Adrenal Disease: Review Questions
... This is a case of an “incidentaloma,” a mass found in imaging studies performed for other reasons. Patients usually have no symptoms related to the mass. The majority of these tumors are nonfunctioning, but a work-up is mandatory to ensure that no hormonal dysfunction exists. The usual tests ordered ...
... This is a case of an “incidentaloma,” a mass found in imaging studies performed for other reasons. Patients usually have no symptoms related to the mass. The majority of these tumors are nonfunctioning, but a work-up is mandatory to ensure that no hormonal dysfunction exists. The usual tests ordered ...
hirsuitism - The Association of Physicians of India
... adrenal androgen production as defined by increased 17-ketosteroid response to ACTH, with the adrenal being the primary source of androgen excess in about one half of those with adrenal hyperandrogenism . Women with PCOS are hyperinsulinemic and insulin resistant compared to age and weight-matched c ...
... adrenal androgen production as defined by increased 17-ketosteroid response to ACTH, with the adrenal being the primary source of androgen excess in about one half of those with adrenal hyperandrogenism . Women with PCOS are hyperinsulinemic and insulin resistant compared to age and weight-matched c ...
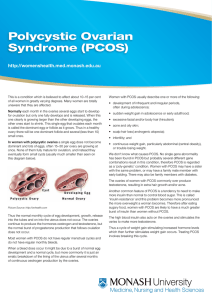
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)
... other ones start to shrink. This single egg that ovulates each month is called the dominant egg or follicle as it grows. Thus in a healthy ovary there will be one dominant follicle and several (less than 10) small ones. In women with polycystic ovaries a single egg does not become dominant and lots ...
... other ones start to shrink. This single egg that ovulates each month is called the dominant egg or follicle as it grows. Thus in a healthy ovary there will be one dominant follicle and several (less than 10) small ones. In women with polycystic ovaries a single egg does not become dominant and lots ...
aaa - E-Learning/An-Najah National University
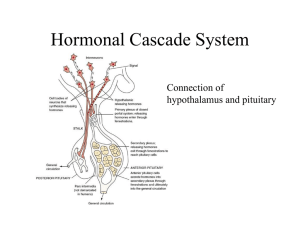
... prolactin production in the pituitary. High prolactin levels will inhibit gonadotrophin releasing hormone (GnRH) production in the hypothalamus, which is needed for LH and FSH production in the pituitary, needed for normal ovarian function thus causing amenorrhea. ...
... prolactin production in the pituitary. High prolactin levels will inhibit gonadotrophin releasing hormone (GnRH) production in the hypothalamus, which is needed for LH and FSH production in the pituitary, needed for normal ovarian function thus causing amenorrhea. ...
Hormonal Cascade System
... Steroid Biosynthesis • Begin by forming D5-pregnenolone • Further modifications for specific steroids • Involves cytochrome P450's ...
... Steroid Biosynthesis • Begin by forming D5-pregnenolone • Further modifications for specific steroids • Involves cytochrome P450's ...
Hormones - NeuroScience, Inc.
... of hormones produced by the thyroid gland, including triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). Another hormone, called thryroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), signals the thyroid gland to produce T3 and T4. T3 is much more potent than T4, however present in smaller quantities. Together, the thyroid horm ...
... of hormones produced by the thyroid gland, including triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). Another hormone, called thryroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), signals the thyroid gland to produce T3 and T4. T3 is much more potent than T4, however present in smaller quantities. Together, the thyroid horm ...
Adrenal Glands
... In response to a __________________, neurons of the ______________ nervous system carry a signal from the __________________ directly to the __________________ __________________. These neurons (rather than __________________) stimulate the adrenal medulla to secrete __________________ and a small a ...
... In response to a __________________, neurons of the ______________ nervous system carry a signal from the __________________ directly to the __________________ __________________. These neurons (rather than __________________) stimulate the adrenal medulla to secrete __________________ and a small a ...
Ch 11 The Endocrine System
... melatonin, important for maintaining Circadian rhythms (light and dark activity) ● Thymus Gland – large in young children, gradually shrinks with age, secretes thymosins, important to immune function ● Reproductive Glands – testes and ovaries ...
... melatonin, important for maintaining Circadian rhythms (light and dark activity) ● Thymus Gland – large in young children, gradually shrinks with age, secretes thymosins, important to immune function ● Reproductive Glands – testes and ovaries ...
FEMALE HORMONES and their activity
... FEMALE HORMONES and their activity Estrogen dominance is a primary cause of almost all female health problems, including: ...
... FEMALE HORMONES and their activity Estrogen dominance is a primary cause of almost all female health problems, including: ...
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
... Cholesterol: A natural substance that serves as a building block for cells and hormones and helps to carry fat through the blood vessels for use or storage in other parts of the body. Cysts: Sacs or pouches filled with fluid or other material. Diabetes Mellitus: A condition in which the levels of su ...
... Cholesterol: A natural substance that serves as a building block for cells and hormones and helps to carry fat through the blood vessels for use or storage in other parts of the body. Cysts: Sacs or pouches filled with fluid or other material. Diabetes Mellitus: A condition in which the levels of su ...
patient glossary
... POLYCYSTIC OVARIAN SYNDROME (PCOS) A condition whereby undeveloped follicles (cysts) form within the ovaries. It is seen in women with high estrogen and low progesterone levels, and/or high androgen (testosterone) and insulin levels. PREMENSTRUAL SYNDROME (PMS) A set of physical and emotional sympto ...
... POLYCYSTIC OVARIAN SYNDROME (PCOS) A condition whereby undeveloped follicles (cysts) form within the ovaries. It is seen in women with high estrogen and low progesterone levels, and/or high androgen (testosterone) and insulin levels. PREMENSTRUAL SYNDROME (PMS) A set of physical and emotional sympto ...
Organization of the Brain - Mr. Van Frachen's Web Page
... The Largest of the glands Regulates metabolism It produces the hormone Thyroxin. (Dysfunction: Hormone deficiency during development leads to stunted growth and mental retardation. Under secretion during adulthood leads to reduction of motivation. Over secretion results in high metabolism, weight lo ...
... The Largest of the glands Regulates metabolism It produces the hormone Thyroxin. (Dysfunction: Hormone deficiency during development leads to stunted growth and mental retardation. Under secretion during adulthood leads to reduction of motivation. Over secretion results in high metabolism, weight lo ...
Chapter 36 Integration: Endocrine Control I. The Endocrine System
... different tissues; they act locally and are swiftly degraded , which are secreted by exocrine glands, have targets outside the body; they integrate social ...
... different tissues; they act locally and are swiftly degraded , which are secreted by exocrine glands, have targets outside the body; they integrate social ...
Healthy Hair - HormoneBalance.org
... testosterone are replaced, the skin and scalp become healthier within days to weeks and new hair growth is noticeable within a month. Some people may be confused over the term ‘androgenic alopecia’. This refers to male pattern baldness and is not usually associated with testosterone or androgen exce ...
... testosterone are replaced, the skin and scalp become healthier within days to weeks and new hair growth is noticeable within a month. Some people may be confused over the term ‘androgenic alopecia’. This refers to male pattern baldness and is not usually associated with testosterone or androgen exce ...
The Endocrine System
... childhood and is important for maintaining a healthy body composition. In adults it is also important for maintaining muscle mass and bone mass. It can affect fat distribution in the body. ...
... childhood and is important for maintaining a healthy body composition. In adults it is also important for maintaining muscle mass and bone mass. It can affect fat distribution in the body. ...
The Endocrine System - Greer Middle College Charter
... melatonin, important for maintaining Circadian rhythms (light and dark activity) Thymus Gland – large in young children, gradually shrinks with age, secretes thymosins, important to immune function Reproductive Glands – testes and ovaries ...
... melatonin, important for maintaining Circadian rhythms (light and dark activity) Thymus Gland – large in young children, gradually shrinks with age, secretes thymosins, important to immune function Reproductive Glands – testes and ovaries ...
The Human Endocrine System: The Glands and Their Hormones
... Estrogen – stimulates development of the female reproductive system Progesterone – regulates the menstrual cycle Testosterone: Testosterone – stimulates development of the male reproductive system Thymus: Thymosin – stimulates development of T cells throughout childhood Pineal gland: Melat ...
... Estrogen – stimulates development of the female reproductive system Progesterone – regulates the menstrual cycle Testosterone: Testosterone – stimulates development of the male reproductive system Thymus: Thymosin – stimulates development of T cells throughout childhood Pineal gland: Melat ...
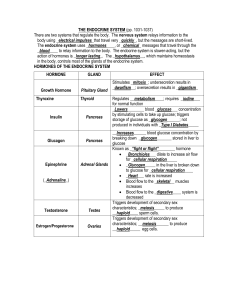
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM (pp
... Regulates __metabolism____; requires _iodine___ for normal function _Lowers________ blood _glucose___ concentration by stimulating cells to take up glucose; triggers storage of glucose as _glycogen______; not produced in individuals with _Type I Diabetes_____ ...
... Regulates __metabolism____; requires _iodine___ for normal function _Lowers________ blood _glucose___ concentration by stimulating cells to take up glucose; triggers storage of glucose as _glycogen______; not produced in individuals with _Type I Diabetes_____ ...
Name Endocrine system Write the letter of the correct match next to
... a. group of cells that produces and secretes chemicals ...
... a. group of cells that produces and secretes chemicals ...
Endocrine System
... melatonin, important for maintaining Circadian rhythms (light and dark activity) • Thymus Gland – large in young children, gradually shrinks with age, secretes thymosins, important to immune function • Reproductive Glands – testes and ovaries ...
... melatonin, important for maintaining Circadian rhythms (light and dark activity) • Thymus Gland – large in young children, gradually shrinks with age, secretes thymosins, important to immune function • Reproductive Glands – testes and ovaries ...
The Endocrine System
... Pituitary Gland – responsible for the secretion of many different hormones that affect various aspects of behavior such as the growth hormone Thyroid Gland – produces thyroxin which affects the body’s metabolism Adrenal Gland – the outer layer of the adrenal gland, or cortex, secretes cortical stero ...
... Pituitary Gland – responsible for the secretion of many different hormones that affect various aspects of behavior such as the growth hormone Thyroid Gland – produces thyroxin which affects the body’s metabolism Adrenal Gland – the outer layer of the adrenal gland, or cortex, secretes cortical stero ...