Continuing Education Independent Study Series
... Gray H. Gray's Anatomy. New York: Bounty Books, 1978. Tortora G, Anagnostakos N. Principles of Anatomy and Physiology. 7th ed. New York: Harper & Row; ...
... Gray H. Gray's Anatomy. New York: Bounty Books, 1978. Tortora G, Anagnostakos N. Principles of Anatomy and Physiology. 7th ed. New York: Harper & Row; ...
Hormones - WordPress.com
... http://www.research.buffalo.edu/quarterly/vol10/num01/n1.shtml http://www.aim-digest.com/gateway/pages/brain/articles/myths.htm http://www.nida.nih.gov/pubs/teaching/Teaching5/Teaching3.html ...
... http://www.research.buffalo.edu/quarterly/vol10/num01/n1.shtml http://www.aim-digest.com/gateway/pages/brain/articles/myths.htm http://www.nida.nih.gov/pubs/teaching/Teaching5/Teaching3.html ...
Hormones and puberty
... Hormones and puberty Hormones play an important role in controlling or regulating many processes in the body, including physical development during youth. They are often referred to as ‘chemical messengers’ because they circulate in the bloodstream and act on various sites in the body, stimulating a ...
... Hormones and puberty Hormones play an important role in controlling or regulating many processes in the body, including physical development during youth. They are often referred to as ‘chemical messengers’ because they circulate in the bloodstream and act on various sites in the body, stimulating a ...
Unit Four - Regulation Unit 4- REGULATORY
... The endocrine system is made up of glands that release their products (hormones) directly into the bloodstream. The response of hormones is slower and longer lasting than those of nerve impulses. The effects may last up to several hours or days. These hormones help to regulate important processes th ...
... The endocrine system is made up of glands that release their products (hormones) directly into the bloodstream. The response of hormones is slower and longer lasting than those of nerve impulses. The effects may last up to several hours or days. These hormones help to regulate important processes th ...
Endocrinology - NCORD Healthcare LLC
... affect the glands mentioned above. An endocrinologist is an expert is treating frequently complex conditions which involved several different systems within the human body. If patients visit their primary care physician (GP, general practitioner, family doctor), and he/she sustpects there is a probl ...
... affect the glands mentioned above. An endocrinologist is an expert is treating frequently complex conditions which involved several different systems within the human body. If patients visit their primary care physician (GP, general practitioner, family doctor), and he/she sustpects there is a probl ...
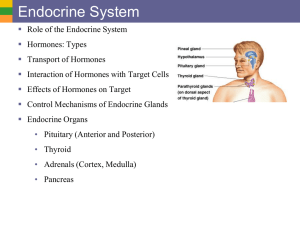
Endocrine System
... Androgens and Estrogens (general development of secondary sexual characteristics) ...
... Androgens and Estrogens (general development of secondary sexual characteristics) ...
Year 12 ATAR Human Biology Unit 3 – Endocrine System
... Endocrine Gland Glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream. Exocrine Gland Glands that secrete their liquids through a duct such as salivary glands. Receptor A structure that receives a stimulus. Modulator A control centre responsible for processing information received from a recept ...
... Endocrine Gland Glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream. Exocrine Gland Glands that secrete their liquids through a duct such as salivary glands. Receptor A structure that receives a stimulus. Modulator A control centre responsible for processing information received from a recept ...
Physio Lab 4 Endocrine in PhysioEx
... cleared from the body more readily by the kidneys. These hormones must also bind to a receptor on the surface of the cell membrane and then activate a second messenger system (e.g., cAMP, IP3/Ca2+, or tyrosine kinase). Your instructor will discuss during lecture some example hydrophilic hormone mech ...
... cleared from the body more readily by the kidneys. These hormones must also bind to a receptor on the surface of the cell membrane and then activate a second messenger system (e.g., cAMP, IP3/Ca2+, or tyrosine kinase). Your instructor will discuss during lecture some example hydrophilic hormone mech ...
Chapter 8: Chemical Signals Maintain Homeostasis
... The body relies on the nervous system and the endocrine system for control of organs and tissues The nervous system allows the body to adjust quickly to environmental changes The endocrine system is designed to maintain ...
... The body relies on the nervous system and the endocrine system for control of organs and tissues The nervous system allows the body to adjust quickly to environmental changes The endocrine system is designed to maintain ...
Chapter 13 Notes
... Endocrine responses are often slower, but have longer lasting effects than nervous system responses Often both the nervous and endocrine systems work together to regulate responses ...
... Endocrine responses are often slower, but have longer lasting effects than nervous system responses Often both the nervous and endocrine systems work together to regulate responses ...
Classification of Hormones Lecture 1
... Mode of action of hormones 2. Hormones which are water soluble and easily transported in plasma in a free state: • Their half-life is very short and their action is also for a very short time. • They bind to receptors on the cell membrane and their further action is mediated through a second messen ...
... Mode of action of hormones 2. Hormones which are water soluble and easily transported in plasma in a free state: • Their half-life is very short and their action is also for a very short time. • They bind to receptors on the cell membrane and their further action is mediated through a second messen ...
Endocrine System
... Human Endocrine System • Endocrine system consists of endocrine glands (organs) that coordinate body activities through hormones (signals for your body). – Glands release hormones directly into the bloodstream – Hormones are chemicals produced by one set of “cells” that affect another set of cells ...
... Human Endocrine System • Endocrine system consists of endocrine glands (organs) that coordinate body activities through hormones (signals for your body). – Glands release hormones directly into the bloodstream – Hormones are chemicals produced by one set of “cells” that affect another set of cells ...
1 Endocrine System
... The Endocrine System A more broad-based and long-lasting communication system than the nervous system Uses chemical messages (hormones) that are released into the blood Hormones control several major processes • Reproduction • Growth and development • Mobilization of body defenses • Maintenan ...
... The Endocrine System A more broad-based and long-lasting communication system than the nervous system Uses chemical messages (hormones) that are released into the blood Hormones control several major processes • Reproduction • Growth and development • Mobilization of body defenses • Maintenan ...
Endocrine PP - Laura Banks
... • Step 3: New hormones are released by the adrenal glands into the body AS WELL AS cutting off the hormone production in the pituitary glands • This allows the hypothalamus to start producing hormones again ...
... • Step 3: New hormones are released by the adrenal glands into the body AS WELL AS cutting off the hormone production in the pituitary glands • This allows the hypothalamus to start producing hormones again ...
Hormones: definition - a chemical signal released into body fluids
... definition - a chemical signal released into body fluids. Generally this regulates or causes a specific action. Usually, only specific cells known as target cells will respond, but some hormones can affect many different systems: A simple example: Adrenal gland -> epinephrine -> ...
... definition - a chemical signal released into body fluids. Generally this regulates or causes a specific action. Usually, only specific cells known as target cells will respond, but some hormones can affect many different systems: A simple example: Adrenal gland -> epinephrine -> ...
Power Point - Science Olympiad
... Images are upside down and backwards when they reach the retina ...
... Images are upside down and backwards when they reach the retina ...
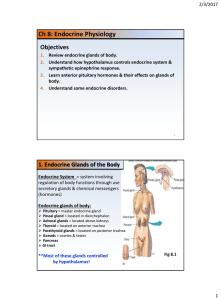
1. Endocrine Glands of the Body
... secretory glands & chemical messengers (hormones) Endocrine glands of body: Pituitary = master endocrine gland Pineal gland = located in dienchephalon Adrenal glands = located above kidneys Thyroid = located on anterior trachea Parathyroid glands = located on posterior trachea Gonads = o ...
... secretory glands & chemical messengers (hormones) Endocrine glands of body: Pituitary = master endocrine gland Pineal gland = located in dienchephalon Adrenal glands = located above kidneys Thyroid = located on anterior trachea Parathyroid glands = located on posterior trachea Gonads = o ...
Volatile Organic Compounds
... alcohols, methacrylates, acrolein, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and pesticides. VOC's are a byproduct of fossil fuel combustion and come from many sources including industrial and combustion processes and petrol stations. The use of organic solvents, certain paint additives, aerosol spray can p ...
... alcohols, methacrylates, acrolein, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and pesticides. VOC's are a byproduct of fossil fuel combustion and come from many sources including industrial and combustion processes and petrol stations. The use of organic solvents, certain paint additives, aerosol spray can p ...
Endocrine System
... slower, longer term responses to stress; secretes steroid hormones – mineralocorticoids (aldosterone), glucocorticoids, and androgens * Glucocorticoids offer relief of pain; suppress body’s defense system ...
... slower, longer term responses to stress; secretes steroid hormones – mineralocorticoids (aldosterone), glucocorticoids, and androgens * Glucocorticoids offer relief of pain; suppress body’s defense system ...
Endocrine Review Package
... This flow diagram shows the balancing effect of insulin and glucagon on blood sugar levels. Study it carefully and answer the related questions. Also use page 341 in Nelson 1) What are the specialized cells that ...
... This flow diagram shows the balancing effect of insulin and glucagon on blood sugar levels. Study it carefully and answer the related questions. Also use page 341 in Nelson 1) What are the specialized cells that ...
Chemical Signals in Animals or The Endocrine System
... 1. Hormone: a chemical signal that . . . 2. Target Cells: have receptors such that hormones have a specific place to cause an effect. 3. Endocrine glands vs. exocrine glands a) Endo: these are ductless glands because they secrete their hormones directly into the blood stream b) Exocrine: secrete che ...
... 1. Hormone: a chemical signal that . . . 2. Target Cells: have receptors such that hormones have a specific place to cause an effect. 3. Endocrine glands vs. exocrine glands a) Endo: these are ductless glands because they secrete their hormones directly into the blood stream b) Exocrine: secrete che ...
Endocrine Notes
... o Activated gene produces an enzyme (protein) that initiates a chemical reaction within the cell. 2. Non-Steroid Hormones – Hormones composed of proteins, peptides or amino acids. These hormones are NOT fat soluble. They are unable to enter cells because they are not solube in the cell membrane. ...
... o Activated gene produces an enzyme (protein) that initiates a chemical reaction within the cell. 2. Non-Steroid Hormones – Hormones composed of proteins, peptides or amino acids. These hormones are NOT fat soluble. They are unable to enter cells because they are not solube in the cell membrane. ...
Endocrine disruptor

Endocrine disruptors are chemicals that, at certain doses, can interfere with the endocrine (or hormone) system in mammals. These disruptions can cause cancerous tumors, birth defects, and other developmental disorders. Any system in the body controlled by hormones can be derailed by hormone disruptors. Specifically, endocrine disruptors may be associated with the development of learning disabilities, severe attention deficit disorder, cognitive and brain development problems; deformations of the body (including limbs); breast cancer, prostate cancer, thyroid and other cancers; sexual development problems such as feminizing of males or masculinizing effects on females, etc. The critical period of development for most organisms is between the transition from a fertilized egg into a fully formed infant. As the cells begin to grow and differentiate, there are critical balances of hormones and protein changes that must occur. Therefore, a dose of disrupting chemicals may do substantial damage to a developing fetus. The same dose may not significantly affect adult mothers.There has been controversy over endocrine disruptors, with some groups calling for swift action by regulators to remove them from the market, and regulators and other scientists calling for further study. Some endocrine disruptors have been identified and removed from the market (for example, a drug called diethylstilbestrol), but it is uncertain whether some endocrine disruptors on the market actually harm humans and wildlife at the doses to which wildlife and humans are exposed. Additionally, a key scientific paper, published in the journal Science, which helped launch the movement of those opposed to endocrine disruptors, was retracted and its author found to have committed scientific misconduct.Found in many household and industrial products, endocrine disruptors are substances that ""interfere with the synthesis, secretion, transport, binding, action, or elimination of natural hormones in the body that are responsible for development, behavior, fertility, and maintenance of homeostasis (normal cell metabolism)."" They are sometimes also referred to as hormonally active agents, endocrine disrupting chemicals, or endocrine disrupting compounds (EDCs).Studies in cells and laboratory animals have shown that EDs can cause adverse biological effects in animals, and low-level exposures may also cause similar effects in human beings.The term endocrine disruptor is often used as synonym for xenohormone although the latter can mean any naturally occurring or artificially produced compound showing hormone-like properties (usually binding to certain hormonal receptors). EDCs in the environment may also be related to reproductive and infertility problems in wildlife and bans and restrictions on their use has been associated with a reduction in health problems and the recovery of some wildlife populations.