FEEDER PROTECTION SySTEM Economical and compact feeder
... • Small footprint and compact design - With or without display, fits into standard Power Control Center buckets • Ease of use - EnerVista™ compatible ...
... • Small footprint and compact design - With or without display, fits into standard Power Control Center buckets • Ease of use - EnerVista™ compatible ...
WT 1600 Total Solution Numerical, Waveform, and Trend Displays
... • Evaluation of characteristics at motor startup including torque and rpms (requires the optional motor evaluation function) • Measurement of rapidly fluctuating secondary voltage and lamp current when a light is turned on ...
... • Evaluation of characteristics at motor startup including torque and rpms (requires the optional motor evaluation function) • Measurement of rapidly fluctuating secondary voltage and lamp current when a light is turned on ...
BD9031FV-C
... Also, be certain to ascertain the operating temperature, load range and MOSFET conditions for the application in which the capacitor will be used, since capacitor performance is heavily dependent on the application’s input power characteristics, substrate wiring and MOSFET gate drain capacity (4) Se ...
... Also, be certain to ascertain the operating temperature, load range and MOSFET conditions for the application in which the capacitor will be used, since capacitor performance is heavily dependent on the application’s input power characteristics, substrate wiring and MOSFET gate drain capacity (4) Se ...
THE FUNDAMENTALS OF AC ELECTRIC INDUCTION MOTOR
... and current are at rated voltage and frequency. Application at other than nameplate voltage will likely produce different performance. It is common for manufacturers to nameplate a wide variety of voltages on one motor nameplate. A common example is a motor wound for 230 and 460 V (230/460 V) but op ...
... and current are at rated voltage and frequency. Application at other than nameplate voltage will likely produce different performance. It is common for manufacturers to nameplate a wide variety of voltages on one motor nameplate. A common example is a motor wound for 230 and 460 V (230/460 V) but op ...
Aalborg Universitet Connected Inverter based on Impedance Based Harmonic Analysis
... kind of harmonic compensation methods have been used in the different topologies [6, 20, 21]. In particular, the most reliable method for harmonic compensation is to increase the gain of the current controller at each harmonic frequency. Hence, only the proportional resonant controller will be consi ...
... kind of harmonic compensation methods have been used in the different topologies [6, 20, 21]. In particular, the most reliable method for harmonic compensation is to increase the gain of the current controller at each harmonic frequency. Hence, only the proportional resonant controller will be consi ...
4.5V to 40V Input Automotive Flyback/Boost/SEPIC Power-Supply Controllers General Description Features
... The controllers integrate all the building blocks necessary for implementing fixed-frequency isolated/nonisolated power supplies. The general-purpose boost, flyback, forward, and SEPIC converters can be designed with ease around the MAX15004/MAX15005. The current-mode control architecture offers exc ...
... The controllers integrate all the building blocks necessary for implementing fixed-frequency isolated/nonisolated power supplies. The general-purpose boost, flyback, forward, and SEPIC converters can be designed with ease around the MAX15004/MAX15005. The current-mode control architecture offers exc ...
Evaluation Board Procedure Document
... (Appendix A) (Appendix B) (Appendix C) (Appendix D) (Appendix E) (Appendix F) ...
... (Appendix A) (Appendix B) (Appendix C) (Appendix D) (Appendix E) (Appendix F) ...
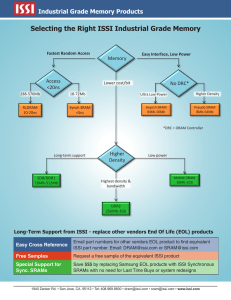
Industrial Grade Memory Products Brochure
... Typical Industrial System Product Life Cycle High-mix, low volume industrial market segments have special needs in terms of industry specifications, strict qualification cycles, long-life requirements (without product changes permitted), and extremely long in-field use with the highest reliability s ...
... Typical Industrial System Product Life Cycle High-mix, low volume industrial market segments have special needs in terms of industry specifications, strict qualification cycles, long-life requirements (without product changes permitted), and extremely long in-field use with the highest reliability s ...
IOSR Journal of VLSI and Signal Processing (IOSR-JVSP)
... equal to the standby leakage component. Hence Present day research is more focused on reduction of runtime leakage current .we present a novel runtime leakage reduction for 70nm technology. As an attempt to save the leakage power in the active mode, run-time power gating is explored at various desig ...
... equal to the standby leakage component. Hence Present day research is more focused on reduction of runtime leakage current .we present a novel runtime leakage reduction for 70nm technology. As an attempt to save the leakage power in the active mode, run-time power gating is explored at various desig ...
APPLICATION NOTE U-134
... There are two modulation processes in an active power factor corrector. The first is the input diode bridge and the second is the multiplier, divider, squarer circuit. Each modulation process generates cross products, harmonics or sidebands between the two inputs. The description of these mathematic ...
... There are two modulation processes in an active power factor corrector. The first is the input diode bridge and the second is the multiplier, divider, squarer circuit. Each modulation process generates cross products, harmonics or sidebands between the two inputs. The description of these mathematic ...
INDUSTRIAL AND POWER ELECTRONICS E
... to another AC waveform of a lower frequency, synthesizing the output waveform from segments of the AC supply without an intermediate direct-current link (Dorf 1993, pp. 2241–2243 and Lander 1993, p. 181). They are most commonly used in three phase applications. In most power systems, the amplitude a ...
... to another AC waveform of a lower frequency, synthesizing the output waveform from segments of the AC supply without an intermediate direct-current link (Dorf 1993, pp. 2241–2243 and Lander 1993, p. 181). They are most commonly used in three phase applications. In most power systems, the amplitude a ...
Steady State Operation and Control of Power
... then to distribution systems and finally to the loads. Therefore, distribution systems were designed as radial systems; and many operation and control in distribution systems, such as voltage control and protection, are based on the assumption that distribution systems are radial. In a radial distri ...
... then to distribution systems and finally to the loads. Therefore, distribution systems were designed as radial systems; and many operation and control in distribution systems, such as voltage control and protection, are based on the assumption that distribution systems are radial. In a radial distri ...
Tesla coil - 50Webs.com
... enthusiasts and has proven very effective of time. This circuit is called a Terry Filter named after the person that developed it Terry Fritz. Below is the circuit diagram of the Terry Filter for 9kV, 12kV and 15kV Tesla coils. ...
... enthusiasts and has proven very effective of time. This circuit is called a Terry Filter named after the person that developed it Terry Fritz. Below is the circuit diagram of the Terry Filter for 9kV, 12kV and 15kV Tesla coils. ...
Motors on Variable Frequency Drives
... NMC’s INVERTER GRADE® insulation system is the first line of defense against corona and phase to phase faults that can be common when a motor is powered using a PWM waveform. The INVERTER GRADE® insulation system is standard on all of NMC’s Inverter Duty products. Along with the INVERTER GRADE® insu ...
... NMC’s INVERTER GRADE® insulation system is the first line of defense against corona and phase to phase faults that can be common when a motor is powered using a PWM waveform. The INVERTER GRADE® insulation system is standard on all of NMC’s Inverter Duty products. Along with the INVERTER GRADE® insu ...
Manual
... Only Switchgear style regulators bearing Crouse-Hinds catalog number series 82XSGS are covered by this manual. Refer to Figure 1 for complete part number information. Instructions for standard options are provided as supplements to this manual. ...
... Only Switchgear style regulators bearing Crouse-Hinds catalog number series 82XSGS are covered by this manual. Refer to Figure 1 for complete part number information. Instructions for standard options are provided as supplements to this manual. ...
MAX16929 Automotive TFT-LCD Power Supply with Boost Converter and Gate Voltage Regulators
... 2mA sink current, TA = +25NC ...
... 2mA sink current, TA = +25NC ...
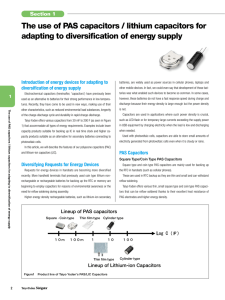
The use of PAS capacitors / lithium capacitors for adapting to
... other mobile devices. In fact, we could even say that development of those bat- ...
... other mobile devices. In fact, we could even say that development of those bat- ...
EVSTF09-10-TF6-01
... For typical vehicle applications it should be noted that LiBs are not using their full physical capacity range, but only a limited window, primarily to ensure reliability, improve degradation and achieve high charging cycle numbers. The sizes of such windows depend on used LiB technologies and the t ...
... For typical vehicle applications it should be noted that LiBs are not using their full physical capacity range, but only a limited window, primarily to ensure reliability, improve degradation and achieve high charging cycle numbers. The sizes of such windows depend on used LiB technologies and the t ...
Zener Diode
... output voltage at a constant value (DC voltage). RS is to limit the zener current, IZ so that it is less than the maximum current, IZM (to avoid the zener diode from broken). RS ...
... output voltage at a constant value (DC voltage). RS is to limit the zener current, IZ so that it is less than the maximum current, IZM (to avoid the zener diode from broken). RS ...
troubleshooting and maintenance guide
... lower output voltage is produced on the secondary side of the transformer. The primary of the transformer consists of at least two inputs (or taps) and may contain several more. Each input tap is designed to produce a calculated voltage on the output windings called a secondary. Various switches are ...
... lower output voltage is produced on the secondary side of the transformer. The primary of the transformer consists of at least two inputs (or taps) and may contain several more. Each input tap is designed to produce a calculated voltage on the output windings called a secondary. Various switches are ...
P82467
... 5. The MT-12/24 model is supplied with four snap-in covers to hide the mounting holes and provide an attractive installation. The snap-in covers are interchangeable and have slots on each end so they can be removed if necessary (by prying them up with a thin blade screwdriver). To insert snap-in cov ...
... 5. The MT-12/24 model is supplied with four snap-in covers to hide the mounting holes and provide an attractive installation. The snap-in covers are interchangeable and have slots on each end so they can be removed if necessary (by prying them up with a thin blade screwdriver). To insert snap-in cov ...
PAH-28/12.5-D48NB-C Datasheet
... applications, wireless networks, and telecom applications. The baseplate provides a means for conduction cooling in demanding thermal environment conditions. ...
... applications, wireless networks, and telecom applications. The baseplate provides a means for conduction cooling in demanding thermal environment conditions. ...
Aalborg Universitet Microgrids
... sources (RESs) including micro-turbines, fuel cells, photovoltaic (PV) systems and wind energy systems have been widely used in the distributed power systems in the past decades [1], [2]. The DG units play an important role in reducing pollution, decreasing power transmission losses and improving lo ...
... sources (RESs) including micro-turbines, fuel cells, photovoltaic (PV) systems and wind energy systems have been widely used in the distributed power systems in the past decades [1], [2]. The DG units play an important role in reducing pollution, decreasing power transmission losses and improving lo ...
Power engineering

Power engineering, also called power systems engineering, is a subfield of energy engineering that deals with the generation, transmission, distribution and utilization of electric power and the electrical devices connected to such systems including generators, motors and transformers. Although much of the field is concerned with the problems of three-phase AC power – the standard for large-scale power transmission and distribution across the modern world – a significant fraction of the field is concerned with the conversion between AC and DC power and the development of specialized power systems such as those used in aircraft or for electric railway networks. It was a subfield of electrical engineering before the emergence of energy engineering.Electricity became a subject of scientific interest in the late 17th century with the work of William Gilbert. Over the next two centuries a number of important discoveries were made including the incandescent light bulb and the voltaic pile. Probably the greatest discovery with respect to power engineering came from Michael Faraday who in 1831 discovered that a change in magnetic flux induces an electromotive force in a loop of wire—a principle known as electromagnetic induction that helps explain how generators and transformers work.In 1881 two electricians built the world's first power station at Godalming in England. The station employed two waterwheels to produce an alternating current that was used to supply seven Siemens arc lamps at 250 volts and thirty-four incandescent lamps at 40 volts. However supply was intermittent and in 1882 Thomas Edison and his company, The Edison Electric Light Company, developed the first steam-powered electric power station on Pearl Street in New York City. The Pearl Street Station consisted of several generators and initially powered around 3,000 lamps for 59 customers. The power station used direct current and operated at a single voltage. Since the direct current power could not be easily transformed to the higher voltages necessary to minimise power loss during transmission, the possible distance between the generators and load was limited to around half-a-mile (800 m).That same year in London Lucien Gaulard and John Dixon Gibbs demonstrated the first transformer suitable for use in a real power system. The practical value of Gaulard and Gibbs' transformer was demonstrated in 1884 at Turin where the transformer was used to light up forty kilometres (25 miles) of railway from a single alternating current generator. Despite the success of the system, the pair made some fundamental mistakes. Perhaps the most serious was connecting the primaries of the transformers in series so that switching one lamp on or off would affect other lamps further down the line. Following the demonstration George Westinghouse, an American entrepreneur, imported a number of the transformers along with a Siemens generator and set his engineers to experimenting with them in the hopes of improving them for use in a commercial power system.One of Westinghouse's engineers, William Stanley, recognised the problem with connecting transformers in series as opposed to parallel and also realised that making the iron core of a transformer a fully enclosed loop would improve the voltage regulation of the secondary winding. Using this knowledge he built a much improved alternating current power system at Great Barrington, Massachusetts in 1886. In 1885 the Italian physicist and electrical engineer Galileo Ferraris demonstrated an induction motor and in 1887 and 1888 the Serbian-American engineer Nikola Tesla filed a range of patents related to power systems including one for a practical two-phase induction motor which Westinghouse licensed for his AC system.By 1890 the power industry had flourished and power companies had built thousands of power systems (both direct and alternating current) in the United States and Europe – these networks were effectively dedicated to providing electric lighting. During this time a fierce rivalry in the US known as the ""War of Currents"" emerged between Edison and Westinghouse over which form of transmission (direct or alternating current) was superior. In 1891, Westinghouse installed the first major power system that was designed to drive an electric motor and not just provide electric lighting. The installation powered a 100 horsepower (75 kW) synchronous motor at Telluride, Colorado with the motor being started by a Tesla induction motor. On the other side of the Atlantic, Oskar von Miller built a 20 kV 176 km three-phase transmission line from Lauffen am Neckar to Frankfurt am Main for the Electrical Engineering Exhibition in Frankfurt. In 1895, after a protracted decision-making process, the Adams No. 1 generating station at Niagara Falls began transmitting three-phase alternating current power to Buffalo at 11 kV. Following completion of the Niagara Falls project, new power systems increasingly chose alternating current as opposed to direct current for electrical transmission.Although the 1880s and 1890s were seminal decades in the field, developments in power engineering continued throughout the 20th and 21st century. In 1936 the first commercial high-voltage direct current (HVDC) line using mercury-arc valves was built between Schenectady and Mechanicville, New York. HVDC had previously been achieved by installing direct current generators in series (a system known as the Thury system) although this suffered from serious reliability issues. In 1957 Siemens demonstrated the first solid-state rectifier (solid-state rectifiers are now the standard for HVDC systems) however it was not until the early 1970s that this technology was used in commercial power systems. In 1959 Westinghouse demonstrated the first circuit breaker that used SF6 as the interrupting medium. SF6 is a far superior dielectric to air and, in recent times, its use has been extended to produce far more compact switching equipment (known as switchgear) and transformers. Many important developments also came from extending innovations in the ICT field to the power engineering field. For example, the development of computers meant load flow studies could be run more efficiently allowing for much better planning of power systems. Advances in information technology and telecommunication also allowed for much better remote control of the power system's switchgear and generators.