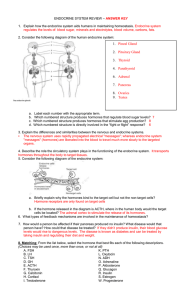
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
... The liver also plays a major role in the handling and processing of nutrients, which are carried to the liver in the blood from the small intestine. ...
... The liver also plays a major role in the handling and processing of nutrients, which are carried to the liver in the blood from the small intestine. ...
7.2 to 7.5 revision notes - Mr Cartlidge`s Saigon Science Blog
... Gastric juice added- contains protease to digest protein and hydrochloric acid to maintain pH 2 and kill bacteria. Receives pancreatic juice containing protease, lipase and amylase. Juice also contains sodium hydrogen carbonate which neutralizes acid from the stomach - giving pH of 8. Secretes pancr ...
... Gastric juice added- contains protease to digest protein and hydrochloric acid to maintain pH 2 and kill bacteria. Receives pancreatic juice containing protease, lipase and amylase. Juice also contains sodium hydrogen carbonate which neutralizes acid from the stomach - giving pH of 8. Secretes pancr ...
C H A P T E R 6 5
... enterocyte and thence into the blood. More than 99 per cent of the final protein digestive products that are absorbed are individual amino acids, with only rare absorption of peptides and very, very rare absorption of whole protein molecules. Even these very few absorbed molecules of whole protein c ...
... enterocyte and thence into the blood. More than 99 per cent of the final protein digestive products that are absorbed are individual amino acids, with only rare absorption of peptides and very, very rare absorption of whole protein molecules. Even these very few absorbed molecules of whole protein c ...
Digestive System
... Tube extended from the mouth to the anus with other organs attached to secrete fluids that aid in the digestion process Gastrointestinal tract (GI tract) is often a synonym, but should only refer to the stomach and intestine ...
... Tube extended from the mouth to the anus with other organs attached to secrete fluids that aid in the digestion process Gastrointestinal tract (GI tract) is often a synonym, but should only refer to the stomach and intestine ...
Endocrine system powerpoint
... Pancreas lies transverse in abdomen between kidneys and near duodenum. Composed of two types of tissue. Exocrine tissue - produces & secretes digestive juices into sm. intestine thru ducts Endocrine tissues pancreatic islets (islets of Langerhans) –produce insulin and glucagon ...
... Pancreas lies transverse in abdomen between kidneys and near duodenum. Composed of two types of tissue. Exocrine tissue - produces & secretes digestive juices into sm. intestine thru ducts Endocrine tissues pancreatic islets (islets of Langerhans) –produce insulin and glucagon ...
Endocrine Lecture Test Questions – Set 5
... Which of the following directly controls metabolic functions of all tissues located throughout the body: a. T4 b. thyrotropin release-stimulating hormone c. melanocyte stimulating hormone d. ACTH e. FSH ...
... Which of the following directly controls metabolic functions of all tissues located throughout the body: a. T4 b. thyrotropin release-stimulating hormone c. melanocyte stimulating hormone d. ACTH e. FSH ...
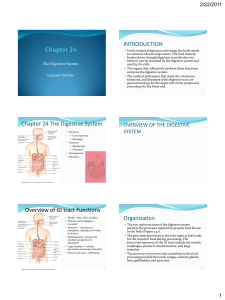
The Digestive System
... 4) Small Intestine (digestion chem, absorption) Associated organs: iii. PANCREAS: Produces pancreatic juice which is released into the duodenum via the pancreatic duct Sodium bicarbonate neutralizes chyme, leaving small intestine basic (pH ~ 9) 28 digestive enzymes, some of which are: a) Try ...
... 4) Small Intestine (digestion chem, absorption) Associated organs: iii. PANCREAS: Produces pancreatic juice which is released into the duodenum via the pancreatic duct Sodium bicarbonate neutralizes chyme, leaving small intestine basic (pH ~ 9) 28 digestive enzymes, some of which are: a) Try ...
digestion
... Sphincters – rings of muscle located along the digestive tract to control the direct and timing of movement ...
... Sphincters – rings of muscle located along the digestive tract to control the direct and timing of movement ...
Science - Heritage School
... environment. When these factors are out of balance, stomach cells are attacked. The result is an ulcer; this may require a change in diet, or surgery. The other end of the stomach also has a sphincter. When it relaxes, partially digested food moves into the small intestine. Pancreas/Liver- These are ...
... environment. When these factors are out of balance, stomach cells are attacked. The result is an ulcer; this may require a change in diet, or surgery. The other end of the stomach also has a sphincter. When it relaxes, partially digested food moves into the small intestine. Pancreas/Liver- These are ...
Liver: Histology
... Villi = within circular folds, small (0.5–1 mm long) hairlike vascularized projections called villi (singular = villus), giving mucosa a furry texture, being about 20 to 40 villi mm2, increasing surface area tremendously; mucosal epithelium, primarily composed of absorptive cells, covering villi, th ...
... Villi = within circular folds, small (0.5–1 mm long) hairlike vascularized projections called villi (singular = villus), giving mucosa a furry texture, being about 20 to 40 villi mm2, increasing surface area tremendously; mucosal epithelium, primarily composed of absorptive cells, covering villi, th ...
The DIGESTIVE System
... Secrete their contents (saliva) into ducts that empty into the mouth Parotid Glands - underneath the ears Submandibular Glands - under the ...
... Secrete their contents (saliva) into ducts that empty into the mouth Parotid Glands - underneath the ears Submandibular Glands - under the ...
File
... In the stomach… • gastric (digestive) juices are released • stomach walls churn and mix, partially digested food in the stomach is called chyme. • small amount of chyme enters duodenum at a time - controlled by pyloric sphincter • takes 2-4 hours for stomach to empty ...
... In the stomach… • gastric (digestive) juices are released • stomach walls churn and mix, partially digested food in the stomach is called chyme. • small amount of chyme enters duodenum at a time - controlled by pyloric sphincter • takes 2-4 hours for stomach to empty ...
Review for Digestive and Urinary System Test
... Review for Digestive and Urinary System Test 1. Mouth, Pharynx, Esophagus, Stomach, Small intestine, Large intestine, Rectum, Anus. 2. Primary teeth – Baby teeth, 20 in total: 8 incisors, 4 cuspids. 8 molars Secondary teeth – Adult teeth, 32 in total: 3rd set of molar may come in after age ...
... Review for Digestive and Urinary System Test 1. Mouth, Pharynx, Esophagus, Stomach, Small intestine, Large intestine, Rectum, Anus. 2. Primary teeth – Baby teeth, 20 in total: 8 incisors, 4 cuspids. 8 molars Secondary teeth – Adult teeth, 32 in total: 3rd set of molar may come in after age ...
Digestion - My Teacher Pages
... the mouth and winds through the body to the anus. • Organs next to the digestive tract also aid in the digestion of food through the secretions that ...
... the mouth and winds through the body to the anus. • Organs next to the digestive tract also aid in the digestion of food through the secretions that ...
1. Under influence of what hormone the absorbtion of Na+ increases
... substance for 15 min ( 37C ) the products of hydrolysis gave the positive Felling’s reaction.The action of what ferments of juice is the cause of forming products of hydrolysis, which were discovered by Felling’s reaction? Polypeptidases Tripsine, chimotripsine DNA-ase Maltose, lactose Lipase,prosp ...
... substance for 15 min ( 37C ) the products of hydrolysis gave the positive Felling’s reaction.The action of what ferments of juice is the cause of forming products of hydrolysis, which were discovered by Felling’s reaction? Polypeptidases Tripsine, chimotripsine DNA-ase Maltose, lactose Lipase,prosp ...
Your Digestive System
... The liver helps figure out how many nutrients will go to the rest of the body, and how many will stay behind in storage. – For example, the liver stores certain vitamins and a type of sugar your body uses for energy. ...
... The liver helps figure out how many nutrients will go to the rest of the body, and how many will stay behind in storage. – For example, the liver stores certain vitamins and a type of sugar your body uses for energy. ...
Chapter 5 Text
... Lubricates the mouth & food Dissolves food so taste receptors can be stimulated. Form Bolus Amylase breaks down starch, chemical digestion. Contains anti-bodies that kill bacteria. ...
... Lubricates the mouth & food Dissolves food so taste receptors can be stimulated. Form Bolus Amylase breaks down starch, chemical digestion. Contains anti-bodies that kill bacteria. ...
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... mineralcorticoids (aldosterone) and androgens.Medulla secretes substances that act as neurotransmitters on sympathetic nervous system. Pancreas: endocrine and exocrine functions Endocrine functions carried out by the Islets of Langerhan which produce insulin and glucagon (regulate blood glucose leve ...
... mineralcorticoids (aldosterone) and androgens.Medulla secretes substances that act as neurotransmitters on sympathetic nervous system. Pancreas: endocrine and exocrine functions Endocrine functions carried out by the Islets of Langerhan which produce insulin and glucagon (regulate blood glucose leve ...
Chapter 23 Digestive System
... – The three parts of the stomach are the fundus, body, and pylorus. – The stomach functions in digestion; its most important role is regulate the rate at which chyme is delivered to the small intestine. Slide 4 ...
... – The three parts of the stomach are the fundus, body, and pylorus. – The stomach functions in digestion; its most important role is regulate the rate at which chyme is delivered to the small intestine. Slide 4 ...
endocrine system review – answer key
... cells be located? The adrenal cortex to stimulate the release of its hormones. 6. What types of feedback mechanisms are involved in the maintenance of homeostasis? 7. How would a person be affected if their pancreas produced no insulin? What disease would that person have? How could that disease be ...
... cells be located? The adrenal cortex to stimulate the release of its hormones. 6. What types of feedback mechanisms are involved in the maintenance of homeostasis? 7. How would a person be affected if their pancreas produced no insulin? What disease would that person have? How could that disease be ...
1. Pineal Gland 2. Pituitary Gland 3. Thyroid 4. Parathyroid 6
... cells be located? The adrenal cortex to stimulate the release of its hormones. 6. What types of feedback mechanisms are involved in the maintenance of homeostasis? 7. How would a person be affected if their pancreas produced no insulin? What disease would that person have? How could that disease be ...
... cells be located? The adrenal cortex to stimulate the release of its hormones. 6. What types of feedback mechanisms are involved in the maintenance of homeostasis? 7. How would a person be affected if their pancreas produced no insulin? What disease would that person have? How could that disease be ...
The_Digestive_System notes
... Gastric Juices contain acids that break down food - secreted by gastric glands PEPSIN - most important digestive enzyme for breaking down food ...
... Gastric Juices contain acids that break down food - secreted by gastric glands PEPSIN - most important digestive enzyme for breaking down food ...
Pancreas

The pancreas /ˈpæŋkriəs/ is a glandular organ in the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. It is an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide which circulate in the blood. The pancreas is also a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. These enzymes help to further break down the carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the chyme.