NCLEX-PN_Chapter_08_.. - Nursing Education Consultants
... Pituitary gland - Often referred to as the “master gland” because it secretes hormones that control hormone secretion of other endocrine glands. Thyroid gland - Primary function of thyroid hormone is to control the level of cellular metabolism by secreting thyroxin (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). Pa ...
... Pituitary gland - Often referred to as the “master gland” because it secretes hormones that control hormone secretion of other endocrine glands. Thyroid gland - Primary function of thyroid hormone is to control the level of cellular metabolism by secreting thyroxin (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). Pa ...
Endocrine System - Nursing Education Consultants
... Pituitary gland - Often referred to as the “master gland” because it secretes hormones that control hormone se- cretion of other endocrine glands. Thyroid gland - Primary function of thyroid hormone is to control the level of cellular metabolism by secreting thyroxin (T4) and triiodothyro ...
... Pituitary gland - Often referred to as the “master gland” because it secretes hormones that control hormone se- cretion of other endocrine glands. Thyroid gland - Primary function of thyroid hormone is to control the level of cellular metabolism by secreting thyroxin (T4) and triiodothyro ...
Common Iliac Arteries External Iliac Artery EMBRYOLOGIC NOTES
... The superior mesenteric vein is a tributary of the portal circulation (Figs. 5.22, 5.26, and 5.48). It begins at the ileocecal junction and runs upward on the posterior abdominal wall within the root of the mesentery of the small intestine and on the right side of the superior mesenteric artery. It ...
... The superior mesenteric vein is a tributary of the portal circulation (Figs. 5.22, 5.26, and 5.48). It begins at the ileocecal junction and runs upward on the posterior abdominal wall within the root of the mesentery of the small intestine and on the right side of the superior mesenteric artery. It ...
Anat2_04_Endocrine
... of target cell receptors may decrease. Down-regulation decreases the responsiveness of the target cell to the hormone. ...
... of target cell receptors may decrease. Down-regulation decreases the responsiveness of the target cell to the hormone. ...
内分泌学―――Lecture Note
... 1) Almost all secretion by the pituitary is controlled by either hormonal or nervous signals from hypothalamus. 2) Hypothalamus is the highest integrative center in the endocrine hierarchy. The secretion of hypothalamic hormones is pulsatile which is critical for maintaining normal secretion of pitu ...
... 1) Almost all secretion by the pituitary is controlled by either hormonal or nervous signals from hypothalamus. 2) Hypothalamus is the highest integrative center in the endocrine hierarchy. The secretion of hypothalamic hormones is pulsatile which is critical for maintaining normal secretion of pitu ...
File
... 1. The substance must be present within the presynaptic neuron. 2. The substance must be released in response to pre-synaptic depolarization, 3. Specific receptors for the substance must be present on the postsynaptic cell. Acetylcholine most often excites gastrointestinal activity. Norepinephrine a ...
... 1. The substance must be present within the presynaptic neuron. 2. The substance must be released in response to pre-synaptic depolarization, 3. Specific receptors for the substance must be present on the postsynaptic cell. Acetylcholine most often excites gastrointestinal activity. Norepinephrine a ...
Anatomy – Whole Block Review
... The functional lobes can actually be further broke down, so that one branch of the Portal Triad goes to each. How many lobes are there? o 8 There are two further lobes, which exist just to the left of the Right Lobe. What are these lobes, and what main lobe do they belong to (functionally)? o Caudat ...
... The functional lobes can actually be further broke down, so that one branch of the Portal Triad goes to each. How many lobes are there? o 8 There are two further lobes, which exist just to the left of the Right Lobe. What are these lobes, and what main lobe do they belong to (functionally)? o Caudat ...
Vertebral Column and Thorax
... Inferior coccygeal elements. Left view anterior, middle view posterior, right view superior articulation. ...
... Inferior coccygeal elements. Left view anterior, middle view posterior, right view superior articulation. ...
Hormone - WordPress.com
... the cells and increase RNA translation and nuclear transcription of DNA to form mRNA, and so increase rate of protein synthesis. GH also reduces the breakdown of cell proteins by decreasing catabolism of protein. ...
... the cells and increase RNA translation and nuclear transcription of DNA to form mRNA, and so increase rate of protein synthesis. GH also reduces the breakdown of cell proteins by decreasing catabolism of protein. ...
Development of the nervous system and sense organs I
... develops into impulse- conducting neuron. 5- The angioblasts develop also from the inner zone, but either remains attached to the inner limiting membrane or migrate and get attached to the outer limiting membrane. - The angioblasts that loose connection with the limiting membranes differentiate into ...
... develops into impulse- conducting neuron. 5- The angioblasts develop also from the inner zone, but either remains attached to the inner limiting membrane or migrate and get attached to the outer limiting membrane. - The angioblasts that loose connection with the limiting membranes differentiate into ...
Fetal Pig Dissection Introduction: Today, we begin a new chapter in
... Now, cut through the rib cage with scissors on a line from the diaphragm to just to the right of the sternum (breastbone) up to your pig’s chin. It is critical the you cut only the ribs so as not to damage the delicate tissues below. Make two lateral cuts just posterior to the front legs to make new ...
... Now, cut through the rib cage with scissors on a line from the diaphragm to just to the right of the sternum (breastbone) up to your pig’s chin. It is critical the you cut only the ribs so as not to damage the delicate tissues below. Make two lateral cuts just posterior to the front legs to make new ...
Renal04-PostAbdominalWall
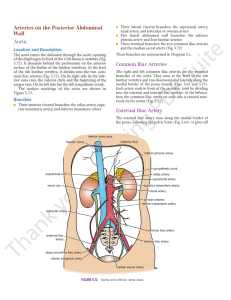
... (main trunk to the thigh) runs on the psoas to the midinguinal point where its changes its name to femoral a.; 2 branches arise from the external iliac a. just before it passes behind the inguinal ligament - the inf. epigastric and deep circumflex iliac aa. (anastomose with iliolumbar aa. from int. ...
... (main trunk to the thigh) runs on the psoas to the midinguinal point where its changes its name to femoral a.; 2 branches arise from the external iliac a. just before it passes behind the inguinal ligament - the inf. epigastric and deep circumflex iliac aa. (anastomose with iliolumbar aa. from int. ...
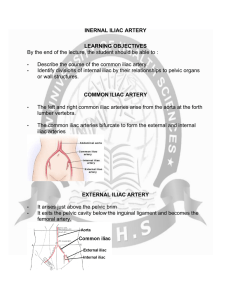
Anatomy - INERNAL ILIAC ARTERY
... INTERNAL ILIAC ARTERY It supplies both the visceral and somatic structures of the pelvis It supplies Pelvic walls Pelvic viscera And the perineum ...
... INTERNAL ILIAC ARTERY It supplies both the visceral and somatic structures of the pelvis It supplies Pelvic walls Pelvic viscera And the perineum ...
Pre-Registration Midwifery Programmes Biological Sciences Pre
... To introduce the structure and functions of the blood vessels and the heart. Learning outcomes 1. Identify the types of vessels that make up the circulatory system. 2. Describe the structure and function of the above. 3. Describe how the pressure changes as blood progresses from the arteries through ...
... To introduce the structure and functions of the blood vessels and the heart. Learning outcomes 1. Identify the types of vessels that make up the circulatory system. 2. Describe the structure and function of the above. 3. Describe how the pressure changes as blood progresses from the arteries through ...
An Overview of Cancer Staging and AJCC Guidelines for the
... It is widely recognized that accurate classification and staging of cancer is an invaluable aid to ensuring that patients receive optimum treatment in accordance with the characteristics their disease in progress. Established staging criteria permit physicians to stratify their patients accurately a ...
... It is widely recognized that accurate classification and staging of cancer is an invaluable aid to ensuring that patients receive optimum treatment in accordance with the characteristics their disease in progress. Established staging criteria permit physicians to stratify their patients accurately a ...
Major arteries of the body
... one another freely providing backup routes for blood to flow if one artery is blocked. • The arteries whose terminal branches do not anastomose with branches of adjacent arteries are called “end arteries or terminal arteries”. End arteries are of two types: Anatomic (True) End Artery: When no anas ...
... one another freely providing backup routes for blood to flow if one artery is blocked. • The arteries whose terminal branches do not anastomose with branches of adjacent arteries are called “end arteries or terminal arteries”. End arteries are of two types: Anatomic (True) End Artery: When no anas ...
ENDOCRINE - Wikispaces
... • Is the study of homeostatic chemical adjustments and other activities of the body, mediated by chemical substances known as HORMONES. -Term Hormone, derived from Greek phrase meaning, (to set in motion) - describes the dynamic actions of hormone as they elicit cellular responses & regulate physiol ...
... • Is the study of homeostatic chemical adjustments and other activities of the body, mediated by chemical substances known as HORMONES. -Term Hormone, derived from Greek phrase meaning, (to set in motion) - describes the dynamic actions of hormone as they elicit cellular responses & regulate physiol ...
Unit III Structures to ID
... Costal margin—The lower edge of the thorax formed by the bottom edge of the rib cage o Costal cartilages 7-10 join to form costal margin Anterior axillary fold—lateral border of the pec. major muscle Ribs—note that first rib is the highest, shortest, broadest, and most sharply curved rib o Hea ...
... Costal margin—The lower edge of the thorax formed by the bottom edge of the rib cage o Costal cartilages 7-10 join to form costal margin Anterior axillary fold—lateral border of the pec. major muscle Ribs—note that first rib is the highest, shortest, broadest, and most sharply curved rib o Hea ...
The Endocrine System
... Lesson 8.1: Functions and Control of the Endocrine System Lesson 8.2: Major Endocrine Organs Lesson 8.3: Endocrine Disorders and ...
... Lesson 8.1: Functions and Control of the Endocrine System Lesson 8.2: Major Endocrine Organs Lesson 8.3: Endocrine Disorders and ...
Practice Questions
... 5. A runner accelerated toward the finish line and suddenly felt a pop on the back of his thigh. He then fell down in excruciating pain. MRI imaging showed an avulsion of tendons from their origin on the innominate bone. A small piece of bone remained attached to the muscle tendons. This bone was pr ...
... 5. A runner accelerated toward the finish line and suddenly felt a pop on the back of his thigh. He then fell down in excruciating pain. MRI imaging showed an avulsion of tendons from their origin on the innominate bone. A small piece of bone remained attached to the muscle tendons. This bone was pr ...
left common carotid artery
... median cubital vein. The cephalic vein begins at the back of the hand where it collects blood from a complex of superficial veins, many of which can be easily seen. It then winds round the radial side to the anterior aspect of the forearm. In front of the elbow it gives off a large branch, the media ...
... median cubital vein. The cephalic vein begins at the back of the hand where it collects blood from a complex of superficial veins, many of which can be easily seen. It then winds round the radial side to the anterior aspect of the forearm. In front of the elbow it gives off a large branch, the media ...
4 BloodVessels
... A simple “tube heart” develops in the embryo and pumps by the fourth week The heart becomes a four-chambered organ by the end of seven weeks Few structural changes occur after the seventh week Congential heart defects sometimes arise ...
... A simple “tube heart” develops in the embryo and pumps by the fourth week The heart becomes a four-chambered organ by the end of seven weeks Few structural changes occur after the seventh week Congential heart defects sometimes arise ...
Pancreas

The pancreas /ˈpæŋkriəs/ is a glandular organ in the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. It is an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide which circulate in the blood. The pancreas is also a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. These enzymes help to further break down the carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the chyme.