the Central Amygdala and Bed Nucleus of
... ment of Health and Human Services). Male Sprague-Dawley rats (225–250 g) were anesthetized with a mixture of ambient air, oxygen, and isoflurane. Atropine (0.05 mg/kg, im) was administered to prevent secretions. The body temperature was maintained at 37–38°C with a heating pad. The level of anesthes ...
... ment of Health and Human Services). Male Sprague-Dawley rats (225–250 g) were anesthetized with a mixture of ambient air, oxygen, and isoflurane. Atropine (0.05 mg/kg, im) was administered to prevent secretions. The body temperature was maintained at 37–38°C with a heating pad. The level of anesthes ...
PREVENTION The Autism-Thyroid Connection
... method of taking body temperature to diagnose hypothyroidism. Unfortunately, this procedure also misses many children with low thyroid, whose body temperature is normal. ...
... method of taking body temperature to diagnose hypothyroidism. Unfortunately, this procedure also misses many children with low thyroid, whose body temperature is normal. ...
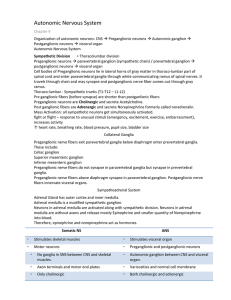
Autonomic Nervous System
... Preganglionic neurons lie in brain nuclei of cranial nerves and sacral part of spinal cord. Cranio-sacral – 3rd, 7th, 9th, 10th cranial nerves and spinal nerve cord through 2nd, 3rd, 4th sacral spinal nerves Pre ganglionic fibers are longer than post ganglionic fibers Preganglionic neurons and Post ...
... Preganglionic neurons lie in brain nuclei of cranial nerves and sacral part of spinal cord. Cranio-sacral – 3rd, 7th, 9th, 10th cranial nerves and spinal nerve cord through 2nd, 3rd, 4th sacral spinal nerves Pre ganglionic fibers are longer than post ganglionic fibers Preganglionic neurons and Post ...
binge eating disorder
... Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a form of therapy that will help you learn to identify the thought patterns that lead to binging episodes. You can do CBT in a group or individually, and your therapist will help you recognize some of the triggers that lead to binges and how to develop new patte ...
... Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a form of therapy that will help you learn to identify the thought patterns that lead to binging episodes. You can do CBT in a group or individually, and your therapist will help you recognize some of the triggers that lead to binges and how to develop new patte ...
1. dia
... physiological functions from food intake, metabolic rate and body composition to thermoregulation and neuronal functions. There is an age-associated reductions in sex steroids in both genders. • In females, this reduction is rapid leading to menopause and infertility between the ages of 45-55 years ...
... physiological functions from food intake, metabolic rate and body composition to thermoregulation and neuronal functions. There is an age-associated reductions in sex steroids in both genders. • In females, this reduction is rapid leading to menopause and infertility between the ages of 45-55 years ...
Pituitary gland and Its Functions Effects of Narcotic Drugs
... cells and do not secrete any hormone. •The unmyelinated nerve fibres come from supra optic and paraventricular nuclei of hypothalamus through pituitary stalk. •Neuohypophysis does not secrete any hormone but stores and releases hormones secreted by neurosecretory cells hypothalamus. ...
... cells and do not secrete any hormone. •The unmyelinated nerve fibres come from supra optic and paraventricular nuclei of hypothalamus through pituitary stalk. •Neuohypophysis does not secrete any hormone but stores and releases hormones secreted by neurosecretory cells hypothalamus. ...
Chapter Four: The Biological Mind - The Physical Basis of Behavior
... d. Daniel, age 35, is considered highly intelligent amongst his peers. 26. Neuronal communication is a two-step process. In the second step, which takes place between two neurons, what does the arrival of an action potential at the axon terminal of the first neuron signal? a. The synthesis of neurot ...
... d. Daniel, age 35, is considered highly intelligent amongst his peers. 26. Neuronal communication is a two-step process. In the second step, which takes place between two neurons, what does the arrival of an action potential at the axon terminal of the first neuron signal? a. The synthesis of neurot ...
Adventure Brochure of the Endocrine System You have been hired
... 2. Describe the endocrine glands and the hormones each secretes. 3. Compare endocrine and exocrine glands. 4. Explain the difference between steroid hormones and nonsteroid hormones. 5. Explain how the endocrine system maintains homeostasis. 6. Identify the functions of the major endocrine glands: p ...
... 2. Describe the endocrine glands and the hormones each secretes. 3. Compare endocrine and exocrine glands. 4. Explain the difference between steroid hormones and nonsteroid hormones. 5. Explain how the endocrine system maintains homeostasis. 6. Identify the functions of the major endocrine glands: p ...
Mary`s Aching Head – Final Report
... which is a very common result from pituitary tumors. Mary portrays blindness in her lateral visual fields. An expanding mass on the pituitary is strong evidence for her re-occurring headaches in which they tend to be worse when first awakened (Willacy and Tidy 2010). Dilation of the left pupil is a ...
... which is a very common result from pituitary tumors. Mary portrays blindness in her lateral visual fields. An expanding mass on the pituitary is strong evidence for her re-occurring headaches in which they tend to be worse when first awakened (Willacy and Tidy 2010). Dilation of the left pupil is a ...
Chapter 10 - Hormonal and Reproductive Drugs
... messengers called hormones into the blood – Hormones are chemical substances produced by cells in one part of the body and transported to another part of the body where they influence cellular activity ...
... messengers called hormones into the blood – Hormones are chemical substances produced by cells in one part of the body and transported to another part of the body where they influence cellular activity ...
Chapter 12 PowerPoint - Hillsborough Community College
... Lateral hypothalamic area Ventromedial nucleus ...
... Lateral hypothalamic area Ventromedial nucleus ...
Growth Hormones - Magellan Health Services || TennCare Portal
... Has the infant exhibited signs of hypoglycemia? Indicate recorded GH level: Yes Has a growth hormone level been obtained for recipient? Has an IGF-1 / IGF Binding Protein #3 level been obtained for the recipient? If yes, was the level low for the patient’s age? ...
... Has the infant exhibited signs of hypoglycemia? Indicate recorded GH level: Yes Has a growth hormone level been obtained for recipient? Has an IGF-1 / IGF Binding Protein #3 level been obtained for the recipient? If yes, was the level low for the patient’s age? ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.