P215 - Basic Human Physiology
... cells in CNS – Hormones typically released directly to target tissues – Principally involved in regeneration, growth, development, and reproduction – Little homeostatic function ...
... cells in CNS – Hormones typically released directly to target tissues – Principally involved in regeneration, growth, development, and reproduction – Little homeostatic function ...
Hormones Endocrine System Function Endocrine Systems
... target tissues – Principally involved in regeneration, growth, development, and reproduction – Little homeostatic function ...
... target tissues – Principally involved in regeneration, growth, development, and reproduction – Little homeostatic function ...
Chapter 45.
... Regulation by chemical messengers Neurotransmitters released by neurons Hormones release by endocrine glands endocrine gland neurotransmitter axon hormone carried by blood ...
... Regulation by chemical messengers Neurotransmitters released by neurons Hormones release by endocrine glands endocrine gland neurotransmitter axon hormone carried by blood ...
SAP 1 – Students will analyze anatomical structures in
... respond to it because there is something wrong with their insulin receptors • this type of diabetes is often called adult onset diabetes because it usually does not develop until later in life • it is not known what causes type 2 diabetes; however, we do know that heredity, obesity, and smoking are ...
... respond to it because there is something wrong with their insulin receptors • this type of diabetes is often called adult onset diabetes because it usually does not develop until later in life • it is not known what causes type 2 diabetes; however, we do know that heredity, obesity, and smoking are ...
BS1060
... in the bloodstream to another organ (Target Organ)where it affects the metabolism of that organ. • First coined in 1902 by Bayliss and Starling who were the first to show the existence of the hormone - secretin. ...
... in the bloodstream to another organ (Target Organ)where it affects the metabolism of that organ. • First coined in 1902 by Bayliss and Starling who were the first to show the existence of the hormone - secretin. ...
Digestive, Urinary and Endocrine Systems Test Review
... During emergency situations (that cause the “fight or flight” response) the ______ is/are stimulated A) Pituitary gland B) Thymus gland C) Thyroid gland D) Adrenal glands ...
... During emergency situations (that cause the “fight or flight” response) the ______ is/are stimulated A) Pituitary gland B) Thymus gland C) Thyroid gland D) Adrenal glands ...
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... • In a woman, the breasts enlarge and fatty tissue is deposited around the hips • In both men and women height and weight increase Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved. ...
... • In a woman, the breasts enlarge and fatty tissue is deposited around the hips • In both men and women height and weight increase Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved. ...
View/Open
... disturbance in hormone biosynthesis, secondary disruption of endocrine tissue – Excessive production: hyperplasia or tumor of the endocrine organ, over stimulation of the endocrine organ (for example autoimmune disease) ...
... disturbance in hormone biosynthesis, secondary disruption of endocrine tissue – Excessive production: hyperplasia or tumor of the endocrine organ, over stimulation of the endocrine organ (for example autoimmune disease) ...
Thyroid hormones
... stimulate its growth and maintain the cyclic change of uterine mucosa, on mammary gland to stimulate ductal growth, on bone to promote linear growth and closure of epiphyseal plates, on HPA to regulate secretion of gonadotropins and prolactin, on metabolic processes to affect adipose tissue distribu ...
... stimulate its growth and maintain the cyclic change of uterine mucosa, on mammary gland to stimulate ductal growth, on bone to promote linear growth and closure of epiphyseal plates, on HPA to regulate secretion of gonadotropins and prolactin, on metabolic processes to affect adipose tissue distribu ...
Endocrine System - walker2016
... Endocrine glands – ductless organs that secrete their molecules directly into the ...
... Endocrine glands – ductless organs that secrete their molecules directly into the ...
HumanEndocrineSystem
... water reabsorption in the kidneys. It is also called vasopressin. The second hormone is oxytocin, which stimulates contractions in the muscles of the uterus during birth. Thyroid gland The thyroid gland lies against the pharynx at the base of the neck. It consists of two lateral lobes connected by a ...
... water reabsorption in the kidneys. It is also called vasopressin. The second hormone is oxytocin, which stimulates contractions in the muscles of the uterus during birth. Thyroid gland The thyroid gland lies against the pharynx at the base of the neck. It consists of two lateral lobes connected by a ...
Chemical messengers - Our eclass community
... of the body or to one of the body’s cavities eg. sweat glands, glands of the alimentary canal have ducts ...
... of the body or to one of the body’s cavities eg. sweat glands, glands of the alimentary canal have ducts ...
PowerPoint to accompany
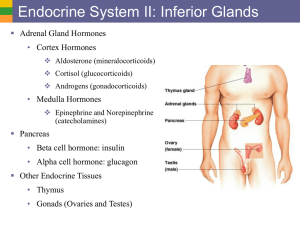
... • Ovaries are located in the pelvic cavity and produce sex hormones (estrogens and progesterone) related to development and maintenance of female sexual characteristics, reproductive cycle, pregnancy, lactation, and normal reproductive functions. The ovaries also produce inhibin and relaxin. • Teste ...
... • Ovaries are located in the pelvic cavity and produce sex hormones (estrogens and progesterone) related to development and maintenance of female sexual characteristics, reproductive cycle, pregnancy, lactation, and normal reproductive functions. The ovaries also produce inhibin and relaxin. • Teste ...
endocrine system
... • Are ductless and secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream • Target Cells – the cells that a hormone directly affects; if a cell does not have receptors or the receptors don’t respond, the hormone has no effect. ...
... • Are ductless and secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream • Target Cells – the cells that a hormone directly affects; if a cell does not have receptors or the receptors don’t respond, the hormone has no effect. ...
McCance: Pathophysiology, 6th Edition
... Key Points – Print SUMMARY REVIEW Mechanisms of Hormonal Regulation 1. The endocrine system has diverse functions, including sexual differentiation, growth and development, and continuous maintenance of the body’s internal environment. 2. Hormones are chemical messengers synthesized by endocrine gla ...
... Key Points – Print SUMMARY REVIEW Mechanisms of Hormonal Regulation 1. The endocrine system has diverse functions, including sexual differentiation, growth and development, and continuous maintenance of the body’s internal environment. 2. Hormones are chemical messengers synthesized by endocrine gla ...
Endocrine System Review
... Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large scale changes ...
... Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large scale changes ...
The Endocrine System
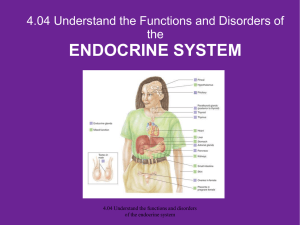
... 4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the ENDOCRINE SYSTEM What are the functions of the endocrine system? What are some disorders of the endocrine system? How do you relate the body’s hormones to the endocrine system? ...
... 4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the ENDOCRINE SYSTEM What are the functions of the endocrine system? What are some disorders of the endocrine system? How do you relate the body’s hormones to the endocrine system? ...
fd endocrine system
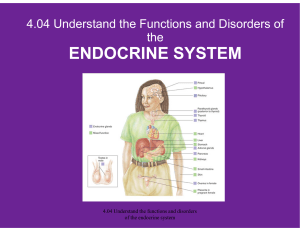
... 4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the ENDOCRINE SYSTEM What are the functions of the endocrine system? What are some disorders of the endocrine system? How do you relate the body’s hormones to the endocrine system? ...
... 4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the ENDOCRINE SYSTEM What are the functions of the endocrine system? What are some disorders of the endocrine system? How do you relate the body’s hormones to the endocrine system? ...
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM - Grade 12 Biology
... Series of glands that produce hormones to help maintain homeostasis. Hormones: Chemical regulators that affect other parts of the body. Insulin Growth Hormone Gastrin ...
... Series of glands that produce hormones to help maintain homeostasis. Hormones: Chemical regulators that affect other parts of the body. Insulin Growth Hormone Gastrin ...
Endocrine System
... Crucial for development and maturation Maintain normal blood pressure, heart rate, and digestion Increase rate of O2 consumption = what effect on metabolism? ...
... Crucial for development and maturation Maintain normal blood pressure, heart rate, and digestion Increase rate of O2 consumption = what effect on metabolism? ...
Endocrine System
... lobes. • Controls many body functions, including: heart rate, temperature, and metabolism. ...
... lobes. • Controls many body functions, including: heart rate, temperature, and metabolism. ...
Lecture #20 - Suraj @ LUMS
... The glucocorticoids get their name from their effect of raising the level of blood sugar (glucose). One way they do this is by stimulating gluconeogenesis in the liver: the conversion of fat and protein into intermediate metabolites that are ultimately converted into glucose. The most abundant gluco ...
... The glucocorticoids get their name from their effect of raising the level of blood sugar (glucose). One way they do this is by stimulating gluconeogenesis in the liver: the conversion of fat and protein into intermediate metabolites that are ultimately converted into glucose. The most abundant gluco ...
Endocrine disruptor

Endocrine disruptors are chemicals that, at certain doses, can interfere with the endocrine (or hormone) system in mammals. These disruptions can cause cancerous tumors, birth defects, and other developmental disorders. Any system in the body controlled by hormones can be derailed by hormone disruptors. Specifically, endocrine disruptors may be associated with the development of learning disabilities, severe attention deficit disorder, cognitive and brain development problems; deformations of the body (including limbs); breast cancer, prostate cancer, thyroid and other cancers; sexual development problems such as feminizing of males or masculinizing effects on females, etc. The critical period of development for most organisms is between the transition from a fertilized egg into a fully formed infant. As the cells begin to grow and differentiate, there are critical balances of hormones and protein changes that must occur. Therefore, a dose of disrupting chemicals may do substantial damage to a developing fetus. The same dose may not significantly affect adult mothers.There has been controversy over endocrine disruptors, with some groups calling for swift action by regulators to remove them from the market, and regulators and other scientists calling for further study. Some endocrine disruptors have been identified and removed from the market (for example, a drug called diethylstilbestrol), but it is uncertain whether some endocrine disruptors on the market actually harm humans and wildlife at the doses to which wildlife and humans are exposed. Additionally, a key scientific paper, published in the journal Science, which helped launch the movement of those opposed to endocrine disruptors, was retracted and its author found to have committed scientific misconduct.Found in many household and industrial products, endocrine disruptors are substances that ""interfere with the synthesis, secretion, transport, binding, action, or elimination of natural hormones in the body that are responsible for development, behavior, fertility, and maintenance of homeostasis (normal cell metabolism)."" They are sometimes also referred to as hormonally active agents, endocrine disrupting chemicals, or endocrine disrupting compounds (EDCs).Studies in cells and laboratory animals have shown that EDs can cause adverse biological effects in animals, and low-level exposures may also cause similar effects in human beings.The term endocrine disruptor is often used as synonym for xenohormone although the latter can mean any naturally occurring or artificially produced compound showing hormone-like properties (usually binding to certain hormonal receptors). EDCs in the environment may also be related to reproductive and infertility problems in wildlife and bans and restrictions on their use has been associated with a reduction in health problems and the recovery of some wildlife populations.