Defective thyroglobulin storage in LDL receptor
... wild-type (WT) mice, suggesting a directional alteration of Tg secretion. In spite of these abnormalities, hormone secretion was maintained as indicated by normal serum thyroxine levels. Because Tg in thyroid extracts from RAP-KO mice contained thyroxine residues as in WT mice, we concluded that in ...
... wild-type (WT) mice, suggesting a directional alteration of Tg secretion. In spite of these abnormalities, hormone secretion was maintained as indicated by normal serum thyroxine levels. Because Tg in thyroid extracts from RAP-KO mice contained thyroxine residues as in WT mice, we concluded that in ...
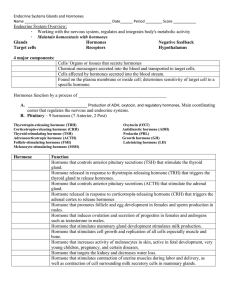
Hypothalamus & Pituitary
... Males: required for sperm production Luteinizing Hormone (LH): Females: responsible for ovulation, formation of corpus luteum in the ovary, and regulation of ovarian secretion of female sex hormones. Males: stimulates cell in the testes to secrete testosterone ...
... Males: required for sperm production Luteinizing Hormone (LH): Females: responsible for ovulation, formation of corpus luteum in the ovary, and regulation of ovarian secretion of female sex hormones. Males: stimulates cell in the testes to secrete testosterone ...
Endocrinology
... loose half of its original effectiveness) ranging from several seconds to about 30 minutes. The time required for hormone effects to take place varies greatly, from almost immediate responses to hours or even days (as often seen in the case of steroid hormones). In addition, some hormones are produc ...
... loose half of its original effectiveness) ranging from several seconds to about 30 minutes. The time required for hormone effects to take place varies greatly, from almost immediate responses to hours or even days (as often seen in the case of steroid hormones). In addition, some hormones are produc ...
melatonin in the thyroid gland - Journal of Physiology and
... oxidation levels crucial for thyroid homeostasis and selfprotection. Many control and thyroid self-protection mechanisms have been described so far (27, 29), and their imbalance has been stated to be responsible for causing thyroid disease (30-32). Therefore, on the basis of its powerful antioxidati ...
... oxidation levels crucial for thyroid homeostasis and selfprotection. Many control and thyroid self-protection mechanisms have been described so far (27, 29), and their imbalance has been stated to be responsible for causing thyroid disease (30-32). Therefore, on the basis of its powerful antioxidati ...
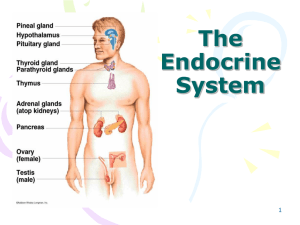
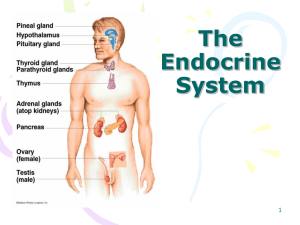
Endocrine System
... glucocorticoids made from cholesterol – glucocorticoid release is stimulated by ACTH (from pituitary gland which is stimulated by hypothalamus releasing hormones) – act similar to glucagon – raise blood glucose levels and promotes use of fats for energy instead of glucose ...
... glucocorticoids made from cholesterol – glucocorticoid release is stimulated by ACTH (from pituitary gland which is stimulated by hypothalamus releasing hormones) – act similar to glucagon – raise blood glucose levels and promotes use of fats for energy instead of glucose ...
Overivew notes
... Hormone released in response to thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) that triggers the thyroid gland to release hormones. Hormone that controls anterior pituitary secretions (ACTH) that stimulate the adrenal gland. Hormone released in response to corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) that triggers th ...
... Hormone released in response to thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) that triggers the thyroid gland to release hormones. Hormone that controls anterior pituitary secretions (ACTH) that stimulate the adrenal gland. Hormone released in response to corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) that triggers th ...
Thyroid hormone upregulates hypothalamic kiss2 gene in the male
... gnrh3) mRNA expression was analyzed by real-time PCR. MMI inhibits thyroperoxidase, which acts in thyroid hormone synthesis by oxidizing the anion iodide (I− ) to iodine (I0), facilitating iodine’s addition to tyrosine residues on the hormone precursor thyroglobulin, a necessary step in the synthesi ...
... gnrh3) mRNA expression was analyzed by real-time PCR. MMI inhibits thyroperoxidase, which acts in thyroid hormone synthesis by oxidizing the anion iodide (I− ) to iodine (I0), facilitating iodine’s addition to tyrosine residues on the hormone precursor thyroglobulin, a necessary step in the synthesi ...
Endocrine System PPT
... • Something in the blood is being monitored. When the level of that substance is too high or low, it stimulates the release of the hormone or stop its production. • Examples are insulin, glucagon, parathyroid hormone, and aldosterone. • When you eat, glucose gets high, releases insulin, which tells ...
... • Something in the blood is being monitored. When the level of that substance is too high or low, it stimulates the release of the hormone or stop its production. • Examples are insulin, glucagon, parathyroid hormone, and aldosterone. • When you eat, glucose gets high, releases insulin, which tells ...
Physiology Ch 74 p881-892 [4-25
... -vesicles stored in cytoplasm bound to cell membrane until secretion by exocytosis (fusion with memb.) -stimulus for exocytosis is usually cytosolic increase in Ca concentration by depolarization of membrane -Can also be caused by increased cAMP and kinase activity Steroid Hormones are Synthesized f ...
... -vesicles stored in cytoplasm bound to cell membrane until secretion by exocytosis (fusion with memb.) -stimulus for exocytosis is usually cytosolic increase in Ca concentration by depolarization of membrane -Can also be caused by increased cAMP and kinase activity Steroid Hormones are Synthesized f ...
The Endocrine System
... • Something in the blood is being monitored. When the level of that substance is too high or low, it stimulates the release of the hormone or stop its production. • Examples are insulin, glucagon, parathyroid hormone, and aldosterone. • When you eat, glucose gets high, releases insulin, which tells ...
... • Something in the blood is being monitored. When the level of that substance is too high or low, it stimulates the release of the hormone or stop its production. • Examples are insulin, glucagon, parathyroid hormone, and aldosterone. • When you eat, glucose gets high, releases insulin, which tells ...
Chapter 17 *Lecture PowerPoint The Endocrine System
... The Pineal Gland • May regulate timing of puberty in humans • Seasonal affective disorder (SAD) occurs in winter or northern climates – Symptoms: depression, sleepiness, irritability, and ...
... The Pineal Gland • May regulate timing of puberty in humans • Seasonal affective disorder (SAD) occurs in winter or northern climates – Symptoms: depression, sleepiness, irritability, and ...
Chapter 17 - Saladin
... The Pineal Gland • May regulate timing of puberty in humans • Seasonal affective disorder (SAD) occurs in winter or northern climates – Symptoms: depression, sleepiness, irritability, and ...
... The Pineal Gland • May regulate timing of puberty in humans • Seasonal affective disorder (SAD) occurs in winter or northern climates – Symptoms: depression, sleepiness, irritability, and ...
Invoice - Molmed
... October in Leiden. This JNVE conference will again take place at the Holiday Inn Hotel in Leiden at October 27 and 28. The conference will offer a varied programme with a workshop on the history of hormone preparations (dr. Toine Pieters, VUMC/UMCU) and furthermore several talks by renowned Dutch se ...
... October in Leiden. This JNVE conference will again take place at the Holiday Inn Hotel in Leiden at October 27 and 28. The conference will offer a varied programme with a workshop on the history of hormone preparations (dr. Toine Pieters, VUMC/UMCU) and furthermore several talks by renowned Dutch se ...
Chemistry Problem Solving Drill
... release their own hormones which affect many different tissues. The hormones released by the hypothalamus towards the anterior pituitary include: TRH, CRH, CHRH, and GnRH which in turn affect the release of TSH, ACTH, GH, FSH and LH from the Anterior Pituitary. These in turn, affect the thyroid glan ...
... release their own hormones which affect many different tissues. The hormones released by the hypothalamus towards the anterior pituitary include: TRH, CRH, CHRH, and GnRH which in turn affect the release of TSH, ACTH, GH, FSH and LH from the Anterior Pituitary. These in turn, affect the thyroid glan ...
Endocrine Lecture Test Questions – Set 5
... Abnormal fat distribution, muscle atrophy, hyperglycemia, hypertension and immune suppression, would indicate: a. myxedema b. diabetes mellitus c. hypoadrenalism (Addison’s disease) d. hyperadrenalism (Cushing’s syndrome) e. hyperthyroidism (Graves disease) ...
... Abnormal fat distribution, muscle atrophy, hyperglycemia, hypertension and immune suppression, would indicate: a. myxedema b. diabetes mellitus c. hypoadrenalism (Addison’s disease) d. hyperadrenalism (Cushing’s syndrome) e. hyperthyroidism (Graves disease) ...
Hypothyroidism in Children with Serous Otitis Media Seröz Otitis
... Otitis media with effusion (OME) is characterised by fluid retention behind the eardrum without general or local infection symptoms. OME is a common disease in children with an incidence of 15% to 20% and may lead to hearing loss or surgical intervention (1). In most children, otitis media improves ...
... Otitis media with effusion (OME) is characterised by fluid retention behind the eardrum without general or local infection symptoms. OME is a common disease in children with an incidence of 15% to 20% and may lead to hearing loss or surgical intervention (1). In most children, otitis media improves ...
Testing During Pregnancy - American Association for Clinical
... Reliability of the Discriminatory Zone • 202 women who met the following ...
... Reliability of the Discriminatory Zone • 202 women who met the following ...
The Human Endocrine System
... Anterior pituitary hormones that affect other glands: Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH) Gonadotropic Hormones ...
... Anterior pituitary hormones that affect other glands: Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH) Gonadotropic Hormones ...
3 Endocrinology
... loose half of its original effectiveness) ranging from several seconds to about 30 minutes. The time required for hormone effects to take place varies greatly, from almost immediate responses to hours or even days (as often seen in the case of steroid hormones). In addition, some hormones are produc ...
... loose half of its original effectiveness) ranging from several seconds to about 30 minutes. The time required for hormone effects to take place varies greatly, from almost immediate responses to hours or even days (as often seen in the case of steroid hormones). In addition, some hormones are produc ...
Prolactinoma - Barts Endocrinology
... used in measuring prolactin levels. In the best medical centers, surgery corrects pro lactin levels in about 80 percent of patients with small tumors and a serum prolactin less than 200 nanograms per milliliter (ng/ml). A surgical cure for large tumors is lower, at 30 to 40 percent. Even in patient ...
... used in measuring prolactin levels. In the best medical centers, surgery corrects pro lactin levels in about 80 percent of patients with small tumors and a serum prolactin less than 200 nanograms per milliliter (ng/ml). A surgical cure for large tumors is lower, at 30 to 40 percent. Even in patient ...
endocr
... loose half of its original effectiveness) ranging from several seconds to about 30 minutes. The time required for hormone effects to take place varies greatly, from almost immediate responses to hours or even days (as often seen in the case of steroid hormones). In addition, some hormones are produc ...
... loose half of its original effectiveness) ranging from several seconds to about 30 minutes. The time required for hormone effects to take place varies greatly, from almost immediate responses to hours or even days (as often seen in the case of steroid hormones). In addition, some hormones are produc ...
Cigarette Smoking and Thyroid Hormone Levels in Males
... deiodinase activity.23,24 The effect of 2,3-hydroxypyridine is similar to that of propylthiouracil. Like propylthiouracil, 2,3-hydroxypyridine may slightly and temporarily elevate serum T4 levels as a consequence of its deiodinase-altering activity prior to decreasing these levels. Thyroxine deiodin ...
... deiodinase activity.23,24 The effect of 2,3-hydroxypyridine is similar to that of propylthiouracil. Like propylthiouracil, 2,3-hydroxypyridine may slightly and temporarily elevate serum T4 levels as a consequence of its deiodinase-altering activity prior to decreasing these levels. Thyroxine deiodin ...
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism, also known as over active thyroid and hyperthyreosis, is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormone by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidism. Some, however, use the terms interchangeably. Signs and symptoms vary between people and may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, poor tolerance of heat, diarrhea, enlargement of the thyroid, and weight loss. Symptoms are typically less in the old and during pregnancy. An uncommon complication is thyroid storm in which an event such as an infection results in worsening symptoms such as confusion and a high temperature and often results in death. The opposite is hypothyroidism, when the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone.Graves' disease is the cause of about 50% to 80% of case of hyperthyroidism in the United States. Other causes include multinodular goiter, toxic adenoma, inflammation of the thyroid, eating too much iodine, and too much synthetic thyroid hormone. A less common cause is a pituitary adenoma. The diagnosis may be suspected based on signs and symptoms and then confirmed with blood tests. Typically blood tests show a low thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and raised T3 or T4. Radioiodine uptake by the thyroid, thyroid scan, and TSI antibodies may help determine the cause.Treatment depends partly on the cause and severity of disease. There are three main treatment options: radioiodine therapy, medications, and thyroid surgery. Radioiodine therapy involves taking iodine-131 by mouth which is then concentrated in and destroys the thyroid over weeks to months. The resulting hypothyroidism is treated with synthetic thyroid hormone. Medications such as beta blockers may control the symptoms and anti-thyroid medications such as methimazole may temporarily help people while other treatments are having effect. Surgery to remove the thyroid is another option. This may be used in those with very large thyroids or when cancer is a concern. In the United States hyperthyroidism affects about 1.2% of the population. It occurs between two and ten times more often in women. Onset is commonly between 20 and 50 years of age. Overall the disease is more common in those over the age of 60 years.