Quick Review of Feedback Systems
... Some Things to Know about a Hormone • Source (what organ/cell produces and/or secretes it?) • What is its target cell(s)? • What is the effect on target cells? • What regulates its production/secretion? • What type of chemical structure? • Details of transport/metabolism? • What type of receptor/si ...
... Some Things to Know about a Hormone • Source (what organ/cell produces and/or secretes it?) • What is its target cell(s)? • What is the effect on target cells? • What regulates its production/secretion? • What type of chemical structure? • Details of transport/metabolism? • What type of receptor/si ...
Thyroid gland
... which's is converted by follicular cells as T3 and T4, realse to circulation and interact with intracellular receptors to up-regulate of CHO and lipid catabolism, and protein synthesis so cause increase basal metabolic rate. Between these follicles there are parafollicular cells secrete calcitonin h ...
... which's is converted by follicular cells as T3 and T4, realse to circulation and interact with intracellular receptors to up-regulate of CHO and lipid catabolism, and protein synthesis so cause increase basal metabolic rate. Between these follicles there are parafollicular cells secrete calcitonin h ...
Document
... conception were included in the study. They were sub-divided into two equal groups. Each group comprised of forty (40) subjects. After detailed history and general physical examination, samples of blood were drawn for the assay of serum thyroid hormone levels. RESULTS: A highly statistically signifi ...
... conception were included in the study. They were sub-divided into two equal groups. Each group comprised of forty (40) subjects. After detailed history and general physical examination, samples of blood were drawn for the assay of serum thyroid hormone levels. RESULTS: A highly statistically signifi ...
It`s All About Balance - Women`s International Pharmacy
... by the ovaries of menstruating women. Progesterone is made by the corpus luteum starting just prior to ovulation. Progesterone is a precursor hormone that can be converted by the body into other steroid hormones. It prepares the lining of the uterus for the fertilized ovum and is necessary for the s ...
... by the ovaries of menstruating women. Progesterone is made by the corpus luteum starting just prior to ovulation. Progesterone is a precursor hormone that can be converted by the body into other steroid hormones. It prepares the lining of the uterus for the fertilized ovum and is necessary for the s ...
Amine-Dependent Synthesis of Peptides and Peptido
... It has been reported that when perifused anterior pituitary glands of di-oestrous female rats were stimulated intermittently with luteinizing-hormone-releasinghormone (Matsuo et al., 1971) a progressively increasing series of peaks of luteinizing-hormone secretion resulted even when the secretion wa ...
... It has been reported that when perifused anterior pituitary glands of di-oestrous female rats were stimulated intermittently with luteinizing-hormone-releasinghormone (Matsuo et al., 1971) a progressively increasing series of peaks of luteinizing-hormone secretion resulted even when the secretion wa ...
Hormonal Responses to Exercise - Yola
... Hormone Receptors • Hormone effects are limited by hormonespecific receptors • No receptor on cell surface = no hormone effect – Hormone only affects tissues with specific receptor – Hormone exerts effects after binding with receptor – Typical cell has 2,000 to 10,000 receptors ...
... Hormone Receptors • Hormone effects are limited by hormonespecific receptors • No receptor on cell surface = no hormone effect – Hormone only affects tissues with specific receptor – Hormone exerts effects after binding with receptor – Typical cell has 2,000 to 10,000 receptors ...
The Endocrine System Negative Feedback Mechanism
... Hormones • The endocrine system releases powerful, stimulating hormones (chemical messengers/catalysts) directly into the bloodstream which target specific cells. – These chemical messengers are like switches which “start” or “stop” various physiological processes in the body. – Hormones increase or ...
... Hormones • The endocrine system releases powerful, stimulating hormones (chemical messengers/catalysts) directly into the bloodstream which target specific cells. – These chemical messengers are like switches which “start” or “stop” various physiological processes in the body. – Hormones increase or ...
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM: INTRODUCTION
... produces pancreatic juice. Pancreatic juice contains a digestive enzyme which gets into the small intestine through a duct. As a ductless gland, the pancreas produces two hormones. One of these is called insulin. Insulin is produced in clusters of cells scattered throughout the pancreas. These group ...
... produces pancreatic juice. Pancreatic juice contains a digestive enzyme which gets into the small intestine through a duct. As a ductless gland, the pancreas produces two hormones. One of these is called insulin. Insulin is produced in clusters of cells scattered throughout the pancreas. These group ...
Endocrine System
... 2. Most of the receptors are bound to the cell membrane but it can be intracellular receptor. E. g. of intracellular receptor hormone:- Steroid hormone , Thyroid hormone , Vit. D 3. Combine with high affinity with the hormone concentrate the hormone in the cell (This is one of the ways to detect h ...
... 2. Most of the receptors are bound to the cell membrane but it can be intracellular receptor. E. g. of intracellular receptor hormone:- Steroid hormone , Thyroid hormone , Vit. D 3. Combine with high affinity with the hormone concentrate the hormone in the cell (This is one of the ways to detect h ...
cells - LPS.org
... The Posterior Pituitary Contains axons of hypothalamic neurons Stores antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and oxytocin ADH and oxytocin are released in response to nerve impulses Both use PIP-calcium second-messenger mechanism at their targets ...
... The Posterior Pituitary Contains axons of hypothalamic neurons Stores antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and oxytocin ADH and oxytocin are released in response to nerve impulses Both use PIP-calcium second-messenger mechanism at their targets ...
Regulating Plasma Hormone Levels
... decay, and are metabolized and excreted from the body through several routes. Shutting off secretion of a hormone that has a very short half-life causes circulating hormone concentration to plummet, but if a hormone's biological half-life is long, effective concentrations persist for some time after ...
... decay, and are metabolized and excreted from the body through several routes. Shutting off secretion of a hormone that has a very short half-life causes circulating hormone concentration to plummet, but if a hormone's biological half-life is long, effective concentrations persist for some time after ...
Endocrine System
... When blood levels of hormone increase, the brain hormones stop Nervous Control – in some cases, sympathetic nervous system causes direct release of hormone from gland (for example, when stress causes the adrenal medulla to secrete adrenalin) ...
... When blood levels of hormone increase, the brain hormones stop Nervous Control – in some cases, sympathetic nervous system causes direct release of hormone from gland (for example, when stress causes the adrenal medulla to secrete adrenalin) ...
Exam
... 59. The female urethra is an inch long; whereas the male urethra is 12 inches long. 60. Hypophysis means “to grow” in Greek. 61. Excessive growth hormone in the adult causes gigantism. 62. Prolactin receptors can be found in the cerebral cortex. 63. Releasing factors from the pituitary act through t ...
... 59. The female urethra is an inch long; whereas the male urethra is 12 inches long. 60. Hypophysis means “to grow” in Greek. 61. Excessive growth hormone in the adult causes gigantism. 62. Prolactin receptors can be found in the cerebral cortex. 63. Releasing factors from the pituitary act through t ...
The Endocrine System
... A) Although hormones are carried to all parts of the body, they produce effects only in cells with proper receptors. B) Hormones are limited to steroid compounds C) Hormones are secreted by specialized exocrine glands. D) Most hormones are controlled by positive feedback mechanisms involving the pit ...
... A) Although hormones are carried to all parts of the body, they produce effects only in cells with proper receptors. B) Hormones are limited to steroid compounds C) Hormones are secreted by specialized exocrine glands. D) Most hormones are controlled by positive feedback mechanisms involving the pit ...
Endocrine System Part 1
... Step 1: The hormone binds to the receptor on the cell membrane causing the G Protein inside the cell to change shape. Step 2: The G protein gets rid of GDP and receives GTP. This is the “on” or “go” signal. Step 3: The GTP activates the effector enzyme adenylate cyclase and the GTP turns back ...
... Step 1: The hormone binds to the receptor on the cell membrane causing the G Protein inside the cell to change shape. Step 2: The G protein gets rid of GDP and receives GTP. This is the “on” or “go” signal. Step 3: The GTP activates the effector enzyme adenylate cyclase and the GTP turns back ...
Slide 1
... Other Chemicals Act Locally • Prostaglandins – Lipid molecules continually released by the plasma membranes of most cells – At least 16 different prostaglandin molecules function within the human body ...
... Other Chemicals Act Locally • Prostaglandins – Lipid molecules continually released by the plasma membranes of most cells – At least 16 different prostaglandin molecules function within the human body ...
endocrine system
... osteoclasts to degrade bone matrix so calcium goes into blood. Hormonal Trigger • This is when one endocrine gland releases a hormone that stimulates another endocrine gland to release its hormone. • Examples are any of the hypothalamus or anterior pituitary hormones, and also the adrenal cortex (st ...
... osteoclasts to degrade bone matrix so calcium goes into blood. Hormonal Trigger • This is when one endocrine gland releases a hormone that stimulates another endocrine gland to release its hormone. • Examples are any of the hypothalamus or anterior pituitary hormones, and also the adrenal cortex (st ...
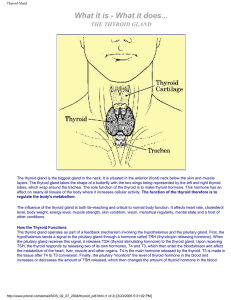
Thyroid Gland
... How the Thyroid Functions The thyroid gland operates as part of a feedback mechanism involving the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland. First, the hypothalamus sends a signal to the pituitary gland through a hormone called TRH (thyrotropin releasing hormone). When the pituitary gland receives this ...
... How the Thyroid Functions The thyroid gland operates as part of a feedback mechanism involving the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland. First, the hypothalamus sends a signal to the pituitary gland through a hormone called TRH (thyrotropin releasing hormone). When the pituitary gland receives this ...
ch_18_Case Study_Answer_Key
... Triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4) are secreted by the follicular cells of the thyroid and are collectively called “thyroid hormone.” Most thyroid hormone is secreted as T4 and converted in target cells to the more potent T3 form by removing one iodine atom. T3 binds to receptors in the nucleu ...
... Triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4) are secreted by the follicular cells of the thyroid and are collectively called “thyroid hormone.” Most thyroid hormone is secreted as T4 and converted in target cells to the more potent T3 form by removing one iodine atom. T3 binds to receptors in the nucleu ...
Answer Key to Short Answer Questions for
... Triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4) are secreted by the follicular cells of the thyroid and are collectively called “thyroid hormone.” Most thyroid hormone is secreted as T4 and converted in target cells to the more potent T3 form by removing one iodine atom. T3 binds to receptors in the nucleu ...
... Triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4) are secreted by the follicular cells of the thyroid and are collectively called “thyroid hormone.” Most thyroid hormone is secreted as T4 and converted in target cells to the more potent T3 form by removing one iodine atom. T3 binds to receptors in the nucleu ...
ABNORMALITIES OF THYROID HORMONE SECRETION
... However, both TRH & TSH will be raised if cause is excess hypothalamic or pituitary secretion: ↑ T3 & T4 & ↑ TRH & TSH • Anti-thyroid antibodies • TSI • Scanning images show thyroid tumor if present ...
... However, both TRH & TSH will be raised if cause is excess hypothalamic or pituitary secretion: ↑ T3 & T4 & ↑ TRH & TSH • Anti-thyroid antibodies • TSI • Scanning images show thyroid tumor if present ...
Antidiuretic Hormone
... • Chemical messengers produced by endocrine glands • Absorbed into blood vessels and will contact all cells of the body. ...
... • Chemical messengers produced by endocrine glands • Absorbed into blood vessels and will contact all cells of the body. ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.