Beloranib_New Obesity Drug on the Horizon
... conditions: Prader-Willi syndrome, acquired Prader-Willi syndrome (resulting from treatment of benign tumors in the middle of the brain), and severe obesity complicated by type 2 diabetes. In clinical trials, beloranib has been shown to burn fat, reduce levels of low density lipoprotein (LDL) choles ...
... conditions: Prader-Willi syndrome, acquired Prader-Willi syndrome (resulting from treatment of benign tumors in the middle of the brain), and severe obesity complicated by type 2 diabetes. In clinical trials, beloranib has been shown to burn fat, reduce levels of low density lipoprotein (LDL) choles ...
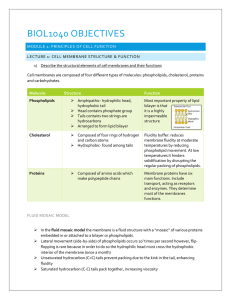
BIOL1040 OBJECTIVES
... Stress is the stimulus and is detected by the hypothalamus which sends nervous impulse via spinal cord to the adrenal medulla. The release of catecholamines (adrenaline and noradrenaline) acts on alphaadrenoreceptors and beta-adrenoreceptors in target tissues. Adrenaline that binds to beta-receptors ...
... Stress is the stimulus and is detected by the hypothalamus which sends nervous impulse via spinal cord to the adrenal medulla. The release of catecholamines (adrenaline and noradrenaline) acts on alphaadrenoreceptors and beta-adrenoreceptors in target tissues. Adrenaline that binds to beta-receptors ...
Recombinant Human Thyroid Stimulating Hormone
... TSH stimulates the thyroid gland to secrete the hormones thyroxine(T4) and triiodothyronine(T3). TSH production is controlled by a Thyrotropin Releasing Hormone, (TRH), which is manufactured in the hypothalamus and transported to the Anterior Pituitary gland, where it increases TSH production and re ...
... TSH stimulates the thyroid gland to secrete the hormones thyroxine(T4) and triiodothyronine(T3). TSH production is controlled by a Thyrotropin Releasing Hormone, (TRH), which is manufactured in the hypothalamus and transported to the Anterior Pituitary gland, where it increases TSH production and re ...
RIKEN CDB labs plan to study human ES cells
... Laboratory for Organogenesis and Neurogenesis, in which the generated self-organizing pituitary tissue in vitro from mouse ESCs, using a 3D floating cell culture method called SFEBq which was developed by the same lab (*Science News: Nov. 14, 2011). The pituitary primordium, also known as Rathke’s p ...
... Laboratory for Organogenesis and Neurogenesis, in which the generated self-organizing pituitary tissue in vitro from mouse ESCs, using a 3D floating cell culture method called SFEBq which was developed by the same lab (*Science News: Nov. 14, 2011). The pituitary primordium, also known as Rathke’s p ...
Structure-Function I
... layer 4, input from thalamus layer 5,output brainstem/spinal cord layer 6 output to thalamus ...
... layer 4, input from thalamus layer 5,output brainstem/spinal cord layer 6 output to thalamus ...
File
... words "endo" meaning inside, within, and "crinis" for secrete. • The endocrine system is an information signal system like the nervous system, yet its effects and mechanism are classifiably different. ...
... words "endo" meaning inside, within, and "crinis" for secrete. • The endocrine system is an information signal system like the nervous system, yet its effects and mechanism are classifiably different. ...
pharmacy technician chapter twenty nine
... Macrophages are cells that engulf and “swallow” invader cell, bacteria and particles Neutrophils are cells that destroy invaders by engulfing these invaders and destroying them by reactive chemical contain oxygen radicals. Sometimes this process causes the rapture of the cell and ...
... Macrophages are cells that engulf and “swallow” invader cell, bacteria and particles Neutrophils are cells that destroy invaders by engulfing these invaders and destroying them by reactive chemical contain oxygen radicals. Sometimes this process causes the rapture of the cell and ...
L10-Internal_Structures_of_Brainstem-20132014-08
... Its red coloration is due to its vascularity and the presence of an iron containing pigment in the cytoplasm of its neurons. It is involved in motor control. ...
... Its red coloration is due to its vascularity and the presence of an iron containing pigment in the cytoplasm of its neurons. It is involved in motor control. ...
Endocrine System - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... Made of amino acids or proteins Cannot cross the cell membrane with ease Binds to receptors on the surface of the cells G-protein is usually activated by the hormone-receptor complex. ...
... Made of amino acids or proteins Cannot cross the cell membrane with ease Binds to receptors on the surface of the cells G-protein is usually activated by the hormone-receptor complex. ...
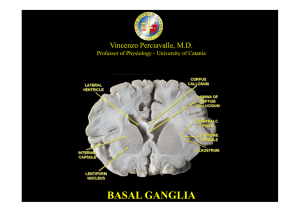
basal ganglia
... into two parts: the pars reticulata (SNpr) and pars compacta (SNpc). The SNpr bears a strong structural and functional resemblance to the internal part of the globus pallidus. The two are sometimes considered parts of the same structure, separated by the white matter of the internal capsule. Like th ...
... into two parts: the pars reticulata (SNpr) and pars compacta (SNpc). The SNpr bears a strong structural and functional resemblance to the internal part of the globus pallidus. The two are sometimes considered parts of the same structure, separated by the white matter of the internal capsule. Like th ...
Endocrine System
... that signals a response • They are secreted in blood stream and go to certain tissues called target tissue/cell • Target cell (tissue)— cell that can only can be signaled by a certain hormone – They get to the tissue by traveling thru blood ...
... that signals a response • They are secreted in blood stream and go to certain tissues called target tissue/cell • Target cell (tissue)— cell that can only can be signaled by a certain hormone – They get to the tissue by traveling thru blood ...
The Endocrine System - Austin Community College
... • Osmoreceptors monitor the solute concentration of the blood • With high solutes, ADH is synthesized and released, thus preserving water • With low solutes, ADH is not released, thus causing water loss from the body • Alcohol inhibits ADH release and causes copious urine output Thyroid Gland • The ...
... • Osmoreceptors monitor the solute concentration of the blood • With high solutes, ADH is synthesized and released, thus preserving water • With low solutes, ADH is not released, thus causing water loss from the body • Alcohol inhibits ADH release and causes copious urine output Thyroid Gland • The ...
(T2877) - Product Information Sheet - Sigma
... The two most important thyroid hormones consist of thyroxine (T4) and 3,3′,5-triiodo-L-thyronine (T3). These compounds contain iodine bound to one or more carbons in the complex ring backbone structure of the hormones. During metabolism, T4 is converted to T3 via removal of an iodine atom from one o ...
... The two most important thyroid hormones consist of thyroxine (T4) and 3,3′,5-triiodo-L-thyronine (T3). These compounds contain iodine bound to one or more carbons in the complex ring backbone structure of the hormones. During metabolism, T4 is converted to T3 via removal of an iodine atom from one o ...
Summary - Union High School
... that release secretions into the bloodstream. The secretions are called hormones. Hormones are chemicals released in one part of the body that travel throughout the body and affect cells elsewhere. Hormones bind to specific chemical receptors on cells called target cells. A gland is an organ that pr ...
... that release secretions into the bloodstream. The secretions are called hormones. Hormones are chemicals released in one part of the body that travel throughout the body and affect cells elsewhere. Hormones bind to specific chemical receptors on cells called target cells. A gland is an organ that pr ...
Endocrine Toxicology
... -- anti-estrogenic action can lead to defeminization through suppression of estrogen levels and normal physiological effects of estrogens -- anti-androgenic action can lead to demasculization through suppression of androgen levels and normal physiological effects of androgens H. Critical periods of ...
... -- anti-estrogenic action can lead to defeminization through suppression of estrogen levels and normal physiological effects of estrogens -- anti-androgenic action can lead to demasculization through suppression of androgen levels and normal physiological effects of androgens H. Critical periods of ...
The Cerebellum
... Function: play an important role in control of muscle tone and coordination of muscle movement on the same side of the body ...
... Function: play an important role in control of muscle tone and coordination of muscle movement on the same side of the body ...
Endocrine_System
... and adrenal glands in females – Males produce 10 times more than females • Primary hormone that interacts with skeletal muscle tissue ...
... and adrenal glands in females – Males produce 10 times more than females • Primary hormone that interacts with skeletal muscle tissue ...
Chapter 2
... either to Broca’s area (impairing speaking) or to Wernicke’s area (impairing understanding). The brain’s capacity for modification; as evident in brain reorganization following damage and in experiments on the effects of experience on brain development. A condition in which the two hemispheres of th ...
... either to Broca’s area (impairing speaking) or to Wernicke’s area (impairing understanding). The brain’s capacity for modification; as evident in brain reorganization following damage and in experiments on the effects of experience on brain development. A condition in which the two hemispheres of th ...
Endocrine System Guide
... Thyroid Gland • ____________________gland • Located in the neck just below the ________________________________________ Thyroid Hormone – ____________________ – Produced by the thyroid which ________________________________________ – ________________________________________ The ability of cells to _ ...
... Thyroid Gland • ____________________gland • Located in the neck just below the ________________________________________ Thyroid Hormone – ____________________ – Produced by the thyroid which ________________________________________ – ________________________________________ The ability of cells to _ ...
Chapter02-edited - Marie-Murphy-WIN13
... • Comprised of ductless glands that release hormones into the bloodstream • Hormones – Regulate growth, metabolism and some behaviors – Maintain steady bodily states ...
... • Comprised of ductless glands that release hormones into the bloodstream • Hormones – Regulate growth, metabolism and some behaviors – Maintain steady bodily states ...
Power Point CH 20
... Organs of the Endocrine System Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Hypothalamus Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) Oxytocin (OT) Regulatory hormones Pituitary gland Anterior pituitary secretes: Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) Follicle-stimulating ...
... Organs of the Endocrine System Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Hypothalamus Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) Oxytocin (OT) Regulatory hormones Pituitary gland Anterior pituitary secretes: Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) Follicle-stimulating ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.