EMT 113 Chapter 2
... -COMMUTATOR : mechanical rectifier, which changes the AC voltage of the rotating conductors to DC voltage - BRUSHES : conduct the current from the commutator to the external circuit - WINDINGS •uniform magnetic flux is established by fixed poles mounted on the inside of the stationary number called ...
... -COMMUTATOR : mechanical rectifier, which changes the AC voltage of the rotating conductors to DC voltage - BRUSHES : conduct the current from the commutator to the external circuit - WINDINGS •uniform magnetic flux is established by fixed poles mounted on the inside of the stationary number called ...
LT3748 – 100V Isolated Flyback Controller
... switching scheme. The external N-channel MOSFET turns on and the inductor current increases until it reaches the VC pin-controlled current limit. After the external MOSFET is turned off, the voltage on the drain of the MOSFET rises to the output voltage multiplied by the primary-to-secondary transfo ...
... switching scheme. The external N-channel MOSFET turns on and the inductor current increases until it reaches the VC pin-controlled current limit. After the external MOSFET is turned off, the voltage on the drain of the MOSFET rises to the output voltage multiplied by the primary-to-secondary transfo ...
An Introduction to Electical Machinery Safety (Paul
... • A supply disconnecting device must be provided: For each incoming source of supply to a machine(s) direct connection or via a feeder system - feeder systems include conductor wires, conductor bars, slip-ring assemblies, flexible cable systems (reeled, festooned) or inductive power supply systems ...
... • A supply disconnecting device must be provided: For each incoming source of supply to a machine(s) direct connection or via a feeder system - feeder systems include conductor wires, conductor bars, slip-ring assemblies, flexible cable systems (reeled, festooned) or inductive power supply systems ...
(Selective).
... Coordination (Selective). Location of an overcurrent condition to restrict outages to the circuit or equipment affected, accomplished by the choice of overcurrent protective devices and their ratings or settings. • The result: NEC 700.27 and 701.18 require “device-todevice” coordination, whereas NEC ...
... Coordination (Selective). Location of an overcurrent condition to restrict outages to the circuit or equipment affected, accomplished by the choice of overcurrent protective devices and their ratings or settings. • The result: NEC 700.27 and 701.18 require “device-todevice” coordination, whereas NEC ...
finfet based sram design for low power applications
... disconnect the cell from the bit lines. The two cross coupled inverters formed by M1-M4 continue to reinforce each other as long as they are disconnected from the outside world. ii. Read - The read cycle starts by pre-charging both the bit lines to a logical 1 level and then asserting the word line, ...
... disconnect the cell from the bit lines. The two cross coupled inverters formed by M1-M4 continue to reinforce each other as long as they are disconnected from the outside world. ii. Read - The read cycle starts by pre-charging both the bit lines to a logical 1 level and then asserting the word line, ...
BH1721FVC - ROHM Semiconductor
... (Topr), etc., can break down devices, thus making impossible to identify breaking mode such as a short circuit or an open circuit. If any special mode exceeding the absolute maximum ratings is assumed, consideration should be given to take physical safety measures including the use of fuses, etc. 2) ...
... (Topr), etc., can break down devices, thus making impossible to identify breaking mode such as a short circuit or an open circuit. If any special mode exceeding the absolute maximum ratings is assumed, consideration should be given to take physical safety measures including the use of fuses, etc. 2) ...
Schneider MV Design Guide
... c Short-circuit power. The voltage, the rated current and the rated frequency are often known or can easily be defined, but how can we calculate the short-circuit power or current at a given point in an installation? Knowing the short-circuit power of the network allows us to choose the various part ...
... c Short-circuit power. The voltage, the rated current and the rated frequency are often known or can easily be defined, but how can we calculate the short-circuit power or current at a given point in an installation? Knowing the short-circuit power of the network allows us to choose the various part ...
ISO5451-Q1 High-CMTI 2.5-A and 5-A Isolated
... When the IGBT is turned off during normal operation with bipolar output supply, the output is hard clamp to VEE2. If the output supply is unipolar, an active Miller clamp can be used, allowing Miller current to sink across a low impedance path, preventing IGBT to be dynamically turned on during high ...
... When the IGBT is turned off during normal operation with bipolar output supply, the output is hard clamp to VEE2. If the output supply is unipolar, an active Miller clamp can be used, allowing Miller current to sink across a low impedance path, preventing IGBT to be dynamically turned on during high ...
Designing Single phase inverter - Faculty of Engineering - An
... Schottkey type, but make sure you specify one that can handle the full voltage difference and peak current. The switch just has to be able to handle the max voltage plus some for safety. Note that this design is meant for 'static' output currents, not for variable current draw designs. There is no f ...
... Schottkey type, but make sure you specify one that can handle the full voltage difference and peak current. The switch just has to be able to handle the max voltage plus some for safety. Note that this design is meant for 'static' output currents, not for variable current draw designs. There is no f ...
department of electrical engineering Subject information (overview of syllabus)
... transmission in communications: source coding, PCM, DPCM, delta modulation, bandwidth requirement of PCM, digital signalling format, multi-level signalling. Channel effect on symbol transmission and inter-symbol interference (ISI) control: ISI, eye diagram as a tool, raised cosine filtering, partial ...
... transmission in communications: source coding, PCM, DPCM, delta modulation, bandwidth requirement of PCM, digital signalling format, multi-level signalling. Channel effect on symbol transmission and inter-symbol interference (ISI) control: ISI, eye diagram as a tool, raised cosine filtering, partial ...
Snubber Circuits
... A turn-on snubber as shown in Figure 7 is used to reduce voltage across the BJT while the current builds up. The reduction in the voltage across the transistor during turnon is due to the voltage drop across the snubber inductance LS. When the transistor turns off, the energy stored in the snubber i ...
... A turn-on snubber as shown in Figure 7 is used to reduce voltage across the BJT while the current builds up. The reduction in the voltage across the transistor during turnon is due to the voltage drop across the snubber inductance LS. When the transistor turns off, the energy stored in the snubber i ...
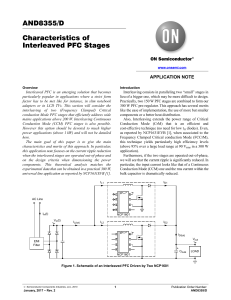
Characteristics of Interleaved PFC Stages
... ON Semiconductor and are trademarks of Semiconductor Components Industries, LLC dba ON Semiconductor or its subsidiaries in the United States and/or other countries. ON Semiconductor owns the rights to a number of patents, trademarks, copyrights, trade secrets, and other intellectual property. A lis ...
... ON Semiconductor and are trademarks of Semiconductor Components Industries, LLC dba ON Semiconductor or its subsidiaries in the United States and/or other countries. ON Semiconductor owns the rights to a number of patents, trademarks, copyrights, trade secrets, and other intellectual property. A lis ...
PKB 4000B series Intermediate Bus Converters Input 36
... the voltage strength requirement for basic insulation according to IEC/EN/UL 60950-1. It is recommended to use a slow blow fuse at the input of each DC/DC converter. If an input filter is used in the circuit the fuse should be placed in front of the input filter. In the rare event of a component pro ...
... the voltage strength requirement for basic insulation according to IEC/EN/UL 60950-1. It is recommended to use a slow blow fuse at the input of each DC/DC converter. If an input filter is used in the circuit the fuse should be placed in front of the input filter. In the rare event of a component pro ...
BD9A300MUV
... 1ch Synchronous Buck DC/DC Converter BD9A300MUV Description BD9A300MUV is a synchronous buck switching regulator with built-in low On-resistance power MOSFETs. It is capable of providing current up to 3A. The SLLMTM control provides excellent efficiency characteristics in light-load conditions whi ...
... 1ch Synchronous Buck DC/DC Converter BD9A300MUV Description BD9A300MUV is a synchronous buck switching regulator with built-in low On-resistance power MOSFETs. It is capable of providing current up to 3A. The SLLMTM control provides excellent efficiency characteristics in light-load conditions whi ...
Characterization of an n-type 4 kV Silicon GTO for pulsed power
... spark/gas-type. These types of devices boast high voltage and high current operation, making them quite desirable for pulsed power applications. Gas/spark-type switching devices do have several intrinsic deficiencies; specifically high conduction losses which must be dealt with via exhaustive coolin ...
... spark/gas-type. These types of devices boast high voltage and high current operation, making them quite desirable for pulsed power applications. Gas/spark-type switching devices do have several intrinsic deficiencies; specifically high conduction losses which must be dealt with via exhaustive coolin ...
- Pcpolytechnic
... • The induction motor operates on the principle of rotating magnetic field(RMF) which is produced by the stator winding of the induction motor in the air gap between the stator and the rotor. • The stator is a three phase stationary winding which can be either star connected or delta connected. • Wh ...
... • The induction motor operates on the principle of rotating magnetic field(RMF) which is produced by the stator winding of the induction motor in the air gap between the stator and the rotor. • The stator is a three phase stationary winding which can be either star connected or delta connected. • Wh ...
Calculating AC Line Voltage Drop for S230
... Circuit length: There is often little control over circuit length, but center-feeding the dedicated branch circuit significantly reduces voltage rise within the branch, as described in Advantages of CenterFeeding the AC Branch Circuits. ...
... Circuit length: There is often little control over circuit length, but center-feeding the dedicated branch circuit significantly reduces voltage rise within the branch, as described in Advantages of CenterFeeding the AC Branch Circuits. ...
2.5 Electrical Power 2.5.1 Class 1E Emergency Power Supply System
... EPSS switchgear, load centers, MCCs, and transformers listed in Table 2.5.1-2 are rated to withstand fault currents for the time required to clear the fault from its power source. ...
... EPSS switchgear, load centers, MCCs, and transformers listed in Table 2.5.1-2 are rated to withstand fault currents for the time required to clear the fault from its power source. ...
Power engineering

Power engineering, also called power systems engineering, is a subfield of energy engineering that deals with the generation, transmission, distribution and utilization of electric power and the electrical devices connected to such systems including generators, motors and transformers. Although much of the field is concerned with the problems of three-phase AC power – the standard for large-scale power transmission and distribution across the modern world – a significant fraction of the field is concerned with the conversion between AC and DC power and the development of specialized power systems such as those used in aircraft or for electric railway networks. It was a subfield of electrical engineering before the emergence of energy engineering.Electricity became a subject of scientific interest in the late 17th century with the work of William Gilbert. Over the next two centuries a number of important discoveries were made including the incandescent light bulb and the voltaic pile. Probably the greatest discovery with respect to power engineering came from Michael Faraday who in 1831 discovered that a change in magnetic flux induces an electromotive force in a loop of wire—a principle known as electromagnetic induction that helps explain how generators and transformers work.In 1881 two electricians built the world's first power station at Godalming in England. The station employed two waterwheels to produce an alternating current that was used to supply seven Siemens arc lamps at 250 volts and thirty-four incandescent lamps at 40 volts. However supply was intermittent and in 1882 Thomas Edison and his company, The Edison Electric Light Company, developed the first steam-powered electric power station on Pearl Street in New York City. The Pearl Street Station consisted of several generators and initially powered around 3,000 lamps for 59 customers. The power station used direct current and operated at a single voltage. Since the direct current power could not be easily transformed to the higher voltages necessary to minimise power loss during transmission, the possible distance between the generators and load was limited to around half-a-mile (800 m).That same year in London Lucien Gaulard and John Dixon Gibbs demonstrated the first transformer suitable for use in a real power system. The practical value of Gaulard and Gibbs' transformer was demonstrated in 1884 at Turin where the transformer was used to light up forty kilometres (25 miles) of railway from a single alternating current generator. Despite the success of the system, the pair made some fundamental mistakes. Perhaps the most serious was connecting the primaries of the transformers in series so that switching one lamp on or off would affect other lamps further down the line. Following the demonstration George Westinghouse, an American entrepreneur, imported a number of the transformers along with a Siemens generator and set his engineers to experimenting with them in the hopes of improving them for use in a commercial power system.One of Westinghouse's engineers, William Stanley, recognised the problem with connecting transformers in series as opposed to parallel and also realised that making the iron core of a transformer a fully enclosed loop would improve the voltage regulation of the secondary winding. Using this knowledge he built a much improved alternating current power system at Great Barrington, Massachusetts in 1886. In 1885 the Italian physicist and electrical engineer Galileo Ferraris demonstrated an induction motor and in 1887 and 1888 the Serbian-American engineer Nikola Tesla filed a range of patents related to power systems including one for a practical two-phase induction motor which Westinghouse licensed for his AC system.By 1890 the power industry had flourished and power companies had built thousands of power systems (both direct and alternating current) in the United States and Europe – these networks were effectively dedicated to providing electric lighting. During this time a fierce rivalry in the US known as the ""War of Currents"" emerged between Edison and Westinghouse over which form of transmission (direct or alternating current) was superior. In 1891, Westinghouse installed the first major power system that was designed to drive an electric motor and not just provide electric lighting. The installation powered a 100 horsepower (75 kW) synchronous motor at Telluride, Colorado with the motor being started by a Tesla induction motor. On the other side of the Atlantic, Oskar von Miller built a 20 kV 176 km three-phase transmission line from Lauffen am Neckar to Frankfurt am Main for the Electrical Engineering Exhibition in Frankfurt. In 1895, after a protracted decision-making process, the Adams No. 1 generating station at Niagara Falls began transmitting three-phase alternating current power to Buffalo at 11 kV. Following completion of the Niagara Falls project, new power systems increasingly chose alternating current as opposed to direct current for electrical transmission.Although the 1880s and 1890s were seminal decades in the field, developments in power engineering continued throughout the 20th and 21st century. In 1936 the first commercial high-voltage direct current (HVDC) line using mercury-arc valves was built between Schenectady and Mechanicville, New York. HVDC had previously been achieved by installing direct current generators in series (a system known as the Thury system) although this suffered from serious reliability issues. In 1957 Siemens demonstrated the first solid-state rectifier (solid-state rectifiers are now the standard for HVDC systems) however it was not until the early 1970s that this technology was used in commercial power systems. In 1959 Westinghouse demonstrated the first circuit breaker that used SF6 as the interrupting medium. SF6 is a far superior dielectric to air and, in recent times, its use has been extended to produce far more compact switching equipment (known as switchgear) and transformers. Many important developments also came from extending innovations in the ICT field to the power engineering field. For example, the development of computers meant load flow studies could be run more efficiently allowing for much better planning of power systems. Advances in information technology and telecommunication also allowed for much better remote control of the power system's switchgear and generators.