Endocrine System Study Questions with answers
... 17. Discuss the adrenal glands. How are they structured? What hormones do they secrete? The adrenal glands are two organs (the adrenal medulla and adrenal cortex) which sit on top of the kidneys. The adrenal cortex functions as a gland. It produces three groups of steroid hormones: mineralocorticoi ...
... 17. Discuss the adrenal glands. How are they structured? What hormones do they secrete? The adrenal glands are two organs (the adrenal medulla and adrenal cortex) which sit on top of the kidneys. The adrenal cortex functions as a gland. It produces three groups of steroid hormones: mineralocorticoi ...
Animal Hormones
... • mediate development of reproductive organs in fetus • mediate sexual maturation & development of secondary sexual characteristics ...
... • mediate development of reproductive organs in fetus • mediate sexual maturation & development of secondary sexual characteristics ...
Endocrine Emergencies
... o The anterior pituitary secretes several hormones: adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH), prolactin, growth hormone (GH), TSH and gonadotrophins (luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) o The posterior pituitary, actually an extension of the hypothalamus, secretes vasopressin ...
... o The anterior pituitary secretes several hormones: adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH), prolactin, growth hormone (GH), TSH and gonadotrophins (luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) o The posterior pituitary, actually an extension of the hypothalamus, secretes vasopressin ...
Anterior Pituitary hormones
... • TSH - stimulates release of hormones from thyroid • ACTH - stimulates release of hormones from adrenal cortex • growth hormone - stimulate growth of somatic tissues • FSH - stimulates gamete formation and follicle development • luteining hormone - affects corpus luteum & Leydig cells • prolactin - ...
... • TSH - stimulates release of hormones from thyroid • ACTH - stimulates release of hormones from adrenal cortex • growth hormone - stimulate growth of somatic tissues • FSH - stimulates gamete formation and follicle development • luteining hormone - affects corpus luteum & Leydig cells • prolactin - ...
Thyroid Hormones
... Endocrine hormones are endogenous chemical mediators that are made at one site, enter the bloodstream, and affect the function of distant organ or of an entire organism ◦ the “wi-fi internet of the human body” ...
... Endocrine hormones are endogenous chemical mediators that are made at one site, enter the bloodstream, and affect the function of distant organ or of an entire organism ◦ the “wi-fi internet of the human body” ...
Endocrine Color Sheet Questions
... Assignment: Read the overview on the Coloring Activity and color when instructed to do so. Then answer the questions below. 1. The endocrine glands are__ductless_glands that secrete _hormones_ directly into body fluids. The job of hormones is to help the body maintain _homeostasis_also known as biol ...
... Assignment: Read the overview on the Coloring Activity and color when instructed to do so. Then answer the questions below. 1. The endocrine glands are__ductless_glands that secrete _hormones_ directly into body fluids. The job of hormones is to help the body maintain _homeostasis_also known as biol ...
The Endocrine System Coloring Activities
... Assignment: Read the overview on the Coloring Activity and color when instructed to do so. Then answer the questions below. 1. The endocrine glands are__ductless_glands that secrete _hormones_ directly into body fluids. The job of hormones is to help the body maintain _homeostasis_also known as biol ...
... Assignment: Read the overview on the Coloring Activity and color when instructed to do so. Then answer the questions below. 1. The endocrine glands are__ductless_glands that secrete _hormones_ directly into body fluids. The job of hormones is to help the body maintain _homeostasis_also known as biol ...
File - Biology with Radjewski
... • Secrete substances into a duct or internal body cavity that communicates with the external world • Example: saliva, sweat ...
... • Secrete substances into a duct or internal body cavity that communicates with the external world • Example: saliva, sweat ...
thyroid gland - Uplift Education
... Reproductive Glands – testes and ovaries – testosterone, progesterone, estrogen ...
... Reproductive Glands – testes and ovaries – testosterone, progesterone, estrogen ...
Slide 1
... that is produced in the hypothalamus and transmitted to the anterior lobe commands release of hormones to their target cells – Posterior: storage area for ...
... that is produced in the hypothalamus and transmitted to the anterior lobe commands release of hormones to their target cells – Posterior: storage area for ...
Notes Chapter 51 Endocrine System
... 1) Describe how hormones work with the feedback system to maintain homeostasis a) The endocrine system consists of glands that transmit chemical messengers throughout the body. These chemical messengers, called hormones, circulate in the bloodstream and affect many types of body cells. b) Types of G ...
... 1) Describe how hormones work with the feedback system to maintain homeostasis a) The endocrine system consists of glands that transmit chemical messengers throughout the body. These chemical messengers, called hormones, circulate in the bloodstream and affect many types of body cells. b) Types of G ...
Chapter 45 Student Guided Notes
... ○ In response to stress, glucocorticoids make more glucose available as fuel AND helps make glucose from non-carbohydrate sources such as fats and proteins this helps in long term environmental issues ...
... ○ In response to stress, glucocorticoids make more glucose available as fuel AND helps make glucose from non-carbohydrate sources such as fats and proteins this helps in long term environmental issues ...
Bolt ModEP7e LG03.9-12B
... the threshold. The neuron’s reaction is an all-or-none response. The impulse, called the action potential, is a brief electrical charge that travels down the axon. Its speed is enhanced with the help of a fatty sheath called myelin. ♦Lecture: The Brain’s Inner Workings CD ♦Exercises: Neural Transmi ...
... the threshold. The neuron’s reaction is an all-or-none response. The impulse, called the action potential, is a brief electrical charge that travels down the axon. Its speed is enhanced with the help of a fatty sheath called myelin. ♦Lecture: The Brain’s Inner Workings CD ♦Exercises: Neural Transmi ...
Endocrine System
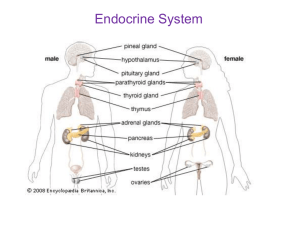
... Endocrine System A. Endocrine System: Overview 1. Endocrine system: Body's 2nd great control system; influences cellular metabolism via hormones 2. Endocrine glands: Pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, pineal, and thymus 3. Pancreas & Gonads produce hormones and exocrine products 4. Hypothalam ...
... Endocrine System A. Endocrine System: Overview 1. Endocrine system: Body's 2nd great control system; influences cellular metabolism via hormones 2. Endocrine glands: Pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, pineal, and thymus 3. Pancreas & Gonads produce hormones and exocrine products 4. Hypothalam ...
the endocrine system
... It is an organ that develops a secretion which performs specific functions. ...
... It is an organ that develops a secretion which performs specific functions. ...
9b-9c-9i LN - Walnut High School
... – What is the function of the pituitary gland? • The pituitary gland secretes nine hormones that directly regulate many body functions and controls the actions of several other endocrine glands. – The _______________ ________ is a structure at the base of the skull. – The gland is divided into two p ...
... – What is the function of the pituitary gland? • The pituitary gland secretes nine hormones that directly regulate many body functions and controls the actions of several other endocrine glands. – The _______________ ________ is a structure at the base of the skull. – The gland is divided into two p ...
Lesson Overview
... insulin, a condition known as diabetes mellitus occurs. The very high blood glucose levels that result from diabetes can damage almost every system and cell in the body. ...
... insulin, a condition known as diabetes mellitus occurs. The very high blood glucose levels that result from diabetes can damage almost every system and cell in the body. ...
chapter 14-the endocrine system
... A. This system is composed of glands that produce and release special chemicals known as hormones. Hormones are special chemicals that function by regulating processes in the human body. B. Hormones function by effecting special target cells in the body. C. Hormones secreted by endocrine glands are ...
... A. This system is composed of glands that produce and release special chemicals known as hormones. Hormones are special chemicals that function by regulating processes in the human body. B. Hormones function by effecting special target cells in the body. C. Hormones secreted by endocrine glands are ...
Endocrine System - Bellefonte Area School District
... There are currently over 84,000 commercial synthetic chemical substances in use around the world. At least 30,000 have been introduced into the U.S. environment since 1979. We do not know the extent to which they can interfere with the endocrine system and cause endocrine system diseases. Based on o ...
... There are currently over 84,000 commercial synthetic chemical substances in use around the world. At least 30,000 have been introduced into the U.S. environment since 1979. We do not know the extent to which they can interfere with the endocrine system and cause endocrine system diseases. Based on o ...
Nonpituitary hormones help regulate metabolism, homeostasis
... The endocrine and nervous systems often function together in maintaining homeostasis, development, and reproduction. Endocrine glands and various organs with primarily nonendocrine functions secrete hormones, and specialized secretory cells derived from nervous tissue secrete neurohormones. Both cla ...
... The endocrine and nervous systems often function together in maintaining homeostasis, development, and reproduction. Endocrine glands and various organs with primarily nonendocrine functions secrete hormones, and specialized secretory cells derived from nervous tissue secrete neurohormones. Both cla ...
Unit07
... Enter the bloodstream and have an effect on a target cell, tissue, or organ Over 50 different hormones Most only affect a few, specific types of cells ...
... Enter the bloodstream and have an effect on a target cell, tissue, or organ Over 50 different hormones Most only affect a few, specific types of cells ...
Hormones 101
... And not to be forgotten: the gonads What are the gonads? An organ that produces gametes (egg or sperm) – the ovary and testes. ...
... And not to be forgotten: the gonads What are the gonads? An organ that produces gametes (egg or sperm) – the ovary and testes. ...
Endocrine disruptor

Endocrine disruptors are chemicals that, at certain doses, can interfere with the endocrine (or hormone) system in mammals. These disruptions can cause cancerous tumors, birth defects, and other developmental disorders. Any system in the body controlled by hormones can be derailed by hormone disruptors. Specifically, endocrine disruptors may be associated with the development of learning disabilities, severe attention deficit disorder, cognitive and brain development problems; deformations of the body (including limbs); breast cancer, prostate cancer, thyroid and other cancers; sexual development problems such as feminizing of males or masculinizing effects on females, etc. The critical period of development for most organisms is between the transition from a fertilized egg into a fully formed infant. As the cells begin to grow and differentiate, there are critical balances of hormones and protein changes that must occur. Therefore, a dose of disrupting chemicals may do substantial damage to a developing fetus. The same dose may not significantly affect adult mothers.There has been controversy over endocrine disruptors, with some groups calling for swift action by regulators to remove them from the market, and regulators and other scientists calling for further study. Some endocrine disruptors have been identified and removed from the market (for example, a drug called diethylstilbestrol), but it is uncertain whether some endocrine disruptors on the market actually harm humans and wildlife at the doses to which wildlife and humans are exposed. Additionally, a key scientific paper, published in the journal Science, which helped launch the movement of those opposed to endocrine disruptors, was retracted and its author found to have committed scientific misconduct.Found in many household and industrial products, endocrine disruptors are substances that ""interfere with the synthesis, secretion, transport, binding, action, or elimination of natural hormones in the body that are responsible for development, behavior, fertility, and maintenance of homeostasis (normal cell metabolism)."" They are sometimes also referred to as hormonally active agents, endocrine disrupting chemicals, or endocrine disrupting compounds (EDCs).Studies in cells and laboratory animals have shown that EDs can cause adverse biological effects in animals, and low-level exposures may also cause similar effects in human beings.The term endocrine disruptor is often used as synonym for xenohormone although the latter can mean any naturally occurring or artificially produced compound showing hormone-like properties (usually binding to certain hormonal receptors). EDCs in the environment may also be related to reproductive and infertility problems in wildlife and bans and restrictions on their use has been associated with a reduction in health problems and the recovery of some wildlife populations.