The Intestines
... smaller microvilli that help absorb and increase surface area even more • The combination of these two create that large surface area ...
... smaller microvilli that help absorb and increase surface area even more • The combination of these two create that large surface area ...
BLOOD SUPPLY OF EYE - Home
... In the upper eyelid,another arcade sup.or peripheral arterial arcade,is formed from the sup.branches of med.palpebral a,which lies near the upper border of tarsal plate. Branches from the arterial arcades go forward to supply orbicularis and skin & backward to supply tarsal glands & conjuctiva. Veno ...
... In the upper eyelid,another arcade sup.or peripheral arterial arcade,is formed from the sup.branches of med.palpebral a,which lies near the upper border of tarsal plate. Branches from the arterial arcades go forward to supply orbicularis and skin & backward to supply tarsal glands & conjuctiva. Veno ...
Small Intestine
... CopyrightThe McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... CopyrightThe McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
Document
... wall , NOW these two reflections of a two double layer of visceral peritoneum forming the: Falciform ligament , sickle shape . NOW , from the greater curvature of the stomach descending anteriorly to all the intestine (large and small) this will be extend much further away , what happen here is this ...
... wall , NOW these two reflections of a two double layer of visceral peritoneum forming the: Falciform ligament , sickle shape . NOW , from the greater curvature of the stomach descending anteriorly to all the intestine (large and small) this will be extend much further away , what happen here is this ...
Anterior Cervical Region - Yeditepe University Dentistry Anatomy
... Role of the carotid bodies Carotid bodies are sensitive to decreased O2 and increased CO2 content of the blood In both cases visseral reflexes are activated leading to increased ventilation (increased depth and rate of repiration) and as well as rise of heart rate and blood pressure Both the ...
... Role of the carotid bodies Carotid bodies are sensitive to decreased O2 and increased CO2 content of the blood In both cases visseral reflexes are activated leading to increased ventilation (increased depth and rate of repiration) and as well as rise of heart rate and blood pressure Both the ...
bilateral non-rotation of kidney with vascular anomalies– a
... abdominal aorta at the level of the first lumbar vertebra. Its length was 3.6cm. It divided into 2 branches, one entering the upper end of hilum & 2nd branch further dividing into two & then entering the upper end of hilum. The additional renal artery originated from the abdominal aorta at the level ...
... abdominal aorta at the level of the first lumbar vertebra. Its length was 3.6cm. It divided into 2 branches, one entering the upper end of hilum & 2nd branch further dividing into two & then entering the upper end of hilum. The additional renal artery originated from the abdominal aorta at the level ...
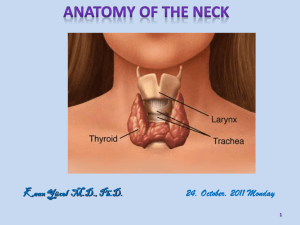
neck topography_engl.2011
... Truncus sympaticus - behind lamina prevertebralis - behind a. carotis communis/interna close to n. vagus - gangl. cervicale superior - over m. longus colli (C2-3) - ganl. cervicale medius – at the levbel of a. thyroidea inferior (C6) - gangl. сervicale inferior (С7 head of І rib) - Innervates upper ...
... Truncus sympaticus - behind lamina prevertebralis - behind a. carotis communis/interna close to n. vagus - gangl. cervicale superior - over m. longus colli (C2-3) - ganl. cervicale medius – at the levbel of a. thyroidea inferior (C6) - gangl. сervicale inferior (С7 head of І rib) - Innervates upper ...
Multiple endocrine neoplasia
... 9. Describe the most common local symptoms and signs of a space occupying lesion affecting the hypothalamus and pituitary gland. 10. Describe the biochemical and clinical features of acromegaly. 11. Describe the causes of hyperprolactinaemia and understand the importance of diagnostic studies in the ...
... 9. Describe the most common local symptoms and signs of a space occupying lesion affecting the hypothalamus and pituitary gland. 10. Describe the biochemical and clinical features of acromegaly. 11. Describe the causes of hyperprolactinaemia and understand the importance of diagnostic studies in the ...
Female Reproductive Organs
... Digestive System (Colon) Arm (Upper Limbs) Hand (Upper Limbs and Torso) Foot (Lower Limbs) Foot (Lower Limbs) Digestive System (Lower GI) Bladder Back (Upper Limbs and Torso) Foot (Lower Limbs) Hand (Upper Limbs) Male Genitalia Male Reproductive Organs Illuminating the Path to Better Health ...
... Digestive System (Colon) Arm (Upper Limbs) Hand (Upper Limbs and Torso) Foot (Lower Limbs) Foot (Lower Limbs) Digestive System (Lower GI) Bladder Back (Upper Limbs and Torso) Foot (Lower Limbs) Hand (Upper Limbs) Male Genitalia Male Reproductive Organs Illuminating the Path to Better Health ...
Triple arterial blood supply to the liver and double cystic arteries: A
... SMA. The three aforementioned embryonic arteries (left, middle and right) anastomose in the hepatic hilum. The central lobe, which later develops in right and left paramedian sectors, grows intensively and overlaps the lateral lobes (future lateral sectors). Lastly, owing to the enlargement of the s ...
... SMA. The three aforementioned embryonic arteries (left, middle and right) anastomose in the hepatic hilum. The central lobe, which later develops in right and left paramedian sectors, grows intensively and overlaps the lateral lobes (future lateral sectors). Lastly, owing to the enlargement of the s ...
video slide
... • The thyroid gland consists of two lobes on the ventral surface of the trachea • It produces two iodine-containing hormones: triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4) Two forms of thyroxine, T3 and T4, are made from tyrosine. T3 (triiodothyronine) has three iodine atoms. T4 has four iodine atoms. Mo ...
... • The thyroid gland consists of two lobes on the ventral surface of the trachea • It produces two iodine-containing hormones: triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4) Two forms of thyroxine, T3 and T4, are made from tyrosine. T3 (triiodothyronine) has three iodine atoms. T4 has four iodine atoms. Mo ...
Board Review for Anatomy - Stritch School of Medicine
... Urinary bladder – relationship of ureter to ductus deferens. Prostate and urethra – Netter 338 Uterus – broad ligament, anteflexed and anteverted, rectouterine pouch. – Netter ...
... Urinary bladder – relationship of ureter to ductus deferens. Prostate and urethra – Netter 338 Uterus – broad ligament, anteflexed and anteverted, rectouterine pouch. – Netter ...
Board Review for Anatomy - Stritch School of Medicine
... Urinary bladder – relationship of ureter to ductus deferens. Prostate and urethra – Netter 338 Uterus – broad ligament, anteflexed and anteverted, rectouterine pouch. – Netter 337, 339 Pelvic diaphragm vs. urogenital diaphragm Formation of greater and lesser ischiadic foramina ...
... Urinary bladder – relationship of ureter to ductus deferens. Prostate and urethra – Netter 338 Uterus – broad ligament, anteflexed and anteverted, rectouterine pouch. – Netter 337, 339 Pelvic diaphragm vs. urogenital diaphragm Formation of greater and lesser ischiadic foramina ...
Slides_4
... 2-The femoral vein has a constant relationship to the medial side of the femoral artery just below the inguinal ligament and is easily cannulated. 3- Because of the high incidence of thrombosis with the possibility of fatal pulmonary embolism, the catheter should be removed once the patient is stabi ...
... 2-The femoral vein has a constant relationship to the medial side of the femoral artery just below the inguinal ligament and is easily cannulated. 3- Because of the high incidence of thrombosis with the possibility of fatal pulmonary embolism, the catheter should be removed once the patient is stabi ...
Blood Vessels Circulat.
... external and internal jugular veins and the subclavian vein; subclavian, external and internal jugulars, vertebral, and internal thoracic veins lead to it; drains the upper thoracic region and flows into the superior vena cava ...
... external and internal jugular veins and the subclavian vein; subclavian, external and internal jugulars, vertebral, and internal thoracic veins lead to it; drains the upper thoracic region and flows into the superior vena cava ...
ppt
... the inguinal ligament and is easily cannulated. 3- Because of the high incidence of thrombosis with the possibility of fatal pulmonary embolism, the catheter should be removed once the patient is stabilized. Anatomy of the Procedure 1-The skin of the thigh below the inguinal ligament is supplied by ...
... the inguinal ligament and is easily cannulated. 3- Because of the high incidence of thrombosis with the possibility of fatal pulmonary embolism, the catheter should be removed once the patient is stabilized. Anatomy of the Procedure 1-The skin of the thigh below the inguinal ligament is supplied by ...
Print this article - Nepal Journals Online
... termination and branching pattern. It may be totally absent and in such case, the transverse facial artery, ophthalmic artery and maxillary artery will supply its territory3,4. Ezure et al2 reported the complete absence of facial artery. There are different patterns of origin of superior thyroid, li ...
... termination and branching pattern. It may be totally absent and in such case, the transverse facial artery, ophthalmic artery and maxillary artery will supply its territory3,4. Ezure et al2 reported the complete absence of facial artery. There are different patterns of origin of superior thyroid, li ...
Variability of the obturator artery with its surgical implications
... Nevertheless the OA origin from the external iliac system was 22.72% (including the dual origin) with found to originate as direct branch of the external iliac artery in 9.09%. This is higher than the findings of oldies studies of 1.1-1.3% (BRAITWAITE, 1952; ROBERTS and KRISHINGNER, 1967) but simila ...
... Nevertheless the OA origin from the external iliac system was 22.72% (including the dual origin) with found to originate as direct branch of the external iliac artery in 9.09%. This is higher than the findings of oldies studies of 1.1-1.3% (BRAITWAITE, 1952; ROBERTS and KRISHINGNER, 1967) but simila ...
Development of HEART 3-ARTERIES
... • In rest of Body- right and left dorsal aortae • The two aortae fuse to form the dorsal aorta from which sprouts various branches. • Vitelline and umbilical arteries also get incorporated in aorta. • Development of aortic sac as the most distal part of the truncus arteriosus) ...
... • In rest of Body- right and left dorsal aortae • The two aortae fuse to form the dorsal aorta from which sprouts various branches. • Vitelline and umbilical arteries also get incorporated in aorta. • Development of aortic sac as the most distal part of the truncus arteriosus) ...
a case of fibular artery variation
... fibular artery and on the left side, lateral and medial plantar arteries were terminal branches of the fibular artery (Fig 2). The levels of the popliteal arterial branching were usual. The right anterior tibial artery and the left posterior tibial artery were weak calibre. Both of them ended near a ...
... fibular artery and on the left side, lateral and medial plantar arteries were terminal branches of the fibular artery (Fig 2). The levels of the popliteal arterial branching were usual. The right anterior tibial artery and the left posterior tibial artery were weak calibre. Both of them ended near a ...
Embryology of the Ophthalmic Artery: a Revived Concept
... We know there are many embryonic variations “normal or abnormal” in all parts of the human body including the vascular system. These variations ought to be seen in clinical practice. For simple example, the trigeminal artery is the persistence of the embryonic connection between the internal carotid ...
... We know there are many embryonic variations “normal or abnormal” in all parts of the human body including the vascular system. These variations ought to be seen in clinical practice. For simple example, the trigeminal artery is the persistence of the embryonic connection between the internal carotid ...
its pulse can be felt
... The deep plantar venous arch gives medial and lateral plantar veins. Medial and lateral plantar veins forms posterior tibial vein behind the medial malleolus. ...
... The deep plantar venous arch gives medial and lateral plantar veins. Medial and lateral plantar veins forms posterior tibial vein behind the medial malleolus. ...
A morphological study of the posterior communicating artery
... internal carotid artery. In 8 hemispheres (26.6%) a foetal type of posterior communicating artery was observed. It was 11.94 mm (8.03–15.07 mm) in length from the origin of the PCoA to the point of union with the posterior cerebral artery. The PCoA gave 5, 8 perforating branches (4–9). The distance ...
... internal carotid artery. In 8 hemispheres (26.6%) a foetal type of posterior communicating artery was observed. It was 11.94 mm (8.03–15.07 mm) in length from the origin of the PCoA to the point of union with the posterior cerebral artery. The PCoA gave 5, 8 perforating branches (4–9). The distance ...
Pancreas

The pancreas /ˈpæŋkriəs/ is a glandular organ in the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. It is an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide which circulate in the blood. The pancreas is also a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. These enzymes help to further break down the carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the chyme.