chapter 15 endocrine system - I
... The major function of the reproductive system is to produce offspring for the survival of the species. The reproductive system operates interdependently along with the endocrine system. As previously specified, hormones are chemicals that regulate processes throughout the body and are produced by th ...
... The major function of the reproductive system is to produce offspring for the survival of the species. The reproductive system operates interdependently along with the endocrine system. As previously specified, hormones are chemicals that regulate processes throughout the body and are produced by th ...
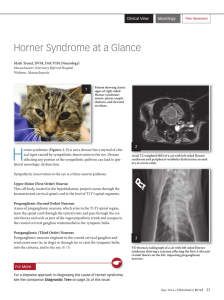
Horner Syndrome at a Glance
... Sympathetic innervation to the eye is a three-neuron pathway: Upper Motor (First Order) Neuron This cell body, located in the hypothalamus, projects axons through the brainstem and cervical spinal cord to the level of T1-T3 spinal segments. Preganglionic (Second Order) Neurons Axons of preganglionic ...
... Sympathetic innervation to the eye is a three-neuron pathway: Upper Motor (First Order) Neuron This cell body, located in the hypothalamus, projects axons through the brainstem and cervical spinal cord to the level of T1-T3 spinal segments. Preganglionic (Second Order) Neurons Axons of preganglionic ...
Document
... 1. Magnetic field causes usually random spin of hydrogen nuclei in water of cells to orient in single direction. Pulses of radio waves jar the hydrogen nuclei which emit faint radio frequency signals when they rebound that depend upon the density of the tissue. The computer constructs images based o ...
... 1. Magnetic field causes usually random spin of hydrogen nuclei in water of cells to orient in single direction. Pulses of radio waves jar the hydrogen nuclei which emit faint radio frequency signals when they rebound that depend upon the density of the tissue. The computer constructs images based o ...
Melannocortin/ Regulation of body weight
... because they consume fewer calories than female syn-3-/- mice in relation to their wild-type counterparts. In contrast, female syn-3-/- mice are resistant to DIO because they show a disproportionate increase in energy expenditure compared to male syn-3-/- and their wild type counterparts. The intere ...
... because they consume fewer calories than female syn-3-/- mice in relation to their wild-type counterparts. In contrast, female syn-3-/- mice are resistant to DIO because they show a disproportionate increase in energy expenditure compared to male syn-3-/- and their wild type counterparts. The intere ...
Hormones - Castle High School
... type of target cells. The receptors are essential because without them the circulating hormones are unable to have the desired effect. Hormones may also be modified during development, with different effects at different stages. ...
... type of target cells. The receptors are essential because without them the circulating hormones are unable to have the desired effect. Hormones may also be modified during development, with different effects at different stages. ...
Hormones - Humble ISD
... type of target cells. The receptors are essential because without them the circulating hormones are unable to have the desired effect. Hormones may also be modified during development, with different effects at different stages. ...
... type of target cells. The receptors are essential because without them the circulating hormones are unable to have the desired effect. Hormones may also be modified during development, with different effects at different stages. ...
File
... steroids. Marathon runners need improved oxygen delivery systems, but not increased muscle mass, which is what growth hormone and anabolic steroids deliver. ...
... steroids. Marathon runners need improved oxygen delivery systems, but not increased muscle mass, which is what growth hormone and anabolic steroids deliver. ...
Endocrine System
... •The bulk of hormone is cleared by the liver and kidneys •Only a small fraction is removed by target tissue – Steroid (and thyroid hormones) are degraded after hormonereceptor complex binds to DNA • action and elimination are slower (hours-days) – protein and amine hormones (non steroids) bind to re ...
... •The bulk of hormone is cleared by the liver and kidneys •Only a small fraction is removed by target tissue – Steroid (and thyroid hormones) are degraded after hormonereceptor complex binds to DNA • action and elimination are slower (hours-days) – protein and amine hormones (non steroids) bind to re ...
Endocrinology Features of Endocrine system:
... • How? By regulating sugar, electrolyte balance in the body fluids such as blood, extra cellular fluid ...
... • How? By regulating sugar, electrolyte balance in the body fluids such as blood, extra cellular fluid ...
AP Biology Notes Outline Chapter 45: Hormones and the Endocrine
... The posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis) stores and secretes two hormones that are made by certain neurosecretory cells located in the hypothalamus. Posterior Pituitary Hormones: The two hormones released from the posterior pituitary act directly on nonendocrine tissues o Oxytocin - induces uteri ...
... The posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis) stores and secretes two hormones that are made by certain neurosecretory cells located in the hypothalamus. Posterior Pituitary Hormones: The two hormones released from the posterior pituitary act directly on nonendocrine tissues o Oxytocin - induces uteri ...
There are two types of glands: Endocrine Glands Hormones
... Glucose in the urine (glycosuria) caused by excretion of glucose by the kidneys as the blood glucose level rises above renal threshold (160mg/100mL of blood) Production of large volumes of urine (diuresis) in order to excrete the glucose results in dehydration and excessive thirst. (This symptom is ...
... Glucose in the urine (glycosuria) caused by excretion of glucose by the kidneys as the blood glucose level rises above renal threshold (160mg/100mL of blood) Production of large volumes of urine (diuresis) in order to excrete the glucose results in dehydration and excessive thirst. (This symptom is ...
MCB 163: Mammalian Neuroanatomy
... 9. LATERAL CORTICOSPINAL TRACT: Upper motoneurons that project the length of the spinal cord to α motoneurons and which are responsible for rapid and precise muscle contractions and powerful movements, especially of the distal extremities; often damage by stroke, these neurons arise from motor and s ...
... 9. LATERAL CORTICOSPINAL TRACT: Upper motoneurons that project the length of the spinal cord to α motoneurons and which are responsible for rapid and precise muscle contractions and powerful movements, especially of the distal extremities; often damage by stroke, these neurons arise from motor and s ...
Endocrine and Special Senses practice Questions Scioly 2016
... A) decreased resistance to disease and infection. B) increased ability to produce glucose from glycogen. C) increased pumping effectiveness of the heart. D) increased protein synthesis. E) both A and C ...
... A) decreased resistance to disease and infection. B) increased ability to produce glucose from glycogen. C) increased pumping effectiveness of the heart. D) increased protein synthesis. E) both A and C ...
Pituitary and Hypothalamus Disorders MBBS III Seminar
... that control the secretion of hormones by other glands. Example: TSH stimulates the thyroid to secrete hormones. • Effector hormones: produce an ...
... that control the secretion of hormones by other glands. Example: TSH stimulates the thyroid to secrete hormones. • Effector hormones: produce an ...
the biology of brain and glandular system in the
... The matrix presentation of the glandular system shows the discussions made by Cornista and Lupato (2000) with is presented in the textual form on the topic “ The Glandular System’”in their book General Psychology with Drug Education. The general emphasis about the presentation of the glandular syste ...
... The matrix presentation of the glandular system shows the discussions made by Cornista and Lupato (2000) with is presented in the textual form on the topic “ The Glandular System’”in their book General Psychology with Drug Education. The general emphasis about the presentation of the glandular syste ...
Thyroid-Adrenal Fatigue Syndrome!
... response to stimulation by the sympathetic nervous system. The first phase of the “flight or fight” response you have to stress or a threat to your life. The outer most layer is the cortex, which secretes hormones, can not only direct the production of energy your cells make, but also makes about 30 ...
... response to stimulation by the sympathetic nervous system. The first phase of the “flight or fight” response you have to stress or a threat to your life. The outer most layer is the cortex, which secretes hormones, can not only direct the production of energy your cells make, but also makes about 30 ...
Introduction to the Endocrine System
... 2. What are the ‘organs’ of the endocrine system and what do they make? ...
... 2. What are the ‘organs’ of the endocrine system and what do they make? ...
Thyroid, pituitary.and adrenal glands.etc
... • All hormones exert their effect at low blood concentrations • Receptors on or within target tissues are needed for all hormones to exert an effect • Most hormones (except for thyroid and adrenal medullary hormones) are not stored to any great extent and must be produced as needed • Hormones in the ...
... • All hormones exert their effect at low blood concentrations • Receptors on or within target tissues are needed for all hormones to exert an effect • Most hormones (except for thyroid and adrenal medullary hormones) are not stored to any great extent and must be produced as needed • Hormones in the ...
Endocrine System - UNT's College of Education
... these clips you will see various types of endocrine disorders. • If you are interested in viewing more endocrine system oddities, you can read the book Freak Show: Presenting Human Oddities for Amusement and Profit by ...
... these clips you will see various types of endocrine disorders. • If you are interested in viewing more endocrine system oddities, you can read the book Freak Show: Presenting Human Oddities for Amusement and Profit by ...
Chapter 11 The Endocrine System
... in which mineralization of bone matrix is deficient, causing the bones to be soft and easily fractured. A major cause of rickets and osteomalacia is deficiency of vitamin D. • Osteoporosis (an imbalance between bone resorption and bone formation) resulting in decreases in bone mass and strength lead ...
... in which mineralization of bone matrix is deficient, causing the bones to be soft and easily fractured. A major cause of rickets and osteomalacia is deficiency of vitamin D. • Osteoporosis (an imbalance between bone resorption and bone formation) resulting in decreases in bone mass and strength lead ...
endocrine system
... Some important glands…. • Hypothalamus – secretes hormones which then influence the pituitary gland to secrete corresponding hormones (see stress response) • The pituitary gland ‘ the pea sized governor’ or ‘master gland’ secretes hormones into the body maintaining homeostasis – this steady state ...
... Some important glands…. • Hypothalamus – secretes hormones which then influence the pituitary gland to secrete corresponding hormones (see stress response) • The pituitary gland ‘ the pea sized governor’ or ‘master gland’ secretes hormones into the body maintaining homeostasis – this steady state ...
File - Dr. Jerry Cronin
... protein hormones (and others with an amine group), and a group of local hormones derived from the arachidonic acid on our cell membranes called eicosanoids – Peptide hormones and protein hormones are ...
... protein hormones (and others with an amine group), and a group of local hormones derived from the arachidonic acid on our cell membranes called eicosanoids – Peptide hormones and protein hormones are ...
SAP 1 – Students will analyze anatomical structures in
... • they can be separated into 2 regions: the adrenal cortex (outer portion) and the adrenal ...
... • they can be separated into 2 regions: the adrenal cortex (outer portion) and the adrenal ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.