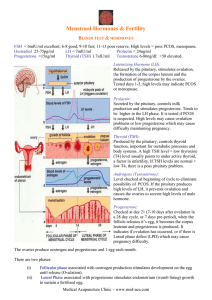
8Aldosterone 8Na + secretion 8 H 2 O reabsorption9 urine volume
... • 5. Define and use the correct terminology associated with the endocrine system. ...
... • 5. Define and use the correct terminology associated with the endocrine system. ...
Thyroid replacement hormone (levothyroxine sodium)
... – If body does not have receptor, hormone will pass by. – Only certain hormones can _______ to receptors and when it occurs, then it changes the activity of the cell. ...
... – If body does not have receptor, hormone will pass by. – Only certain hormones can _______ to receptors and when it occurs, then it changes the activity of the cell. ...
w3.lphs.org
... A general hormonal response to stress would be 1. An increase in epinephrine 2. A decrease in cortisol 3. A decrease in glucagon 4. An increase in FSH ...
... A general hormonal response to stress would be 1. An increase in epinephrine 2. A decrease in cortisol 3. A decrease in glucagon 4. An increase in FSH ...
Hormonal Imbalance In Men And Women
... They are powerful substances secreted into the bloodstream from these glands. But only the cells that use the hormone will respond. The pineal gland helps regulate sleep and the pituitary gland regulates growth. The other glands included in the system are the thyroid, pituitary, thymus, parathyroid, ...
... They are powerful substances secreted into the bloodstream from these glands. But only the cells that use the hormone will respond. The pineal gland helps regulate sleep and the pituitary gland regulates growth. The other glands included in the system are the thyroid, pituitary, thymus, parathyroid, ...
138 Hormones and the Body
... The anterior pituitary, which is a separate organ from the posterior pituitary, synthesizes and secretes hormones based on hormonal signals from the hypothalamus. Hormones secreted from the anterior pituitary include growth hormone (GH), thyroidstimulating hormone (TSH), folliclestimulating hormon ...
... The anterior pituitary, which is a separate organ from the posterior pituitary, synthesizes and secretes hormones based on hormonal signals from the hypothalamus. Hormones secreted from the anterior pituitary include growth hormone (GH), thyroidstimulating hormone (TSH), folliclestimulating hormon ...
Anti-Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone (GnRH) antibody produced
... system.1 The frequency and amplitude of GnRH pulses determine secretion of follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) from the pituitary. Higher frequencies (greater than one pulse per hour) stimulate LH secretion, while lower frequencies stimulate FSH secretion. The generation ...
... system.1 The frequency and amplitude of GnRH pulses determine secretion of follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) from the pituitary. Higher frequencies (greater than one pulse per hour) stimulate LH secretion, while lower frequencies stimulate FSH secretion. The generation ...
Glands, hormones and disorders
... Promotes muscle and skeletal development in both males and females, including the development of secondary sexual characteristics. Prepares the body for the fight or flight response including increased heart rate, blood pressure, vasodilation. It stimulates the liver to convert glycogen into glucose ...
... Promotes muscle and skeletal development in both males and females, including the development of secondary sexual characteristics. Prepares the body for the fight or flight response including increased heart rate, blood pressure, vasodilation. It stimulates the liver to convert glycogen into glucose ...
15 Role of endocrine glands in regulation of body functions
... islets, lowers blood glucose level. ...
... islets, lowers blood glucose level. ...
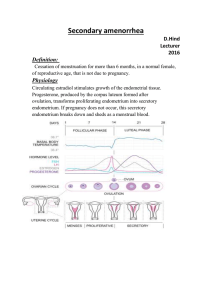
The ovaries produce oestrogen and progesterone and 1 egg each
... increases oestrogen, If deficient, some of the causes include long-term stress, and poor nutrition. Stress causes glucocorticoids (steroid) levels in blood to rise, this activates the hypothalamus to secrete corticotrophin-releasing hormone (CRH), which causes the pituitary gland to release adrinoco ...
... increases oestrogen, If deficient, some of the causes include long-term stress, and poor nutrition. Stress causes glucocorticoids (steroid) levels in blood to rise, this activates the hypothalamus to secrete corticotrophin-releasing hormone (CRH), which causes the pituitary gland to release adrinoco ...
29.6 The Endocrine System and Hormones
... • Cell division • Cell death • Sexual development • Body temperature • Alertness • Salt levels… ...
... • Cell division • Cell death • Sexual development • Body temperature • Alertness • Salt levels… ...
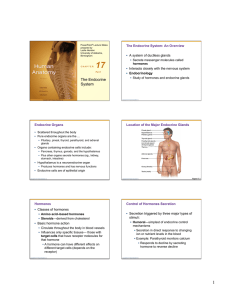
The Endocrine System
... (hypothalamohypophyseal portal system) • From the secondary capillary plexus, hormones secreted by the anterior lobe enter general circulation and travel to target organs ...
... (hypothalamohypophyseal portal system) • From the secondary capillary plexus, hormones secreted by the anterior lobe enter general circulation and travel to target organs ...
Pituitary Gland Hormones
... Gland Source: Adenohypophysis Target: prim. target is the mammary glands (breasts) Action: stim. Mammary glands to produce milk in females; in males, it enhances the effects of ICSH (LH) Stimulus for release: PRF from hypothalamus, also when already breastfeeding, the infant sucking on the nipple wi ...
... Gland Source: Adenohypophysis Target: prim. target is the mammary glands (breasts) Action: stim. Mammary glands to produce milk in females; in males, it enhances the effects of ICSH (LH) Stimulus for release: PRF from hypothalamus, also when already breastfeeding, the infant sucking on the nipple wi ...
Nucleus basalis of Meynert - Viktor`s Notes for the Neurosurgery
... component in which the input to the higher visual cortex (where conscious perception takes place) comes from the retina via the lateral geniculate body and V1. This carries information about what is actually outside. The second (B) is a top-down component in which the input to the higher visual cort ...
... component in which the input to the higher visual cortex (where conscious perception takes place) comes from the retina via the lateral geniculate body and V1. This carries information about what is actually outside. The second (B) is a top-down component in which the input to the higher visual cort ...
CLinical Manifestations
... stimulating hormone) and high TRH (thyroid releasing hormone) because of the lack of negative feedback on the pituitary and hypothalamus by TH. -If hypothyroidism results from pituitary malfunction, low levels of TH are caused by low TSH. TRH from the hypothalamus is high because there is no negativ ...
... stimulating hormone) and high TRH (thyroid releasing hormone) because of the lack of negative feedback on the pituitary and hypothalamus by TH. -If hypothyroidism results from pituitary malfunction, low levels of TH are caused by low TSH. TRH from the hypothalamus is high because there is no negativ ...
The thyroid gland, the largest endocrine gland, is
... The thyroid gland is made up of many spherical thyroid follicles which are lined with a simple cuboidal epithelium. These follicles contain a viscous fluid, called colloid, which stores the glycoprotein thyroglobulin. This glycoprotein is the precursor to the thyroid hormones. The follicles produce ...
... The thyroid gland is made up of many spherical thyroid follicles which are lined with a simple cuboidal epithelium. These follicles contain a viscous fluid, called colloid, which stores the glycoprotein thyroglobulin. This glycoprotein is the precursor to the thyroid hormones. The follicles produce ...
eprint_2_7692_493
... controlled by the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland. This gland is located at the base of the brain. These pituitary hormones are transported to other glands, such as adrenal cortex, thyroid, and sex glands, etc. to stimulate the production of other hormones. Hormones are highly potent and so ar ...
... controlled by the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland. This gland is located at the base of the brain. These pituitary hormones are transported to other glands, such as adrenal cortex, thyroid, and sex glands, etc. to stimulate the production of other hormones. Hormones are highly potent and so ar ...
pan hypopituitirism
... pituitary gland. Panhypopituitarism refers to an absence of all hormones released by the pituitary gland. Pituitary insufficiency in the adult is most commonly caused by a nonfunctioning tumor, surgical removal or irradiation of the pituitary gland. What are the symptoms? The lack of pituitary hormo ...
... pituitary gland. Panhypopituitarism refers to an absence of all hormones released by the pituitary gland. Pituitary insufficiency in the adult is most commonly caused by a nonfunctioning tumor, surgical removal or irradiation of the pituitary gland. What are the symptoms? The lack of pituitary hormo ...
Adrenal The Role of Stress
... S t • Tired for no reason. • Trouble getting up in the morning, even when you go to bed at a reasonable hour hour. • Feeling rundown or overwhelmed. • Difficulty bouncing back from stress or illness. • F Feell more awake, k alert l t and d energetic ti after ft 6PM than you do all day. ...
... S t • Tired for no reason. • Trouble getting up in the morning, even when you go to bed at a reasonable hour hour. • Feeling rundown or overwhelmed. • Difficulty bouncing back from stress or illness. • F Feell more awake, k alert l t and d energetic ti after ft 6PM than you do all day. ...
Pituitary Gland - inetTeacher.com
... What are some risk factors for this disease? How do you treat Type II Diabetes? What is another name for Type I Diabetes? What age groups is usually affected? What is the cause of the Type I Diabetes? How would you treat Type I Diabetes? Which is more common – Type I or Type II? ...
... What are some risk factors for this disease? How do you treat Type II Diabetes? What is another name for Type I Diabetes? What age groups is usually affected? What is the cause of the Type I Diabetes? How would you treat Type I Diabetes? Which is more common – Type I or Type II? ...
Chapter 3
... •Resistance exercise protocols that use high volume, large muscle groups, and short rest periods result in increased serum cortisol values. Though chronic high levels of cortisol may have adverse catabolic effects, acute increases may contribute to the remodeling of muscle tissue. The Adrenal Hormon ...
... •Resistance exercise protocols that use high volume, large muscle groups, and short rest periods result in increased serum cortisol values. Though chronic high levels of cortisol may have adverse catabolic effects, acute increases may contribute to the remodeling of muscle tissue. The Adrenal Hormon ...
CHEMICAL SENSES: SMELL AND TASTE Smell = Olfaction
... Flavor of food is a composite of both taste and smell sensation. - when nose is congested by infection, food “tastes” different because the olfactory system is “blocked” In humans, the senses of taste and smell have lost important survival characteristics In many animal species, taste (especially of ...
... Flavor of food is a composite of both taste and smell sensation. - when nose is congested by infection, food “tastes” different because the olfactory system is “blocked” In humans, the senses of taste and smell have lost important survival characteristics In many animal species, taste (especially of ...
Minireview: Role of Glia in Neuroendocrine Function
... Integration of hormonal signaling by glial cells occurs in at least two fundamental ways: 1) the hormone acts directly on the glia, which in turn signals to the neuron to modulate its function (5, 6). Signaling to the neuron may involve secretion of a growth factor, neurohormone, or transmitter-like ...
... Integration of hormonal signaling by glial cells occurs in at least two fundamental ways: 1) the hormone acts directly on the glia, which in turn signals to the neuron to modulate its function (5, 6). Signaling to the neuron may involve secretion of a growth factor, neurohormone, or transmitter-like ...
growth hormone
... production: • Uptake of glucose by cells blood glucose (diabetogenic effect). • Use of glucose for energy production due to utilization of fatty acids for energy. • It inhibits hexokinase enzyme inhibits glucose uptake by muscles (opposite to insulin effect). ...
... production: • Uptake of glucose by cells blood glucose (diabetogenic effect). • Use of glucose for energy production due to utilization of fatty acids for energy. • It inhibits hexokinase enzyme inhibits glucose uptake by muscles (opposite to insulin effect). ...
Central nervous system functions in familial
... where it is transported to and stored in the posterior pituitary from where the hormone is released into the general circulation. Parvocellular vasopressin containing cells are found in the hypothalamus as well as in extrahypothalamic sites and constitute different anatomical and functional vasopres ...
... where it is transported to and stored in the posterior pituitary from where the hormone is released into the general circulation. Parvocellular vasopressin containing cells are found in the hypothalamus as well as in extrahypothalamic sites and constitute different anatomical and functional vasopres ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.