* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Endocrine Glands
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
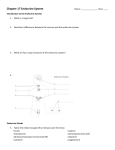
Endocrine Glands Pituitary gland: releases human growth hormone which regulates body growth; releases other hormones that control most of the other endocrine glands; controlled by the brain (hypothalamus) Thyroid gland: releases the hormone thyroxin which regulates the body’s metabolism and activity level (how fast it breaks down food for energy); requires the element iodine to make thyroxin Thymus: releases hormones that help the body’s immune system (fight infection) Ovaries: release the hormone estrogen which control puberty in females (breast development, hips widening, etc.) and causes the release of eggs from the ovaries; also produces progesterone which helps with the release of eggs from ovaries Pancreas: releases the hormones insulin and glucagon; insulin controls the removal of glucose from the blood, and glucagon controls the increase of glucose in the blood Adrenal glands: produce the hormone adrenaline (epinephrine) which allows the body to respond to emergency/dangerous situations (increased heart rate, more air-flow, and brief bursts of energy in muscles) Parathyroid glands: produce a hormone that regulates the amount of calcium in the blood; too much or too little calcium disrupts the functions of nerves and muscles Testes: release the hormone testosterone which controls puberty in boys (facial and body hair, deepening voice, etc.) and causes sperm production to begin Hormones Human Growth Hormone: controls the growth rate of human bodies; produced by the pituitary Thyroxin: controls the metabolic rate of humans; helps maintain internal body temperatures; requires iodine to be produced by the thyroid gland; also found in small quantities in males Estrogen: sex hormone that controls puberty in females (breast development, hips widening, etc.) and causes the release of eggs from the ovaries Progesterone: female sex hormone that works together with estrogen to cause the release of eggs from the ovaries Insulin: hormone produced by the pancreas which reduces the amount of glucose (blood sugar) in the blood after a meal Glucagon: hormone produce by the pancreas which increases the amount of glucose (blood sugar) in the blood when you have gone without eating for a while Adrenaline (Epinephrine): hormone produced by the adrenal glands which allows the body to respond to emergency situations (increased heart rate, more air-flow, and brief bursts of energy in muscles Testosterone: sex hormone which controls puberty in boys (facial and body hair, deepening voice, etc.) and causes sperm production to begin; also found in small quantities in females; contributes to aggressive behavior Endocrine Gland Locations Station #1 1. This female did not have enough iodine in her diet, which caused a growth in this woman’s neck is called a goiter. What endocrine gland is responsible for creating a goiter? Explain why this is the correct answer. Station #2 2. This person has a condition called dwarfism. What hormonal problem can cause this condition? Explain why this is the correct answer. Station #3 3. Nadya Suleman (a.k.a. The Octomom) underwent fertility treatments in which she received injections of a hormone that caused her to ovulate (release) multiple eggs at one time. What hormone was in the fertility injections? Explain why this is the correct answer. Station # 4 This lady grew to be 7 feet, 7 inches because of a tumor that developed in one of her endocrine glands. In which endocrine gland was the tumor located? Explain why this is the correct answer. Station # 5 The woman above recorded a blood sugar (glucose) level of 400 (this is very high)! Based on this information, what organ in the endocrine system is not functioning properly? Explain why this is the correct answer. Station # 6 The skydivers in the picture love to participate in dangerous activities (like skydiving, bungee jumping, mountain biking, white water rafting, etc.) because it triggers the “stress response” and they feed off of the “rush” they get when doing the activity. What hormone is being released that gives them this feeling? Explain why this is the correct answer. Station #7 Addie Jones Elliot is a woman who had a visible beard and had a long career in the circus. What hormone is being overproduced in her body that could be responsible for the hair growth on Addie’s face? Explain why this is the correct answer. Station #8 Gynecomastia is breast development that occurs in males. This condition causes men to abnormally develop breasts. Some males choose to live with the disorder; however there are some that opt for surgery. What hormone could be responsible for this abnormal development? Explain why this is the correct answer. Station #9 Hypoglycemia is a condition in which a person has very low levels of glucose in the blood (blood sugar) after they skip a meal. Those who suffer from this condition need to eat every few hours to maintain correct glucose levels. What hormone is not working in people who have hypoglycemia? Explain why this is the correct answer. Station #10 Neutering is a process in which a veterinarian will remove one of the endocrine glands from male dogs/other pets. When male dogs are neutered it lowers their aggression level. Which endocrine gland is removed when a dog is neutered? Explain why this is the correct answer. Station #11 This man has a condition in which one of his endocrine glands is overactive, resulting in high levels of calcium in the blood and urine. High levels of calcium can cause muscle, joint, and bone pain/aches/weakness (especially in the legs). Which endocrine gland is overactive? Explain why this is the correct answer. Station #12 This little boy has SCID, often referred to as “bubble boy disease.” Throughout his young life he has already had to deal with the onset of one or more serious infections that is often life threatening. He is extremely vulnerable to infectious disease and has to remain in a sterile environment at all times. What endocrine gland is not functioning correctly? Explain why this is the correct answer. Name________________________________________ Period____ Teacher_____________________ Endocrine System Gallery Walk In this activity you will be presented with 12 situations in which there is a problem or issue with the endocrine system of a living organism. It is your job as an endocrinologist (a doctor specialized in the endocrine system and hormones) to diagnose the problem and explain why your diagnosis is correct at each station. ____________________________________________________________________________________ Station #1 Answer: Explain: ____________________________________________________________________________________ Station #2 Answer: Explain: ____________________________________________________________________________________ Station #3 Answer: Explain: ____________________________________________________________________________________ Station #4 Answer: Explain: ____________________________________________________________________________________ Station #5 Answer: Explain: ____________________________________________________________________________________ Station #6 Answer: Explain: ____________________________________________________________________________________ Station #7 Answer: Explain: ____________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ Station #8 Answer: Explain: ____________________________________________________________________________________ Station #9 Answer: Explain: ____________________________________________________________________________________ Station #10 Answer: Explain: ____________________________________________________________________________________ Station #11 Answer: Explain: ____________________________________________________________________________________ Station #12 Answer: Explain: ____________________________________________________________________________________ Analysis Questions 1. How are the nervous and endocrine systems connected? 2. How does the endocrine system affect the reproductive system? 3. What are some changes in the human body that are controlled by the endocrine system? 4. How do hormones get from one part of the body to the other?