Endocrine System
... hormones which influence the anterior pituitary. – Anterior pituitary releases hormones which influence other endocrine glands, such as thyroid stimulating hormone -TSH. An example of hypothalmicpituitary-target pathway ...
... hormones which influence the anterior pituitary. – Anterior pituitary releases hormones which influence other endocrine glands, such as thyroid stimulating hormone -TSH. An example of hypothalmicpituitary-target pathway ...
E5 - The human brain - IBDPBiology-Dnl
... secreted by posterior pituitary; controls hormonal secretion by pituitary; maintains homeostasis such as; control of body temperature, hunger, thirst, fatigue, circadian cycles ...
... secreted by posterior pituitary; controls hormonal secretion by pituitary; maintains homeostasis such as; control of body temperature, hunger, thirst, fatigue, circadian cycles ...
Unit 3_Lesson 74_Endocrine - DPH6Science
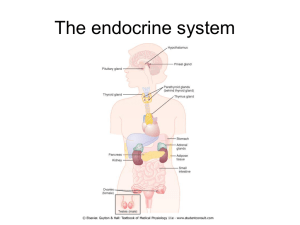
... are coordinated. It’s made up groupings of cells called glands. There are eight major endocrine glands: the pituitary gland, the thyroid gland, the adrenal glands, the pineal gland, the pancreas, the thymus, the parathyroids, the ovaries in women, and the testes in men. _____________________________ ...
... are coordinated. It’s made up groupings of cells called glands. There are eight major endocrine glands: the pituitary gland, the thyroid gland, the adrenal glands, the pineal gland, the pancreas, the thymus, the parathyroids, the ovaries in women, and the testes in men. _____________________________ ...
Transcript I
... minutes before inactivation and/or removal by tissues like the liver, kidney, or lungs or even the cells themselves that they bind too. The reason for all this is that the body must retain tight control over its functions—so synthesis and release can take place very quickly in an active state. O ...
... minutes before inactivation and/or removal by tissues like the liver, kidney, or lungs or even the cells themselves that they bind too. The reason for all this is that the body must retain tight control over its functions—so synthesis and release can take place very quickly in an active state. O ...
Direct stimulation from the nervous system
... thyroid gland and Causes thyroid to produce its hormones. ...
... thyroid gland and Causes thyroid to produce its hormones. ...
Neurotransmitters and Sleep
... a wide reaching and general effect when stimulated. As with ACh, both of these neurotransmitters, and the corresponding brain structures play an important role in cortical activation in general, though their specific effects are more complex. Experiments with lab animals have found that stimulation ...
... a wide reaching and general effect when stimulated. As with ACh, both of these neurotransmitters, and the corresponding brain structures play an important role in cortical activation in general, though their specific effects are more complex. Experiments with lab animals have found that stimulation ...
systems of the body #1
... bloodstream and enter the bones. When calcitonin is present in the bloodstream it also keeps the bones from releasing much needed calcium. The thyroid gland is the only endocrine gland that stores its products in large quantity—normally about a 100-day supply. The main physiological actions of thyro ...
... bloodstream and enter the bones. When calcitonin is present in the bloodstream it also keeps the bones from releasing much needed calcium. The thyroid gland is the only endocrine gland that stores its products in large quantity—normally about a 100-day supply. The main physiological actions of thyro ...
The hormones estrogen and progesterone have a very close
... Low libido Depression, anxiety and emotional swings Food cravings and weight gain Bloating and cramps Insomnia ...
... Low libido Depression, anxiety and emotional swings Food cravings and weight gain Bloating and cramps Insomnia ...
document
... 22. Signs and symptoms common to both type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM) include all of the following EXCEPT: A) polyphagia. B) weight loss. C) polydipsia. D) polyuria. 23. The pathophysiology of type 1 diabetes mellitus (DM) involves: A) autoimmune destruction of pancreatic beta cells. B) pro ...
... 22. Signs and symptoms common to both type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM) include all of the following EXCEPT: A) polyphagia. B) weight loss. C) polydipsia. D) polyuria. 23. The pathophysiology of type 1 diabetes mellitus (DM) involves: A) autoimmune destruction of pancreatic beta cells. B) pro ...
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... bloodstream and enter the bones. When calcitonin is present in the bloodstream it also keeps the bones from releasing much needed calcium. The thyroid gland is the only endocrine gland that stores its products in large quantity—normally about a 100-day supply. The main physiological actions of thyro ...
... bloodstream and enter the bones. When calcitonin is present in the bloodstream it also keeps the bones from releasing much needed calcium. The thyroid gland is the only endocrine gland that stores its products in large quantity—normally about a 100-day supply. The main physiological actions of thyro ...
Nucleic acids and amino acids as drug targets
... Let’s consider its structure and how it is made. Adrenalin is one of a number of catecholamines made from tyrosine. This family also includes such famous members as L-Dopa, dopamine and noradrenalin (norepinephrin). The best part of this scheme is they are all on the same pathway; each is a step in ...
... Let’s consider its structure and how it is made. Adrenalin is one of a number of catecholamines made from tyrosine. This family also includes such famous members as L-Dopa, dopamine and noradrenalin (norepinephrin). The best part of this scheme is they are all on the same pathway; each is a step in ...
Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants
... levels were >2 times higher than in the control lake, abnormal ovarian morphology. Males: <3x testosterone levels than in control males, poorly organized testes and abnormally small phalli Decreased egg availability and juvenile recruitment, altered gonadal morphology and serum hormone concentration ...
... levels were >2 times higher than in the control lake, abnormal ovarian morphology. Males: <3x testosterone levels than in control males, poorly organized testes and abnormally small phalli Decreased egg availability and juvenile recruitment, altered gonadal morphology and serum hormone concentration ...
Certificate in Human Biology
... that are necessary to maintain homeostasis. Using reference materials or the internet, distinguish between grey and white matter and describe where they are found and their differences. Using the internet or other reference material define the following: resting membrane potential, depolarization, r ...
... that are necessary to maintain homeostasis. Using reference materials or the internet, distinguish between grey and white matter and describe where they are found and their differences. Using the internet or other reference material define the following: resting membrane potential, depolarization, r ...
Phylogenetic Distribution and Function of the Hypophysiotropic
... located in the gastrointestinal tract of vertebrates where it may have a physiologic role in the secretion of gastrointestinal hormones. TRH, also, has been located outside the nervous system, occurring in large quantities in the skin ofRana species where it may be of physiologic importance in skin ...
... located in the gastrointestinal tract of vertebrates where it may have a physiologic role in the secretion of gastrointestinal hormones. TRH, also, has been located outside the nervous system, occurring in large quantities in the skin ofRana species where it may be of physiologic importance in skin ...
ENDOCRINOLOGY
... hypophyseal arteries • Directly innervated by hypothalamic neurons – (supraopticohypophyseal and tuberohypophyseal nerve tracts) via the pituitary stalk ...
... hypophyseal arteries • Directly innervated by hypothalamic neurons – (supraopticohypophyseal and tuberohypophyseal nerve tracts) via the pituitary stalk ...
Hyperthyroidism and Graves Disease
... in the blood. There are many different causes. If a person takes thyroid hormone pills inappropriately, or in too strong a dose, hyperthyroidism may result. Sometimes, a nodule (usually a small, noncancerous tumor) within the thyroid gland itself starts "doing its own thing" and produces excess amou ...
... in the blood. There are many different causes. If a person takes thyroid hormone pills inappropriately, or in too strong a dose, hyperthyroidism may result. Sometimes, a nodule (usually a small, noncancerous tumor) within the thyroid gland itself starts "doing its own thing" and produces excess amou ...
Facts of Hormone Balance Issues
... of waxing and waning hormones during these years may be all they need. All of the sex hormones, especially progesterone, estrogens and androgens have a potent effect upon state of mind, mood, and memory. So when they are out of balance (too high, too low, or up and down) as is not uncommon in mid-li ...
... of waxing and waning hormones during these years may be all they need. All of the sex hormones, especially progesterone, estrogens and androgens have a potent effect upon state of mind, mood, and memory. So when they are out of balance (too high, too low, or up and down) as is not uncommon in mid-li ...
Calm Your Hormones or Everything You Should Know About
... • All three estrogens are produced from androgens through enzyme action • E2 produced from testosterone and • E1produced from androstenedione • Androstenedione is made in the theca interna cells (in the ovary) from cholesterol • Your body has receptor sites everywhere! • There are more than 400 know ...
... • All three estrogens are produced from androgens through enzyme action • E2 produced from testosterone and • E1produced from androstenedione • Androstenedione is made in the theca interna cells (in the ovary) from cholesterol • Your body has receptor sites everywhere! • There are more than 400 know ...
Pons - Anatomy and Physiology
... heartbeat, digestive tract motility, pupil size) • Physical responses to emotions (limbic system) – Perception of pleasure, fear, and rage, and in biological rhythms and drives ...
... heartbeat, digestive tract motility, pupil size) • Physical responses to emotions (limbic system) – Perception of pleasure, fear, and rage, and in biological rhythms and drives ...
9 Endocrine physiology
... Thyroid Hormone • The hypothalamus releases its hormone (TSH-RH) to the pituitary, telling the pituitary to release its hormone (TSH), which tells the thyroid gland to release thyroid hormone (TH). • When thyroid hormone is released, it will circulate throughout the body, causing an increase in met ...
... Thyroid Hormone • The hypothalamus releases its hormone (TSH-RH) to the pituitary, telling the pituitary to release its hormone (TSH), which tells the thyroid gland to release thyroid hormone (TH). • When thyroid hormone is released, it will circulate throughout the body, causing an increase in met ...
File
... tela chorioidea ventriculi IV, covered on the inside by а layer of epithelium, lamina chorioidea epithelialis, the choroid plexus of the fourth ventricle is connected with it. There are three openings in the cavity of the ventricle: а median aperture (apertura mediana ventriculi quarti), or Magendie ...
... tela chorioidea ventriculi IV, covered on the inside by а layer of epithelium, lamina chorioidea epithelialis, the choroid plexus of the fourth ventricle is connected with it. There are three openings in the cavity of the ventricle: а median aperture (apertura mediana ventriculi quarti), or Magendie ...
Overview of Addiction Related Brain Regions Nucleus Accumbens
... pleasure. Its size is positively correlated with aggressive behavior across species. In humans, it is the most sexually-dimorphic brain structure, and shrinks by more than 30% in males upon castration. Conditions such as anxiety, autism, depression, post-traumatic stress disorder, and phobias are su ...
... pleasure. Its size is positively correlated with aggressive behavior across species. In humans, it is the most sexually-dimorphic brain structure, and shrinks by more than 30% in males upon castration. Conditions such as anxiety, autism, depression, post-traumatic stress disorder, and phobias are su ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.