Document
... is a form of defence that allows organisms to survive. The endocrine system is a group of specialised tissues (glands) that produce chemicals called hormones, many of which are proteins. ...
... is a form of defence that allows organisms to survive. The endocrine system is a group of specialised tissues (glands) that produce chemicals called hormones, many of which are proteins. ...
The Endocrine System
... •Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) •Regulates endocrine activity of the adrenal cortex •Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) •Influences growth and activity of the thyroid gland © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... •Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) •Regulates endocrine activity of the adrenal cortex •Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) •Influences growth and activity of the thyroid gland © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Current recommendations for the diagnostic evaluation of patients
... have ovulatory abnormalities and usually have normal levels of circulating androgens • In many of these patients, skin 5-reductase activity is excessive, leading to higher skin concentrations of the active androgen dihydrotestosterone • It is important to note that approximately 40% of hirsute women ...
... have ovulatory abnormalities and usually have normal levels of circulating androgens • In many of these patients, skin 5-reductase activity is excessive, leading to higher skin concentrations of the active androgen dihydrotestosterone • It is important to note that approximately 40% of hirsute women ...
Figure 4.8 The human brain stem This composite structure extends
... Most inferior portion, functions as a conduction pathway (descending motor neuron pathways decussate here) Reflex centers for: regulating heart rate blood vessel diameter coughing, sneezing ...
... Most inferior portion, functions as a conduction pathway (descending motor neuron pathways decussate here) Reflex centers for: regulating heart rate blood vessel diameter coughing, sneezing ...
The Endocrine System - Part 1
... Pituitary gland - the major endocrine gland. A pea-sized body attached to the base of the brain, the pituitary is important in controlling growth and development and the functioning of the other endocrine glands. Pineal gland - a pea-sized conical mass of tissue behind the third ventricle of the bra ...
... Pituitary gland - the major endocrine gland. A pea-sized body attached to the base of the brain, the pituitary is important in controlling growth and development and the functioning of the other endocrine glands. Pineal gland - a pea-sized conical mass of tissue behind the third ventricle of the bra ...
Genetic analysis of dopaminergic system development in zebrafish
... numbering established for mammalian systems (Smeets and Gonzalez, 2000), as there is so far little information on potential functional similarities. The first dopaminergic neurons differentiate at about 18 hours post fertilization (hpf) in the prospective posterior tuberculum (basal plate area of pro ...
... numbering established for mammalian systems (Smeets and Gonzalez, 2000), as there is so far little information on potential functional similarities. The first dopaminergic neurons differentiate at about 18 hours post fertilization (hpf) in the prospective posterior tuberculum (basal plate area of pro ...
How Does the Brain Sense Osmolality?
... The pioneering investigations of Verney in the 1940s1 found infusion of hyperosmotic solutions into blood vessels that perfused the anterior hypothalamus produced an antidiuresis in dogs, thereby identifying this area as the site of osmoresponsive elements in the brain. The most parsimonious explana ...
... The pioneering investigations of Verney in the 1940s1 found infusion of hyperosmotic solutions into blood vessels that perfused the anterior hypothalamus produced an antidiuresis in dogs, thereby identifying this area as the site of osmoresponsive elements in the brain. The most parsimonious explana ...
The Endocrine System Collin College
... • The hormone is considered as the 1st messenger • A second messenger is a non-protein product, produced by the activation of a specific enzyme via the G-protein, and released inside the cell. • Produced and Released into the cell, the 2nd messenger can now activate and influence other cellular e ...
... • The hormone is considered as the 1st messenger • A second messenger is a non-protein product, produced by the activation of a specific enzyme via the G-protein, and released inside the cell. • Produced and Released into the cell, the 2nd messenger can now activate and influence other cellular e ...
Endocrine System - Bellefonte Area School District
... Hormones secreted by endocrine cells into interstitial fluid, and distributed through bloodstream Only cells that posses receptors for that particular hormone can be affected -“target cell/target organ” Effect of hormones is on the metabolic activity of cells, via activation/inactivation of sp ...
... Hormones secreted by endocrine cells into interstitial fluid, and distributed through bloodstream Only cells that posses receptors for that particular hormone can be affected -“target cell/target organ” Effect of hormones is on the metabolic activity of cells, via activation/inactivation of sp ...
Title: Biopsychology
... Q5 Spot the mistakes Below is an answer to the following question: Describe the functions of the endocrine system. (6 marks) The answer contains 6 mistakes. Can you highlight all 6 mistakes and say why they’re wrong? The function of the endocrine system is to regulate the activity of organs within t ...
... Q5 Spot the mistakes Below is an answer to the following question: Describe the functions of the endocrine system. (6 marks) The answer contains 6 mistakes. Can you highlight all 6 mistakes and say why they’re wrong? The function of the endocrine system is to regulate the activity of organs within t ...
Review Questions
... B. eye movements. C. diffuse touch bilaterally. D. pain and temperature universally. E. motor control bilaterally. ...
... B. eye movements. C. diffuse touch bilaterally. D. pain and temperature universally. E. motor control bilaterally. ...
Endocrine Test - The Science of Payne
... 22. Glands that release their secretion into ducts leading to a body surface are called _______________. 23. The central portion of the adrenal gland is the adrenal ____________. 24. A group of lipids called __________ have powerful, regulating effects on a variety of tissues. 25. The hormone that s ...
... 22. Glands that release their secretion into ducts leading to a body surface are called _______________. 23. The central portion of the adrenal gland is the adrenal ____________. 24. A group of lipids called __________ have powerful, regulating effects on a variety of tissues. 25. The hormone that s ...
Role of Melatonin and/or Vitamin B Complex against Hormonal
... in rats (Konakchieva et al., 1997). Alonso-Vale et al. (2004) suggested that MT has a negative CORT modulator in normal as well as stress situations. This view was strongly supported another in vitro study describing MT functional receptors in adrenal gland cortex and their inhibitory effect on cort ...
... in rats (Konakchieva et al., 1997). Alonso-Vale et al. (2004) suggested that MT has a negative CORT modulator in normal as well as stress situations. This view was strongly supported another in vitro study describing MT functional receptors in adrenal gland cortex and their inhibitory effect on cort ...
Steroids
... Artificially produced hormones Nearly identical to male sex hormones, like testosterone 100+ variations ...
... Artificially produced hormones Nearly identical to male sex hormones, like testosterone 100+ variations ...
Endocrine Disruptors - University of Massachusetts Boston
... Hormone binding will alter binding to other cellular proteins & may activate any receptor protein enzyme actions. ...
... Hormone binding will alter binding to other cellular proteins & may activate any receptor protein enzyme actions. ...
Endocrine Disruptors
... Hormone binding will alter binding to other cellular proteins & may activate any receptor protein enzyme actions. ...
... Hormone binding will alter binding to other cellular proteins & may activate any receptor protein enzyme actions. ...
Overivew notes
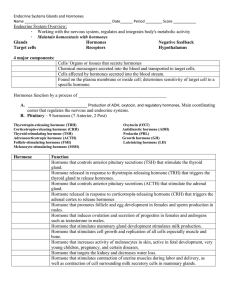
... Cells/ Organs or tissues that secrete hormones Chemical messengers secreted into the blood and transported to target cells. Cells affected by hormones secreted into the blood stream. Found on the plasma membrane or inside cell; determines sensitivity of target cell to a specific hormone. Hormones fu ...
... Cells/ Organs or tissues that secrete hormones Chemical messengers secreted into the blood and transported to target cells. Cells affected by hormones secreted into the blood stream. Found on the plasma membrane or inside cell; determines sensitivity of target cell to a specific hormone. Hormones fu ...
Hormones
... The hypothalamus has both neural functions and releases hormones Other tissues and organs that produce hormones – adipose cells, pockets of cells in the walls of the small intestine, stomach, kidneys, and heart ...
... The hypothalamus has both neural functions and releases hormones Other tissues and organs that produce hormones – adipose cells, pockets of cells in the walls of the small intestine, stomach, kidneys, and heart ...
Vestibular modulation of endocrine secretions
... neurons are located in paraventricular nucleus. Electrical and caloric stimulation of vestibular pathways results in a response in PVN (para ventricular neurons) neurons in the guinea pig. Retrograde viral tracing in the rat brain has demonstrated the presence of a direct vestibuloparaventricular pr ...
... neurons are located in paraventricular nucleus. Electrical and caloric stimulation of vestibular pathways results in a response in PVN (para ventricular neurons) neurons in the guinea pig. Retrograde viral tracing in the rat brain has demonstrated the presence of a direct vestibuloparaventricular pr ...
The Endocrine System
... of the body. Some of your body’s glands, such as sweat glands, release their chemicals into tiny tubes called ducts. The ducts carry the chemicals to the place where they will be used. Endocrine glands, on the other hand, do not have ducts. Instead, they release substances directly into the bloodstr ...
... of the body. Some of your body’s glands, such as sweat glands, release their chemicals into tiny tubes called ducts. The ducts carry the chemicals to the place where they will be used. Endocrine glands, on the other hand, do not have ducts. Instead, they release substances directly into the bloodstr ...
Hormones
... The hypothalamus has both neural functions and releases hormones Other tissues and organs that produce hormones – adipose cells, pockets of cells in the walls of the small intestine, stomach, kidneys, and heart ...
... The hypothalamus has both neural functions and releases hormones Other tissues and organs that produce hormones – adipose cells, pockets of cells in the walls of the small intestine, stomach, kidneys, and heart ...
Introduction to the Mechanism of Actions
... 1. Rate of production: Synthesis and secretion of hormones are the most highly regulated aspect of endocrine control. Such control is mediated by positive and negative feedback circuits. 2. Rate of delivery: An example of this effect is blood flow to a target organ or group of target cells: TRANSPOR ...
... 1. Rate of production: Synthesis and secretion of hormones are the most highly regulated aspect of endocrine control. Such control is mediated by positive and negative feedback circuits. 2. Rate of delivery: An example of this effect is blood flow to a target organ or group of target cells: TRANSPOR ...
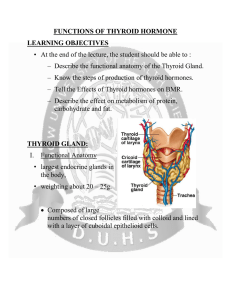
FUNCTIONS OF THYROID HORMONE
... – Describe the functional anatomy of the Thyroid Gland. – Know the steps of production of thyroid hormones. – Tell the Effects of Thyroid hormones on BMR. – Describe the effect on metabolism of protein, carbohydrate and fat. ...
... – Describe the functional anatomy of the Thyroid Gland. – Know the steps of production of thyroid hormones. – Tell the Effects of Thyroid hormones on BMR. – Describe the effect on metabolism of protein, carbohydrate and fat. ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.